The word dependent comes from the Latin dependere meaning to ‘hang from’.
For those of you out there with a ‘dependent’ — I have a 4-year old — doesn’t that seem somehow apt?
It’s the same in project-land where some tasks determinedly cling to others for dear life, resolutely refusing to get started until someone has shown them the way.
Or gives them a cookie. Oh no wait, that’s just kids.
Anyhoo, this article will explain why it’s important to identify which tasks ‘hang from’ others, why failing to manage your dependencies can have such an impact on your project timeline, and what we think is the best tool for the job.
Remind me: what are dependencies?
Dependencies are tasks that are dependent on other tasks for their successful completion.
It’s not always necessary for predecessor tasks to be completed before the successor task can start.
There are actually 4 different ways tasks can be dependent on one another:
- Finish to start (FS). These are the most easily understood dependencies. The successor (second) task cannot start until the predecessor (first) task has finished.
- Finish to finish (FF). In this case, the successor task cannot finish until the predecessor task has finished.
- Start to start (SS). In this relationship, the successor task cannot start until the predecessor task has also started
- Start to finish (SF). These dependencies can be challenging to understand as it seems a little topsy-turvy. In this case, the successor task cannot finish until the predecessor task has started.
If you’d like to know more, we’ve got a whole article on dependencies that also gives examples of these relationships in practice.
Dependencies can also be classed as internal or external.
An internal dependency is one that is dependent on another project task. The management of internal dependencies is within the control of the project manager.
External dependencies are dependent on a task external to the project, an external supply chain for example. The completion of an external dependency is not within the control of the project manager so they carry a higher risk to the project and must be monitored carefully.
Why is tracking dependencies important?
Tracking dependencies are essential for 4 key reasons:
Schedule management
Project dependencies bring risk to a project, especially when they involve tasks on the critical path. The critical path is the longest string of dependent tasks within a project.
On a Gantt chart, it’s easy to see which string of tasks is the longest:
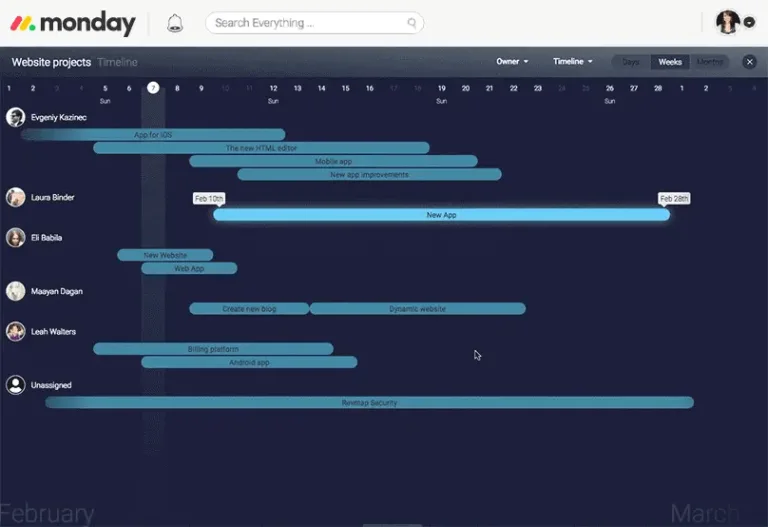
By estimating the duration of each task on the critical path, you can estimate overall project duration. Any delays to tasks on the critical path will also delay the project overall unless other tasks on the path are shortened.
Less than 1/3 of projects are completed on time. Monitoring and managing tasks on the critical path are key to ensuring on-time delivery.
Risk management
Identifying external dependencies, and those tasks on the critical path, shows where the greatest amount of project risk lies.
This means project managers can prioritize which tasks they monitor most closely and make sure they’ve got a Plan B should things go wrong.
They can set expectations with stakeholders about the level of risk attached to the project and help them understand the consequences of changes to those tasks.
