If you’ve been in business for a while, then you understand the importance of your processes. Your profitability is completely tied to your ability to design, manage, and optimize your business processes and operations.
Sadly, many business owners never take the time to actually map and model their processes in a visual way, leading to a lack of understanding of their own business. In this blog, we’ll take you through why business process modeling is essential for modern organizations and how to implement it today. Let’s start with the basics.
What is business process modeling?
First, we need to make sure we’re all in sync about what a process is.
A business process is the logical sequence of events that lead to a particular outcome relevant to your organization. A process includes all the activities or tasks in a chain of events that accomplishes something. Some examples of common business processes are issuing purchase orders, product assembly, shipping products, invoicing clients, and estimating project costs.
Business process modeling is the practice of back-engineering each process in your business to understand the different components needed to achieve the goal and finding potential improvements for each component.
It’s a business process analysis and continuous improvement discipline that helps you maximize any process through critical examination. For example, a typical business process model might look something like this:
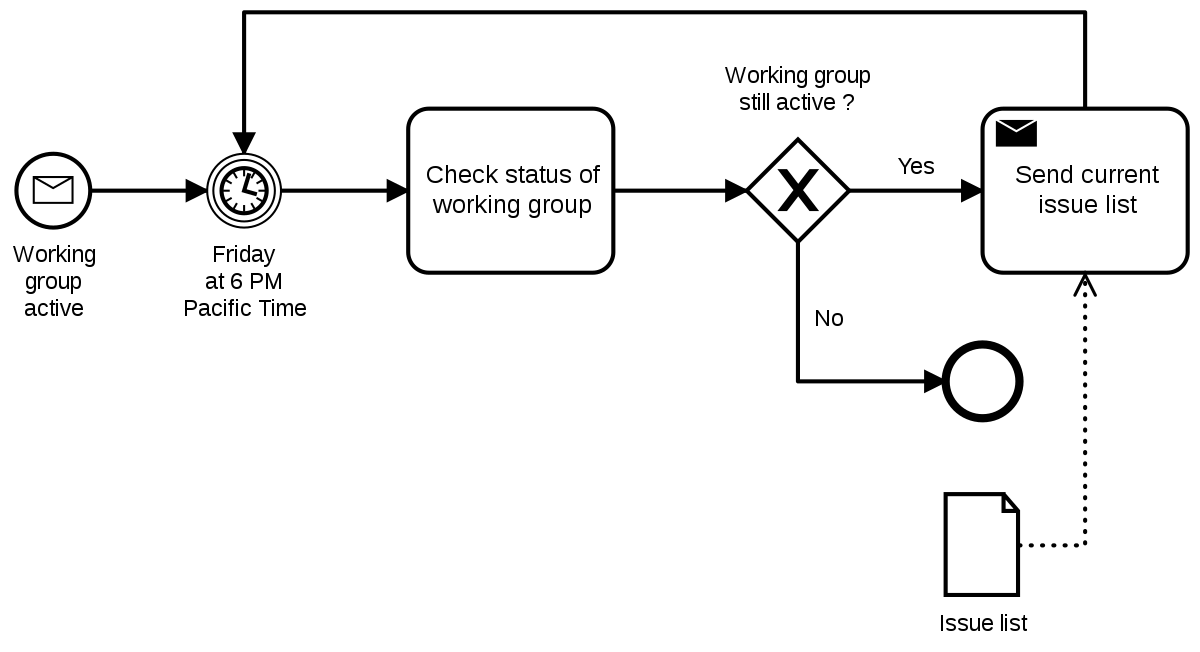
Though the above is only one example, there are other popular techniques for business process modeling. We’ll discuss some of these techniques more in-depth a bit later, but first, we’ll look into how process modeling can impact your company.
Benefits of business process modeling
As organizations evolve, so do their processes. We live in a hyper-accelerated world where businesses face massive changes almost overnight. If you don’t have a strategy in place to adapt to this constantly changing environment, your organization won’t survive for long. Cultivating a culture of learning and innovation within your organization is paramount. This fosters an environment that not only adapts to change but also anticipates it, staying one step ahead of industry dynamics.
In short, if you don’t model your processes, you’ll never know whether you’re operating at your best, and you’ll miss out on huge opportunities.
