A critical path is a method used by project managers to prioritize tasks and deliver a project on time. But unlike most project management concepts, the title of this one doesn’t give much away.
That’s why we’ve created this no-nonsense guide to help you understand what critical paths are, why they’re important, and how to implement them. Plus, we’ll show you how the critical path feature in monday work management can make your job easier.
What is a critical path?
A critical path is the longest sequence of dependent tasks that must be completed to execute a project. The tasks are called critical activities because the whole project runs over if they’re delayed.
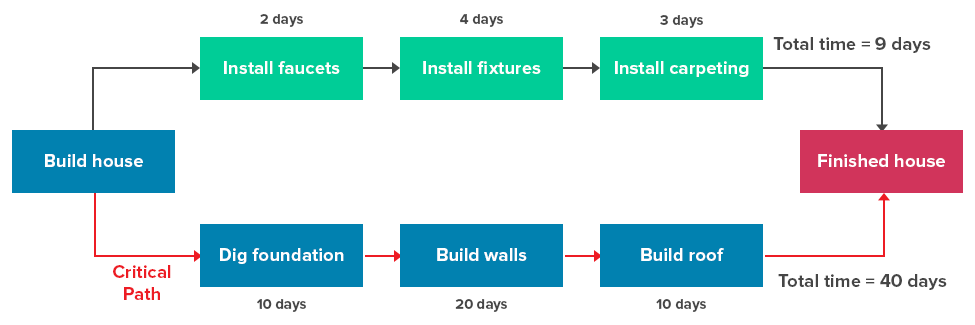
For example, if you’re building a house, the critical path might include activities like digging the foundations, building the walls, and installing the roof. If any of these critical activities fall behind schedule the whole project gets delayed.
Project managers use the critical path method (CPM) to find the critical path. The CPM — also known as critical path analysis (CPA) — is a project management technique used to plan and schedule complex projects. It’s an algorithm that identifies the longest sequence of dependent activities and measures the time required to complete them from start to finish.
What does a critical path look like?
Asking what a critical path looks like is like asking, “how long is a piece of string?” — i.e. there’s no definitive answer.
Traditionally, the critical path was a flow chart. For example, some house-building activities take longer than others, so the critical path highlights the longest duration:
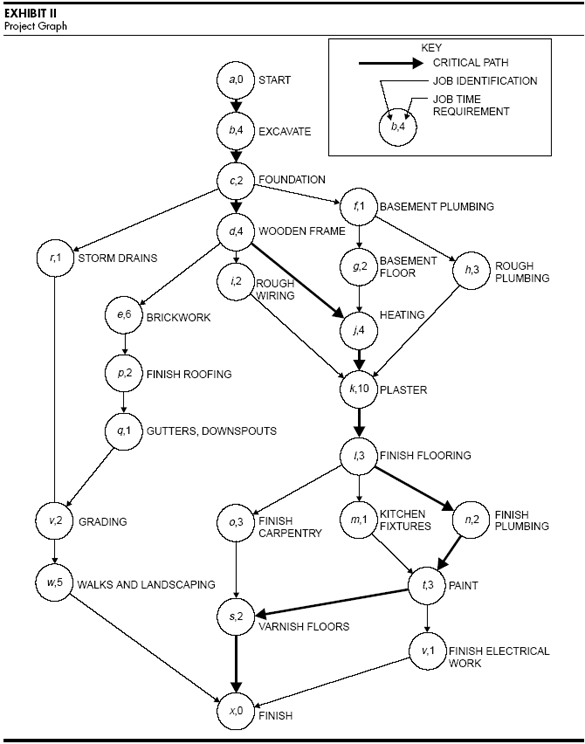
A more complex diagram might look like this:
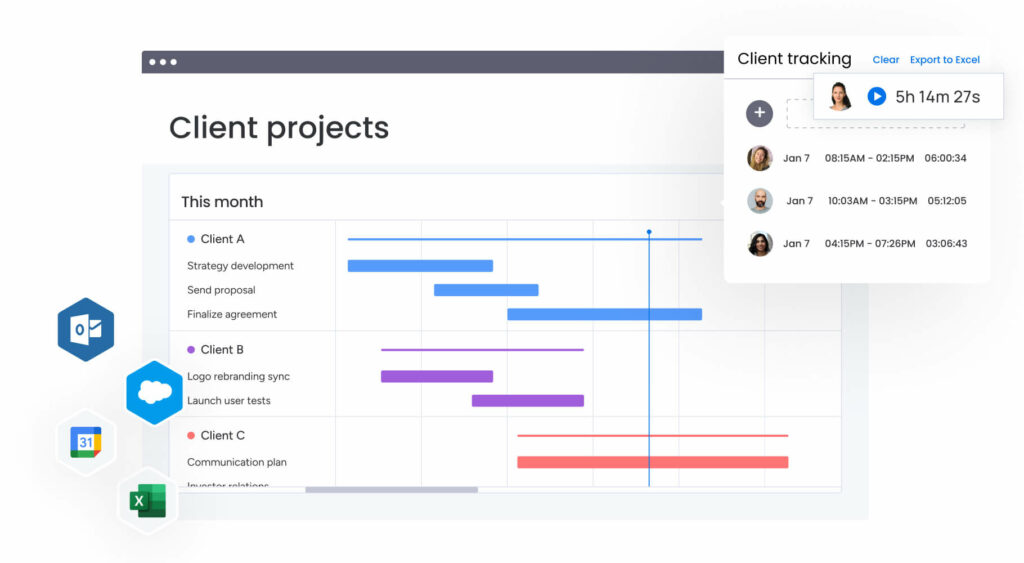
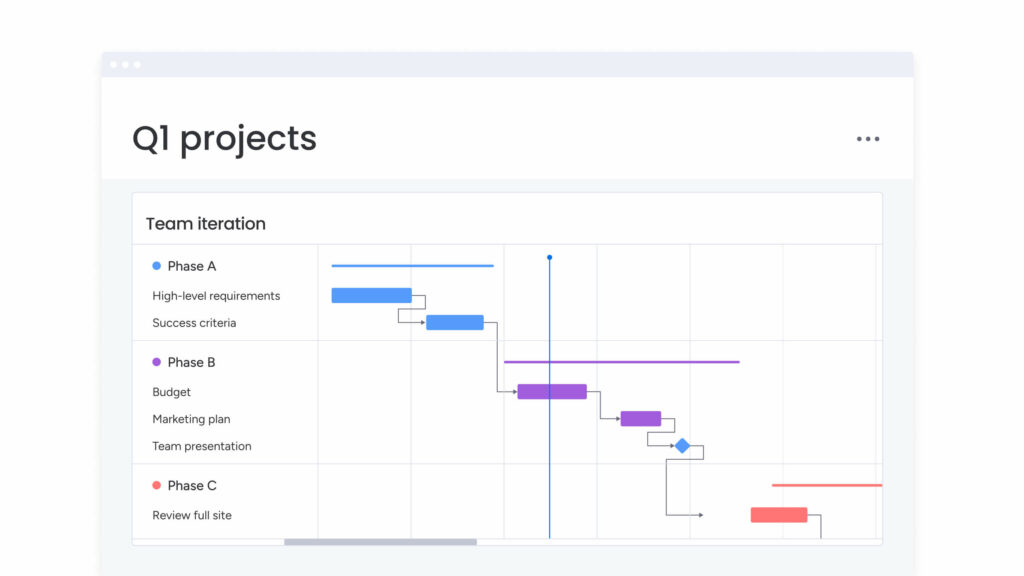
Nowadays, other more visually appealing ways of presenting a critical path exist. For example, using a Gantt chart allows you to visualize the critical activities:
Critical path vs. critical chain
Critical path and critical chain are two different approaches to completing a project.