Resource management
Project managers voted resource management as the 2nd most challenging process to get right. Understanding the sequencing of tasks, and their expected duration, makes it far easier to allocate resources.
Visibility of how resources are allocated is important if there is a delay to a task on the critical path. In order not to impact the project duration, other critical path tasks have to be shortened.
This can be achieved by adding extra resources to delayed tasks, so understanding who on the team is fully committed, and who’s available to help, is important.
Here’s how resource loading looks in monday.com:
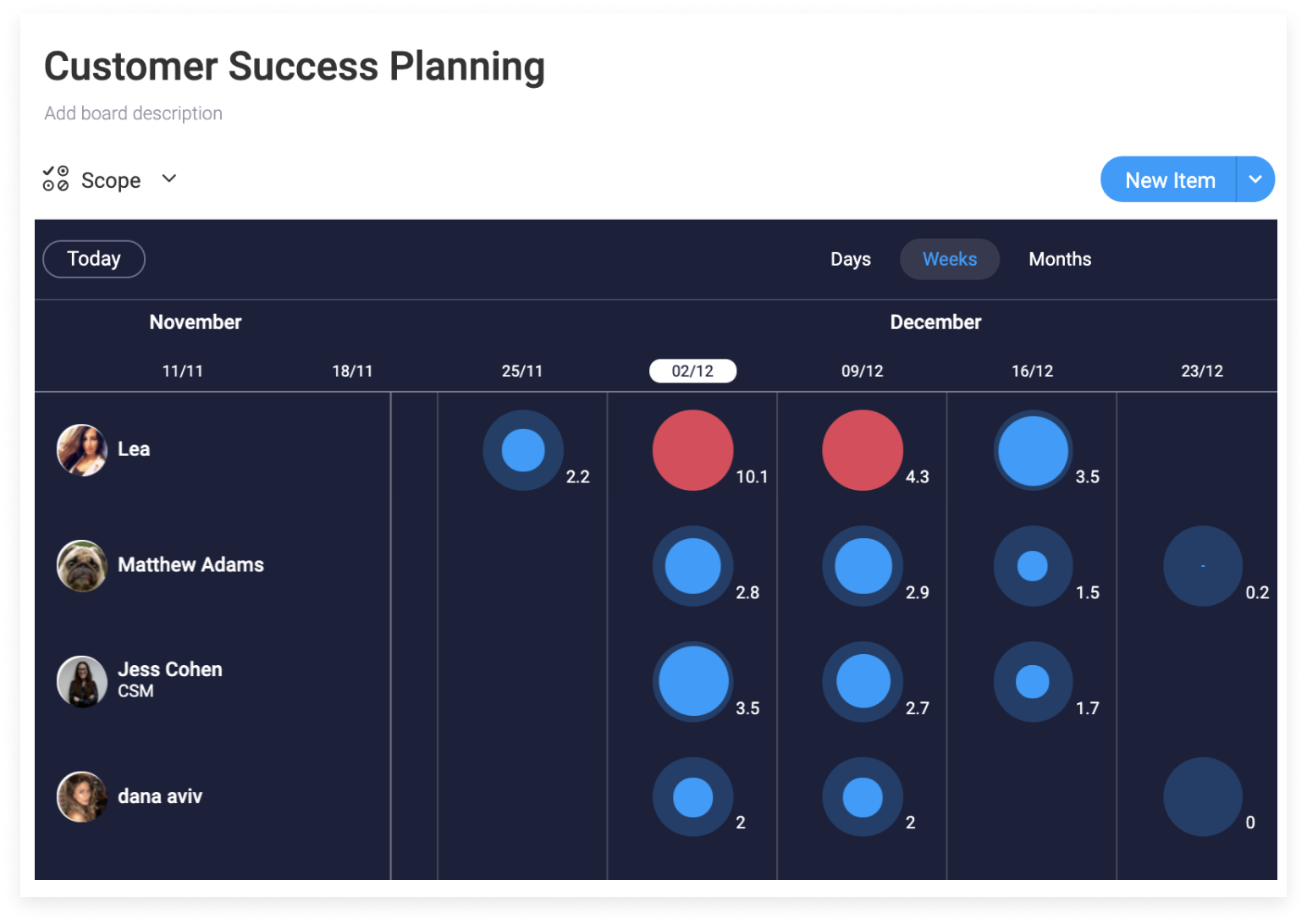
If the project requires external resources, understanding how tasks are related to one another makes scheduling contractors more accurate which can save time and money.