Some key benefits of process modeling are:
- Better alignment: align your activities with the core goals of your business
- More control: improve the way you control your activities and resources
- Better productivity: maximize your time and focus on what really matters
- Improve your bottom line: reduce inefficiencies, costs, and bottlenecks
- Produce better products and services: build more efficient production processes that delight your customers
A solid process model isn’t just a drawing or visual representation of your process—you’ll need other elements to really get the most out of this strategy.
8 critical elements of business process modeling
Diagrams —like the example we saw above—are just one of the many elements involved. To fully model a process, you must create a document with the following elements:
- Scope statement: a relevant description of the process name, as well as when the process starts and ends
- Outcome: a definition of the desired outcome of the process
- Description: a step-by-step walkthrough of the process description (i.e., the different steps that need to be executed to achieve the desired outcome)
- Exceptions and variations: a description of potential alternative process paths based on conditional data or action triggers
- Entry criteria and inputs: the elements you must have in place to execute the business process
- Exit criteria and output: what must be true once the process is completed
- Dependencies: a description of any other process or activity that’s dependent on this one
- Process flow diagram: a visual representation of the business process and its components
By documenting the entire process using these elements, you’ll have a clearer idea of where to start, as well as be able to communicate your full plan to your team and stakeholders.
It’s important to remember that business process models should include both visual and textual information to analyze each process at a more granular level. With that said, let’s look at some examples.

What are 5 business process modeling techniques?
Now that you understand the elements of a business model, let’s examine how can you represent your processes visually, starting with these five techniques:
- BPMN diagram
- Flowchart
- UML diagram
- Gantt chart
- PERT diagram
1. Business process modeling notation (BPMN) diagram
BPMN stands for Business Process Modeling Notation, and it’s a technique that helps you represent your processes in a visual manner through 100+ proprietary objects.
Some of these objects include:
- Process flow object: represents the sequence flow and execution of tasks
- Pool: represents process participants
- Swimlane: define sub-groups and divisions within pools
- Data object: represents information flowing through the process
- Artifacts: used to define how tasks and activities are organized
BPMN provides you with clear specifications for each diagram. By having a unified strategy or “language” to model your processes, you can make sure everyone is on the same page.
The example we shared earlier is a fairly simple business model diagram. Here’s an example of a more complex one:
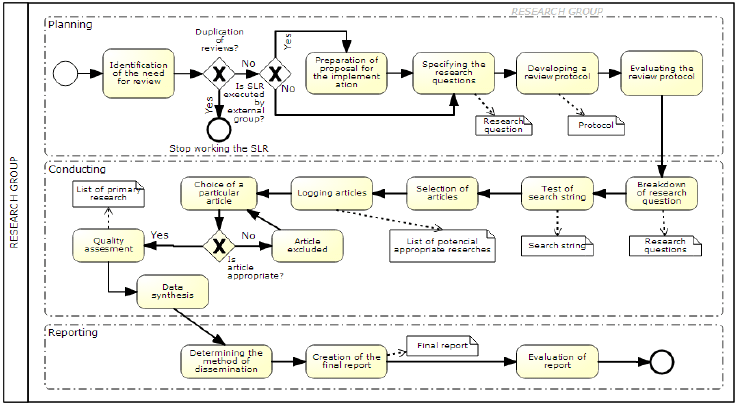
2. Flowchart
Flowcharts are one of the simplest and most widely-used techniques for process modeling. As the name suggests, flowcharts help you map out the sequence flow of activities you need to perform to complete a specific process.
In a flowchart, you should represent each step in the process with a shape. Then, you should connect those shapes with lines or arrows to indicate the logical progression of each step.