The critical chain methodology pinpoints the bottlenecks or limiting factors that can cause businesses to miss project deadlines. It focuses on monitoring the use of resources — like materials and labor. For example, a project manager might delay the start of one task so that a skilled worker does not have to perform two tasks at the same time.
The critical path focuses on task management, assumes unlimited resources, and identifies the longest track of tasks. It helps identify tasks that may cause project delays and guides project managers to take preventive measures from the start.
On the other hand, the critical chain focuses on resource and buffer management, assumes limited resources, and identifies the longest chain of dependent events. It inserts buffers between dependent events to protect the project from delays.
Critical path vs. critical activity
Critical path and critical activity are related concepts in project management, both determined by the critical path method (CPM).
The critical path is the longest sequence of tasks that must be completed for the project and comprises critical activities. Any delay in completing tasks on the critical path will also delay the project.
A critical activity is a specific scheduled activity that is part of the critical path. It’s essential to the project’s timeline, and any delay in completing a critical activity will delay the entire project.
For example, if it takes twice as long to dig the foundations for a new house, then the entire house building project gets delayed. A critical activity typically has zero float, meaning there’s no flexibility in the start or finish dates.
Critical path vs. PERT
The critical path and PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) are tools for planning and controlling projects.
PERT is a framework to map out task dependencies and estimate how long a project will last. It’s a statistical tool to visualize the overall project schedule — not just the critical path — and shows the relationship between tasks as well as the overall project duration.