Scenario planning
Linked to risk management, identifying dependencies between tasks also helps with scenario planning.
As tasks are dependent on one another, project managers can show the impact on a successor activity, of making a change to its predecessor.
If there are project constraints, such as a fixed duration or budget, this means project managers can play with task duration, scope, and resources to identify the optimal project schedule to satisfy stakeholders.
If you’re new to scenario planning, find out more in our article.
How can using a dependencies diagram help?
Dependencies diagrams are a visual way to present information.
It can be much easier to understand how tasks hang together if they are presented in a way that clearly shows their sequencing rather than in a spreadsheet list.
They can also show the same information, such as task duration, in a way that’s much easier to read. It’s also simpler to identify and monitor the critical path.
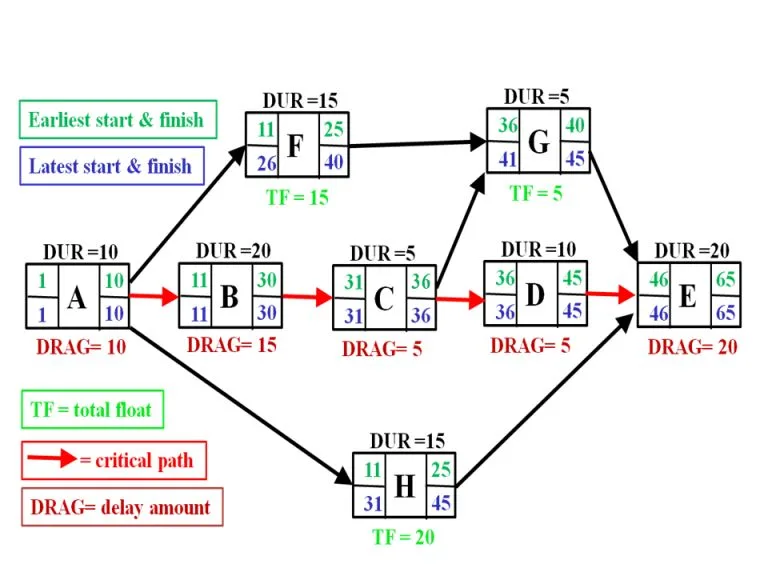
Representing tasks in this way can make it easier to engage stakeholders in a conversation about dependencies.
This is critical as it’s unlikely the project team will fully understand all the task dependencies without a visual aid.
Holding a dependencies workshop with business stakeholders is important to identify and verify all dependent tasks, and walking them through a diagram helps ensure nothing is missed.What types of dependencies diagrams are there?
There are 2 popular types of dependency diagrams:
PERT chart
The Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is a method used to analyze project activities in order to calculate the overall project duration. A PERT chart is a way to visually represent those activities.
A type of network diagram, a PERT chart uses lines to connect nodes, often depicted by circles or rectangles, to show the relationships between tasks.