Here’s a simple process model example:
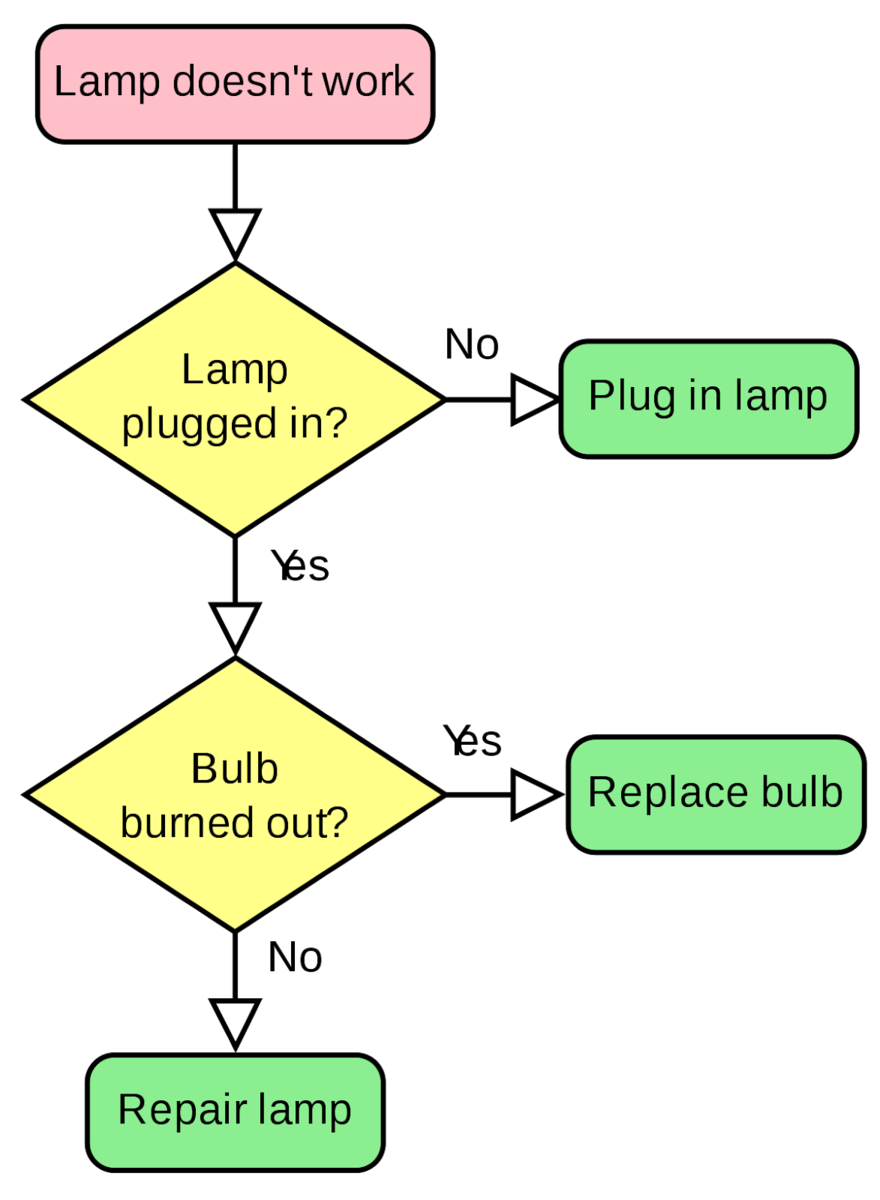
As you can see, flowcharts can use different process diagram shapes to represent different stages of the process. In the example above, we have two different shapes:
- Rectangle: represents start and end points
- Diamond: represents specific activities
In practice, you can use many different shapes to represent the different components of your processes — especially when you’re dealing with a complex process.
Flowcharts are simple yet powerful tools to communicate a business process in a way everyone can understand.
3. UML diagram
Communicating the value of software design isn’t always easy, especially when you’re dealing with a non-technical audience.
This is where UML comes in handy.
UML stands for Unified Modeling Language. It’s a modeling technique that helps you describe the elements that make up a specific software system and how such elements interact with each other.
UML involves different types of diagrams, which can be broken down into 2 main categories: structural diagrams and behavioral diagrams.
