Your organization runs dozens of projects simultaneously, but when executives ask for portfolio health insights, teams scramble through spreadsheets and email threads to piece together answers. This delays strategic decisions, overallocates resources, and lets high-priority initiatives slip through the cracks.
This guide explores what separates true PMIS solutions from basic project tools, the five essential components of effective implementations, and how AI is transforming portfolio management. We’ll walk through a proven 7-step implementation framework and show how visual, flexible platforms deliver enterprise-grade PMIS capabilities without the complexity of traditional systems.
Try monday work managementKey takeaways
- A PMIS connects projects, resources, and data across the organization to deliver real-time portfolio visibility — not just individual project tracking.
- Enterprise-wide resource planning helps prevent burnout, surface skill gaps, and align capacity with strategic priorities.
- Automated reporting replaces manual status updates and audit prep with insights generated from live project data.
- Cross-functional visibility ensures teams like marketing, sales, and operations stay aligned as work moves between departments.
- Cloud-based platforms like monday work management enable PMIS implementation in weeks, not months, using visual boards, automation, AI, and 200+ integrations.
What is a project management information system (PMIS)?
A project management information system (PMIS) is a centralized digital platform that connects project data, resources, and workflows across an organization. It gives leaders and PMOs real-time insight into how projects are performing collectively — not just whether individual initiatives are on track.
Unlike basic project management tools that focus on task execution within a single team, a PMIS operates at the enterprise level. It connects hundreds of concurrent projects to strategic objectives while providing visibility into organizational capacity, resource allocation, financial performance, and portfolio risk.
At its core, a PMIS exists to answer higher-order questions: Which projects support our strategic goals? Where are we overcommitted? What risks threaten delivery? And where should we invest resources next?
To function effectively, a PMIS must include the following essential capabilities:
- Centralized project data: A single source of truth that eliminates silos, version conflicts, and fragmented reporting.
- Portfolio-level visibility: Cross-project insight that reveals dependencies, conflicts, and competing priorities.
- Resource management: Capacity planning and skills-based allocation across teams and departments.
- Financial integration: Budget tracking and forecasting connected to accounting and financial systems.
- Strategic reporting: Executive dashboards that tie project performance directly to business outcomes.
Modern PMIS platforms increasingly layer AI on top of these capabilities, shifting project management from reactive reporting to predictive, insight-driven execution.
How PMIS differs from project management software
The difference between basic project management software and a true PMIS comes down to scale, portfolio intelligence, and strategic alignment.
| Capability | PMIS | Basic project management software |
|---|---|---|
| User capacity | Hundreds to thousands of users across the organization | Single team or department (typically under 50 users) |
| Project scope | Portfolio management with cross-project visibility | Individual project tracking |
| Integration depth | Native connections to ERP, CRM, financial, and HR systems | Limited integrations, often requiring custom development |
| Resource management | Enterprise-wide resource optimization and capacity planning | Team-level resource assignment |
| Reporting sophistication | Executive dashboards, predictive analytics, strategic alignment tracking | Basic status reports and Gantt charts |
| Governance features | Multi-level permissions, audit trails, compliance reporting | Simple access controls |
| Financial tracking | Budget management, cost forecasting, financial system integration | Basic budget tracking without financial integration |
A PMIS enables leaders to understand how projects interact, where resources conflict, and how delivery impacts strategic goals. Basic project tools, by contrast, are optimized for execution within isolated teams rather than portfolio-wide decision-making.
5 core components of an effective PMIS
A powerful PMIS brings together 5 key elements that turn your fragmented project data into actionable insights. Each component addresses specific operational challenges while contributing to the unified system that enables portfolio-level decision-making. Together, these components give you a complete picture of how projects are performing across your entire company.
1. Centralized project repository
The project repository eliminates version control nightmares by keeping all your project information in one place that everyone can trust. This component stores project charters, timelines, budgets, deliverables, communications, and documentation in a structured, searchable format.
Key capabilities include:
- Version control: Teams always access the most current information while maintaining audit trails of changes
- Access management: Controls who can view, edit, or approve information based on role and responsibility
- Information accessibility: Eliminates critical project information scattered across email threads, shared drives, and individual computers
When a project manager needs to understand project history or a new team member requires onboarding, the centralized repository provides immediate access to complete project context.
2. Resource management engine

When a new project requires specialized expertise, the system identifies available resources with the necessary skills and current capacity. The engine prevents overallocation by flagging when individuals are assigned beyond sustainable workloads and suggests reallocation options.
3. Financial tracking and budgeting
Financial components integrate project budgets with organizational accounting systems to provide real-time visibility into project costs, budget consumption, and financial forecasts. Budget planning features help project managers develop realistic cost estimates based on resource rates, vendor costs, and historical data.