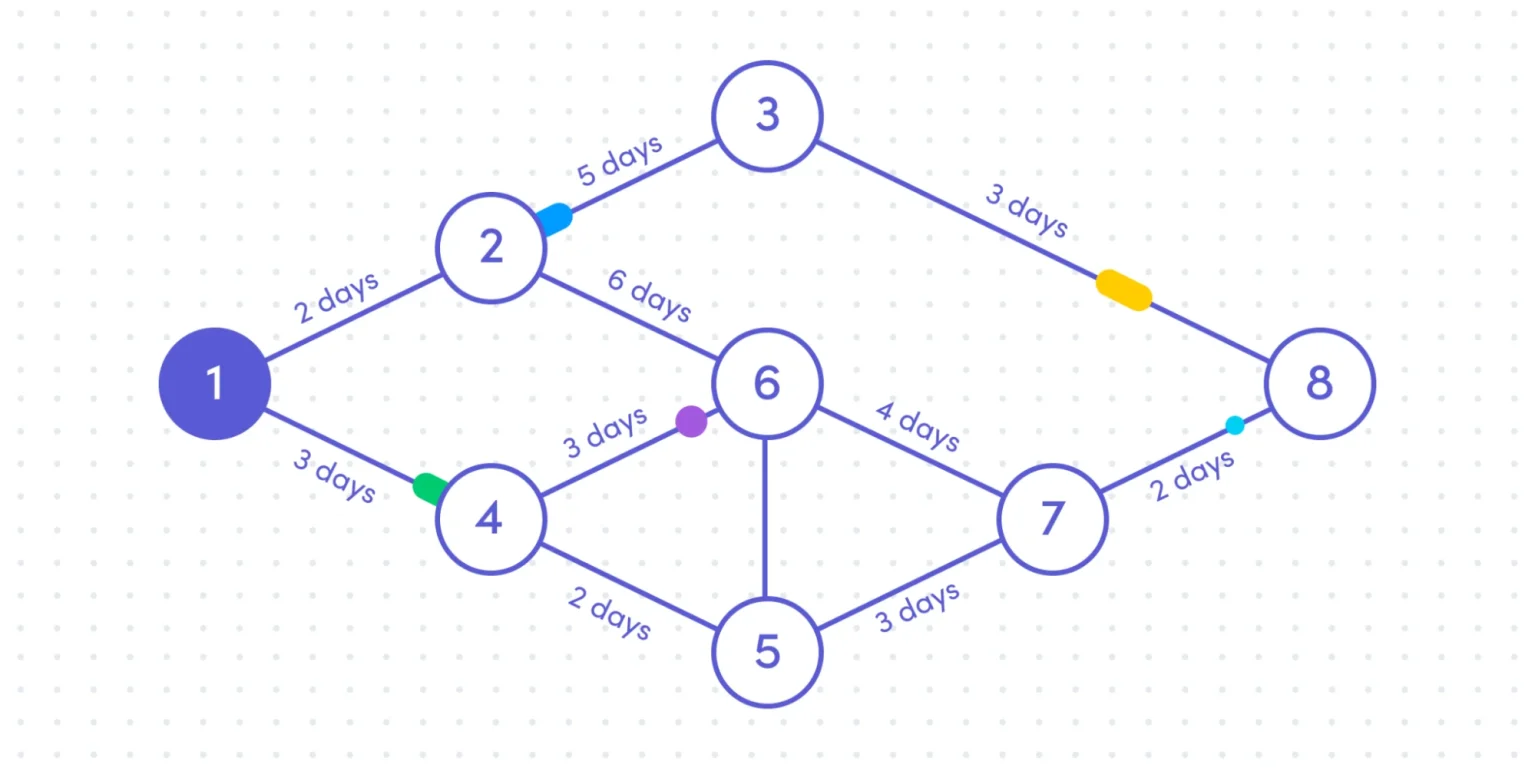
In PERT charts, arrows are used to show the flow of activity through the chart.
Solid directional arrows show dependent tasks that must be completed in sequence. Arrows that divert — for example, 4 to 5 and 4 to 6 — show tasks that could be completed concurrently.
PERT charts are most often used during project initiation and planning, to agree the scope and expected overall duration of the project.