Structural diagrams represent the structure of a system. That is, the different elements and objects that make up the software. Some of the most popular structural diagrams include:
- Class diagram: mainly used for data modeling in a system
- Component diagram: describes the physical structure of the system in question
- Deployment diagram: describes the execution strategy and structure of the system
Behavioral diagrams, on the other hand, focus on the relationship between the objects in a system — how the different objects interact with each other to achieve a particular goal. A few common behavioral diagrams are:
- Use case diagram: describe the possible interactions between user and system
- Activity diagram: graphical representation of a user’s activities and actions when using a system
- State machine diagram: represent the behavior of an object within a system
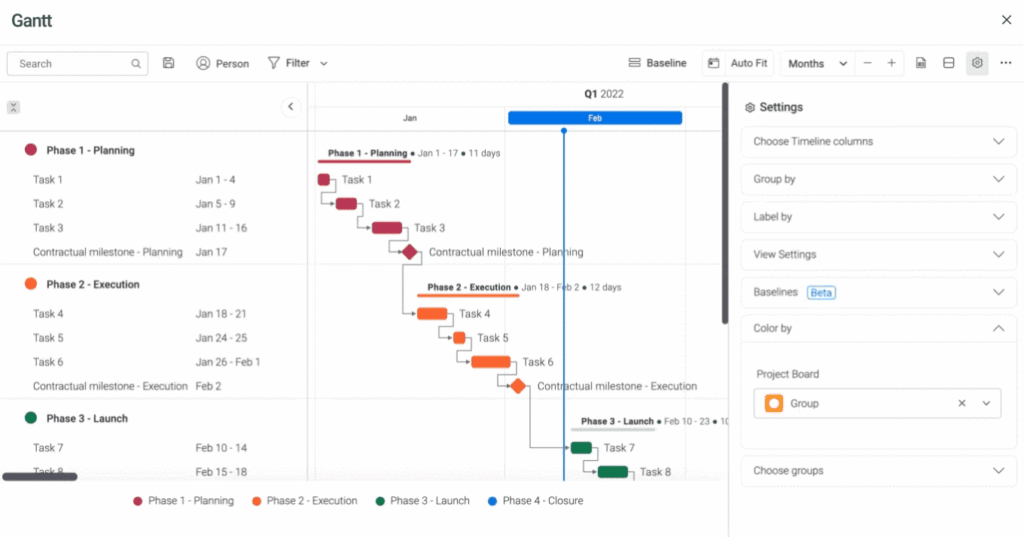
4. Gantt charts
Gantt charts are used to plan a project’s schedule against tasks and dependencies on a horizontal bar chart.
Setting up a Gantt chart is easy on monday.com because you have access to a built-in Gantt View and a widget for your project dashboard. You can also make changes to tasks directly in the Gantt View.
5. PERT diagrams
Similar to Gantt charts, PERT, or Program Evaluation and Review Technique, is a framework to map out task dependencies and estimations for a project’s duration.
This type of flowchart is useful for the early stages of planning when sorting through how all the pieces go together.
Let’s pause quickly; we’ve already covered the importance of business process modeling, as well as some of the most common techniques for visual process representation.
But if you want to achieve the highest level of performance in every one of your processes, you need the right system — a system that helps you centralize all your workflows onto a single place and can automate repetitive activities.
Business modeling processes and monday.com — how to
monday.com is a powerful Work OS that helps you build a custom digital workspace for any type of process, regardless of its complexity. To show you how it works, let’s follow a four-step process to model, manage, and improve your processes and operations.
1. Streamline the process
To improve any existing process, you must break it down into components. Consider what you need to achieve the goal. With the answer to that question in mind, you then need to prioritize those activities based on the impact they make on your bottom line.
Once you organize your activities in a progressive order, coordinate the execution with your team. You may also want to identify which activities can be automated and how.
To achieve all this, you need a flexible system that adapts to your needs and helps you streamline your processes. With monday.com Work OS, you can access fully customizable, pre-built templates to structure different processes in various industries, including:
- Advanced Project Management Template
- CRM Template
- Recruitment and Onboarding Template
- Social Media Planner Template
You can explore our complete list of templates in our Templates Center. We also provide you with over 250,000 automations, so you can speed up your operations and improve your productivity. A few tasks you can easily automate include:
- Recurring activities
- Notifications
- Item creation
- Tagging
- Dependencies
- Integration recipes
For more on monday.com Work OS automations, watch this short video below:
Finally, monday.com helps you centralize your entire organization into a single workplace, which makes it easier for you to streamline your workflows and improve your processes. You can create or add documents, files, automations, various views, data, and more all from monday.com Work OS.