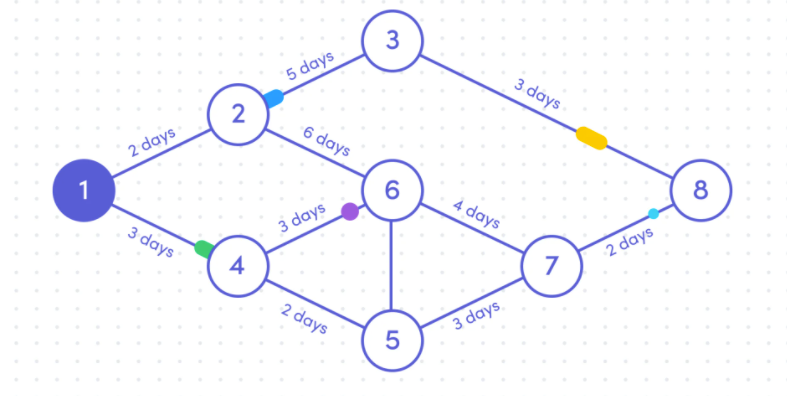
For example, a project with seven key activities and a total project duration of 14 days, could have a chart that looks like this:
The critical path is used to schedule and manage project tasks, focusing on the longest sequence of tasks and considering task dependencies and slack time. It is suitable for projects with predictable task durations.
On the other hand, PERT is used to calculate the time required to complete project activities, especially when task durations are variable and uncertain. It allows for flexibility in project scheduling and focuses on time estimation and uncertainty.
Critical path vs. Gantt chart
The critical path and Gantt chart are both project management visualization tools, but they serve different purposes.
The critical path helps schedule and manage project tasks, taking into account task dependencies and slack time. It’s suitable for projects with predictable task durations.
On the other hand, a Gantt chart provides a visual overview of tasks, durations, and dependencies in a project schedule. It helps track progress, allocate resources, and communicate project timelines.
While a Gantt chart can highlight the critical path, its primary purpose is to visualize the project schedule.
What are the benefits of the critical path method?
The critical path method (CPM) offers improved project planning, enhanced scheduling, clearer communication, effective resource management, tighter cost control, risk detection, and better project management.
1. Enhances project planning
The CPM provides a structured approach to project planning by identifying the sequence of activities and their dependencies. This helps project managers create a realistic and robust project schedule.
2. Helps prioritize tasks
The CPM identifies the critical tasks and determines the critical path. This helps project managers prioritize tasks effectively and determine where and how to allocate resources.
3. Improves team communication
The CPM requires input from key stakeholders, including team members and subcontractors. This collaboration ensures everyone understands the project timeline and dependencies, leading to better communication and coordination.
4. Facilitates more effective resource management
The CPM helps project managers identify resource requirements for each activity. Project managers can allocate resources efficiently by understanding the critical path and resource dependencies, minimizing bottlenecks and unexpected delays.
5. Tightens cost control
The CPM assists project managers in controlling costs by allocating the right resources to the right places. This reduces the chances of unexpected delays that may incur additional costs.
6. Detects potential risks
The CPM allows project managers to identify potential risks and their impact on the project schedule. By analyzing the critical path and considering the float or slack time, project managers can predict the effects of delays and make adjustments to mitigate risks.
7. Improves project management
The CPM enables project managers to clearly communicate project plans, schedules, and performance. This clarity helps them monitor progress, identify issues, and make informed decisions to solve project management challenges.
To summarize: by utilizing the CPM, project managers can optimize project timelines, allocate resources effectively, and mitigate risks, leading to successful projects.
How to find the critical path
Now, let’s identify the critical path from start to finish.
1. List all your project tasks
Before you even think about a critical path, you need to list what tasks to include in the project — i.e. your work breakdown structure.
Spend some time speaking with stakeholders to confirm the project details. Once you have all the information, you can identify all the activities that must happen to complete the project.
2. Put all the tasks in order
Once you’ve identified the tasks, it’s time to put them in chronological order and identify any task dependencies. This will help you work out the project timeline.
So what’s the best way to put them in order?