Core financial capabilities include:
- Expense tracking: Captures actual costs as they occur, comparing them against budgets to identify variances early
- Cost forecasting: Uses current burn rates and remaining work to predict final project costs
- Proactive intervention: Enables action when projects trend over budget
4. Risk management framework
The risk management component provides structured approaches to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks across the portfolio. Risk identification features prompt teams to consider common risk categories including scope, schedule, resource, technical, and external risks.
Assessment capabilities evaluate risk probability and impact, prioritizing which risks require immediate attention. PMIS systems increasingly incorporate predictive analytics that scan project data for early warning signs of potential issues. These systems might flag projects with declining velocity, identify resource constraints that could cause delays, or detect scope creep patterns.
5. Reporting and analytics dashboard
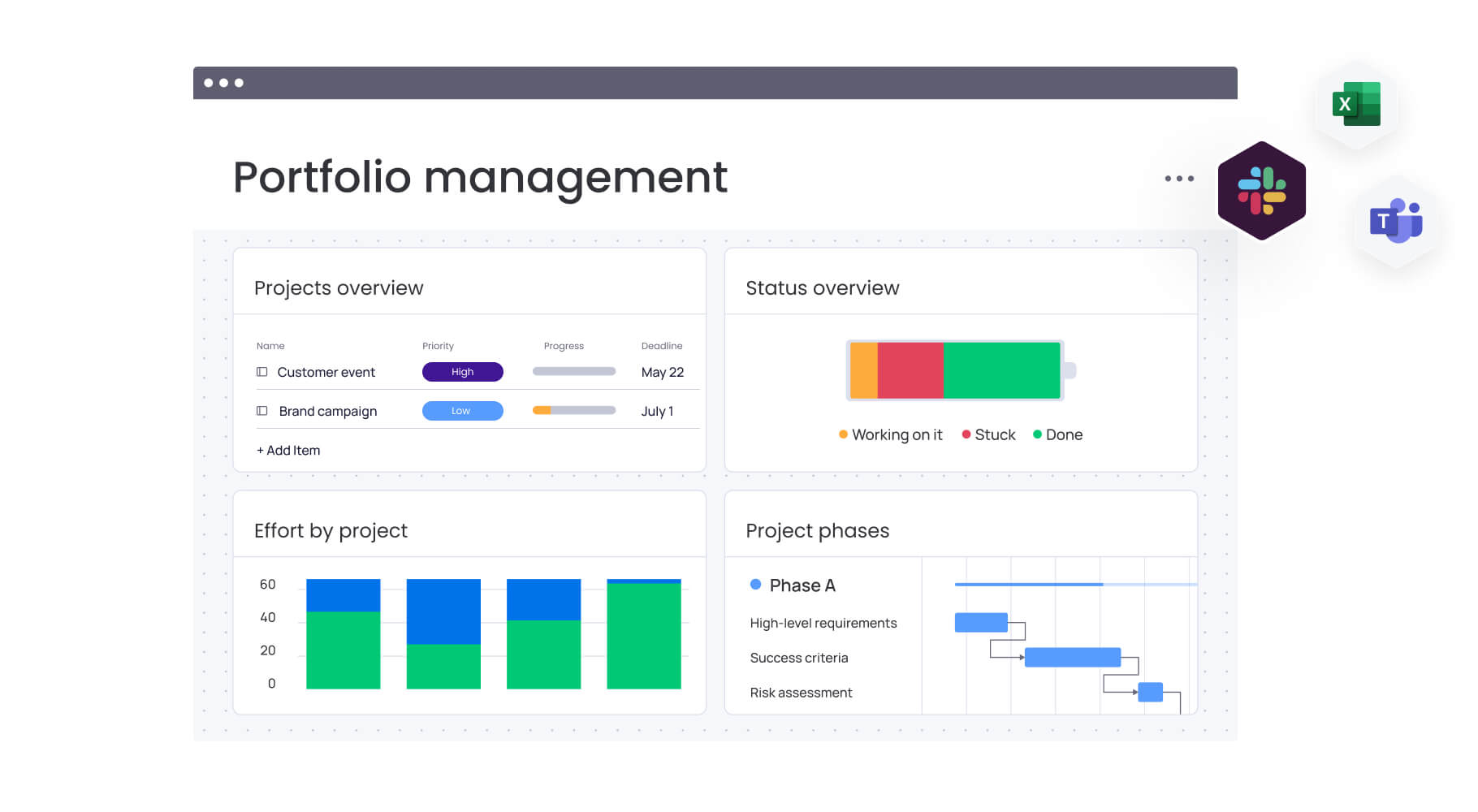
The reporting component transforms raw project data into actionable insights through executive dashboards, KPI tracking, trend analysis, and customizable reports. Executive dashboards provide at-a-glance portfolio health indicators including project status distribution, budget consumption, resource utilization, and progress toward strategic goals.