2. Implement
Once you’ve defined your processes, it’s time to implement them. Start with a platform that allows you to collaborate with your entire team, remove silos between departments, and track progress with ease.
For instance, on monday.com Work OS, you can invite your entire team from the start and access powerful collaboration tools to improve your communication, including:
- File sharing
- Instant-messaging
- Video conferencing
- Tagging
- Notifications
For instance, you can click any of your items on your boards and add context to each task in real-time. This way, you can brainstorm ideas, get direct feedback from your peers, and improve your operations much faster.
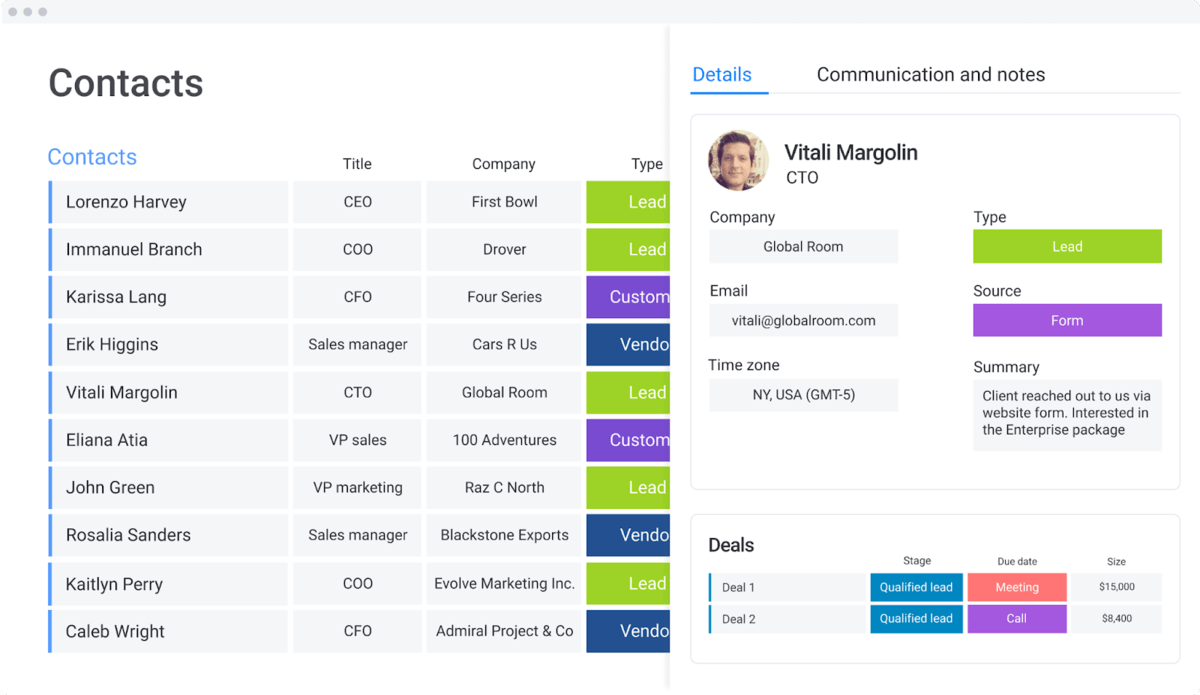
From goal management to resource allocation, you can structure and manage all your business processes more efficiently with monday.com work management.
3. Monitor
You can’t improve what you can’t measure. That’s why you need a system that helps you monitor all the information that’s important to you and analyze your progress.
Access powerful reporting dashboards that help you track everything from revenue to productivity, time, sales, tasks, performance, and more on monday.com.