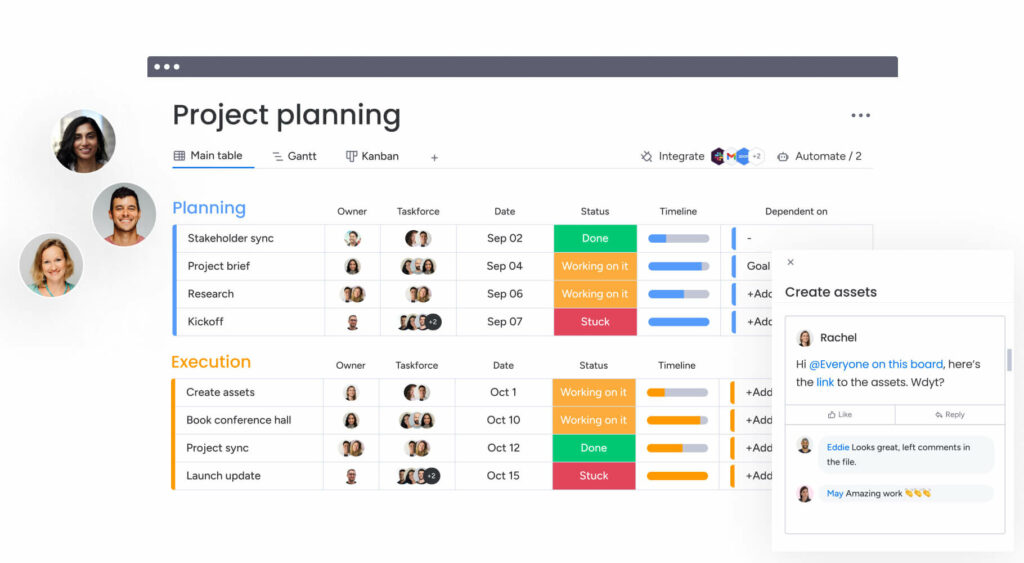
Whether you’d prefer to create a project roadmap, tracker, or overview, using an efficient, easy-to-use work management software — like monday work management — simplifies the process by giving you a clear visualization of all your tasks:
3. Estimate how long each task will take
There are several ways to estimate activity duration. To save you from sifting through all the methods out there, we’ve outlined our top three:
- Bottom-up estimating: Add up the estimates of the lowest-level work tasks to arrive at your summary total. Bottom-up estimates take more time to complete, but they also are more accurate than other estimates.
- Comparative estimating: Base your estimates on similar work or projects completed in the past. If you used time tracking in previous tasks, you’ll see precisely how long they took.
- Parametric estimating: Calculate a portion of the work and then multiply to get the overall estimate — e.g. if you believe one ad takes 2 hours and you have five ads to do, it should take 10 hours in total.
Read also: Bottom-up vs. top-down
4. Find all the potential ‘paths’ or ‘strings’
Any project can have multiple paths or strings of connected and dependent tasks.
This part of the process involves finding all these possible paths and calculating how long each one will take so that you can pinpoint the one with the longest duration.
By hand, this can be a headache with a high chance of error, which is not ideal. Fortunately, project management platforms, like monday work management, can do this automatically.
5. Identify the critical path
Now for the main event — it’s time to find the critical path.
Once you — or your work management software — have listed all the paths and strings, you need to identify the longest path through the project from start to finish.
So, if you’ve got a string of tasks that takes eight days, one that takes six days, and another that takes 12, then the 12-day string is the critical path. It’s the one that can’t have any delays without moving out your project end date.
6. Monitor the critical path
The critical path can, and most likely will, change throughout the project. Some tasks may take longer than expected, or new tasks get added over time.
Any changes to the project can have a knock-on effect on the critical path. This means you’ll need to check continuously throughout the project and update your critical path diagram accordingly.
We know it’s not ideal. One of the limitations of using the critical path project management method is its lack of flexibility. That’s why we created a critical path feature in monday work management that accounts for more flexibility.
Manage your critical paths with monday work management
The monday work management critical path feature makes your team more aware and efficient by visually displaying each project’s duration.
Once you add this feature to your Gantt Chart, it highlights the critical path in your project’s timeline — the events that must be completed on time for the overall project to finish on schedule.
Moreover, the software monitors any changes in critical path activity and automatically updates the current critical path in your project plan, so you don’t have to.
Start identifying critical paths today
So there you have it — a simple, no-nonsense guide to critical paths, including their definition, benefits, and how to identify them in your projects.
Now you know what’s what, why not check out some project management software that enables you to implement critical paths within your projects?
Critical path FAQs
Why is the critical path important in project management?
The critical path is important in project management because it helps estimate the project duration accurately, identify critical activities that must be completed on time, and highlight task dependencies, resource constraints, and potential risks.
What are non-critical activities?
Non-critical activities are tasks that can be delayed beyond their allotted deadline without affecting the project's overall duration. These activities have slack time and are not part of the critical path.
Can a project have multiple critical paths?
Yes, a project can have multiple critical paths. In complex projects, you can have multiple sequences of activities that are equally critical and must be completed on time for the project to run on schedule.