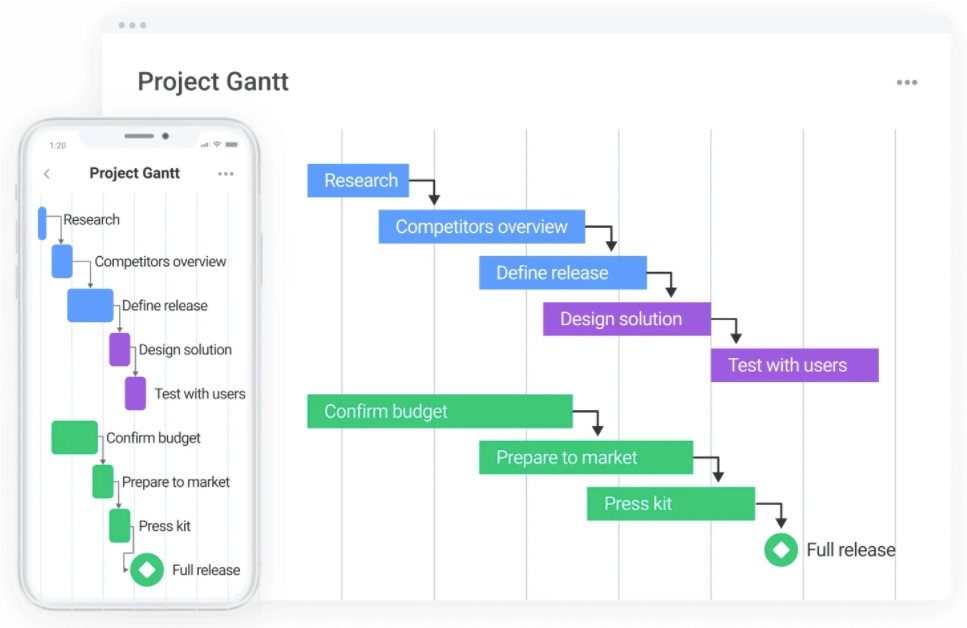
Gantt chart
Gantt charts are a popular project management tool where the project workflow is represented in a bar chart.
It can be used in planning but is predominantly used during project execution to track project progress.
Gantt charts are valuable as they can be overlaid with the project timeline to easily visualize whether tasks are being completed on schedule.
Like on PERT charts, dependencies can be represented by arrows or lines linking tasks together.
How can monday.com help create and track dependencies
As a Work OS, monday.com has all the tools you need to create and track dependencies effectively.
Using our work breakdown structure (WBS) template can be a helpful first step in identifying the tasks that make up the project.
Within the template you can also add all the information you need to effectively create a dependency diagram: task duration, predecessor tasks, and start/finish dates.
All the information from the WBS can then be displayed in a number of different formats — including our Gantt chart — which can act as a visual way to display dependencies between tasks.