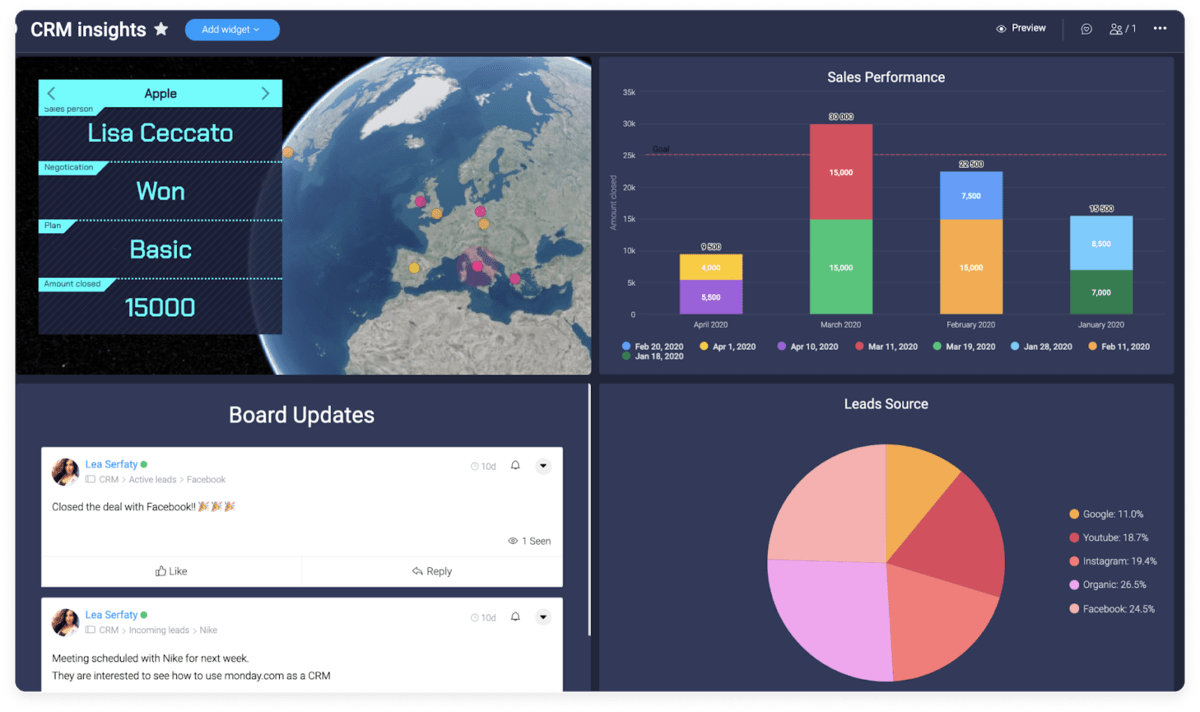
Dashboards make it easy to understand the overall performance of your processes and optimize accordingly. The best part? These dashboards are fully customizable, and you can adapt them to your exact needs.
4. Optimize
Finally, you should schedule a meeting with your team to analyze the data you collected in the last step and brainstorm how to improve current process. Consider asking:
- Where are the major bottlenecks?
- Is the team working productively?
- Are you using your resources wisely?
- Where are your biggest revenue leaks?
By answering these questions, you’ll be able to spot major issues in your processes before they start snowballing and fix them fast. Since monday.com Work OS is fully customizable, optimizing and adapting your processes to your new process ideas is completely feasible for any type of organization.
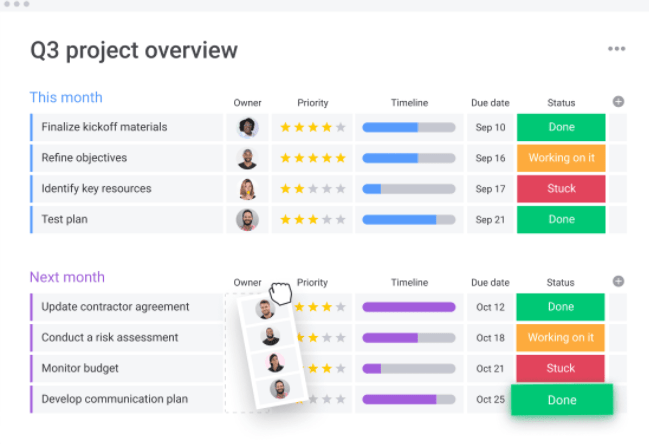

Ready to improve your business processes?
Hopefully, now you have enough understanding of the overall process, as well as why it’s crucial for the success of your business. And if you’re looking for a platform that helps you optimize each of your processes with surgical precision, then monday.com Work OS may be a great fit for you.
To see for yourself, we suggest you start with our Advanced Project Management Template. It’ll help you get your business process modeling off to a great start.