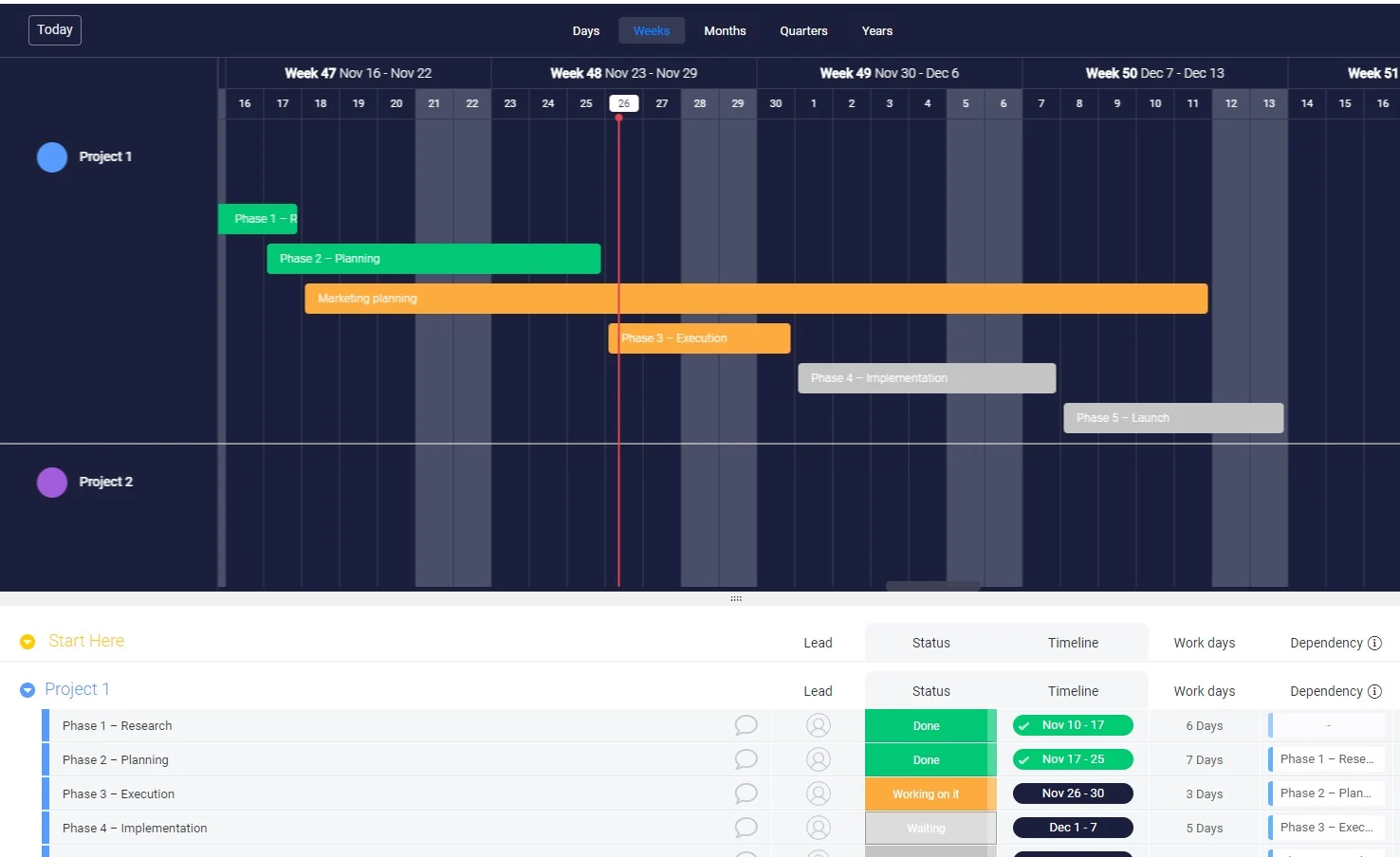
The monday.com Gantt chart is totally customizable and makes it simple to track project progress. You can group activities by status, priority, or owner and easily edit information with drag and drop functionality.
You can also set tasks to be dependent on other tasks. If you make any changes to the predecessor tasks, the successor task also updates. Which is really helpful if you’re scenario planning.
And because you’re working across an integrated platform, any task updates automatically sync wherever the data is stored.
This integration helps with other work activities too.
Documents, such as your risk register or resource tracker, can be stored and accessed from a single, shared workspace, and updated in real-time, which means you’re always working from the correct version.
Organizing and running dependency workshops is also a cinch. You can communicate within the monday.com digital platform or integrate an external collaboration tool.
Dependencies diagrams offer a simple way to show task relationships
In this article we’ve explained what dependencies are and why tracking them is so important to project success.
While dependencies diagrams are an awesome way to visualize how tasks ‘hang together’, creating and managing them manually is something no-one has time for in today’s volatile project environments.
Save your patience for wrangling an overtired child/dog/hamster and use the monday.com Work OS to do the job for you. Why not use our work breakdown structure template to get started?