KPI tracking monitors metrics that matter to the organization, from on-time delivery rates to customer satisfaction scores. Platforms like monday work management incorporate these reporting capabilities through portfolio dashboards and automated reporting features that generate insights without requiring manual data compilation.
Try monday work managementHow PMIS supports the complete project lifecycle
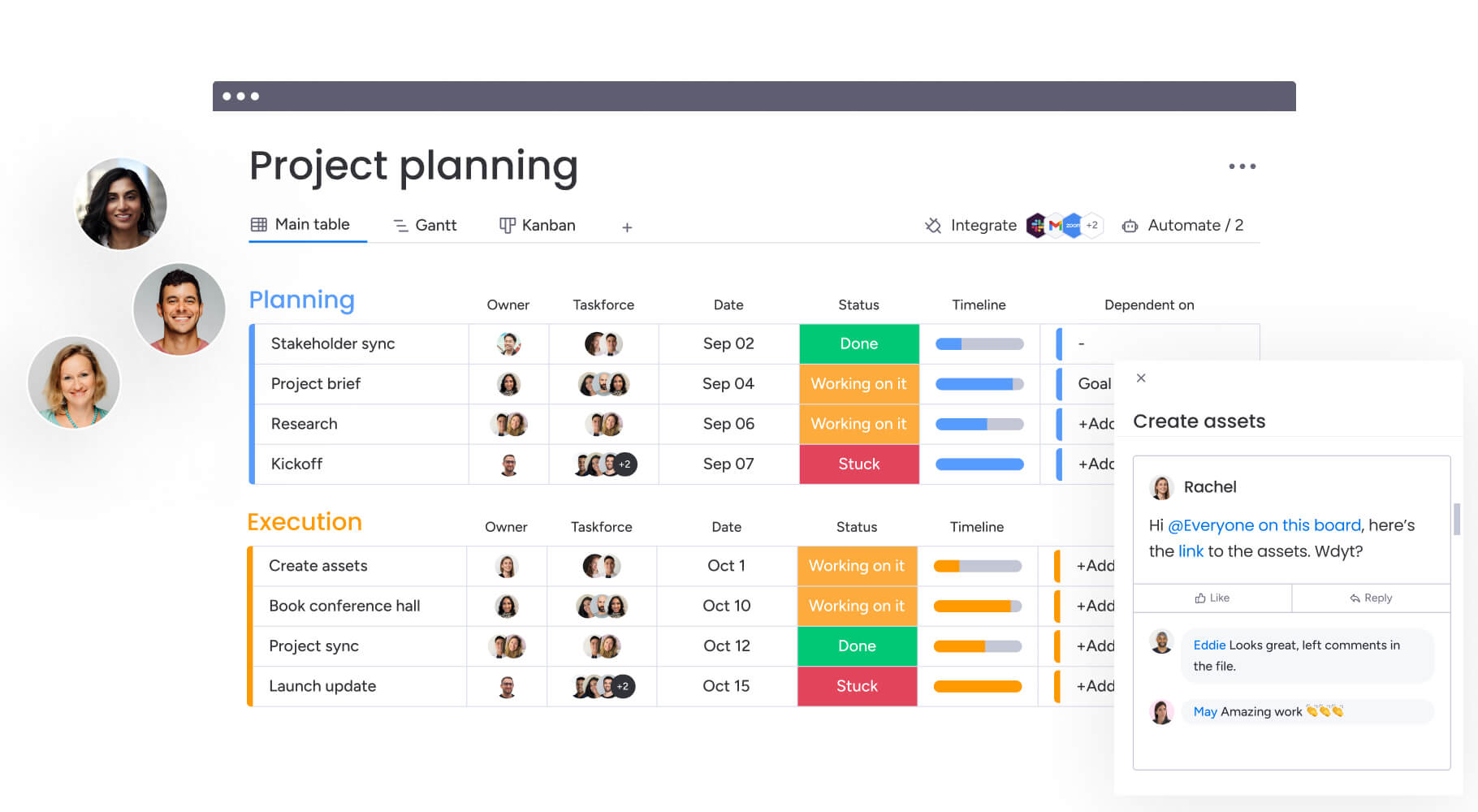
- Initiation: Evaluate proposals against strategy and capacity using standardized templates.
- Planning: Build realistic timelines based on dependencies and available resources.
- Execution: Coordinate work through real-time tracking, automation, and collaboration.
- Monitoring: Compare actual performance to baselines for schedule, scope, and budget.
- Closure: Capture lessons learned and release resources for future initiatives.
AI-powered PMIS platforms enhance execution by identifying risks early and recommending corrective actions rather than waiting for post-mortems.
6 key benefits of PMIS implementation
Organizations implementing PMIS capabilities gain measurable advantages that transform how work management flows across the enterprise. The impact goes well beyond just delivering projects on time — it improves how your entire business executes on its strategy. The following advantages demonstrate why organizations invest in comprehensive PMIS solutions rather than continuing with fragmented project management approaches.
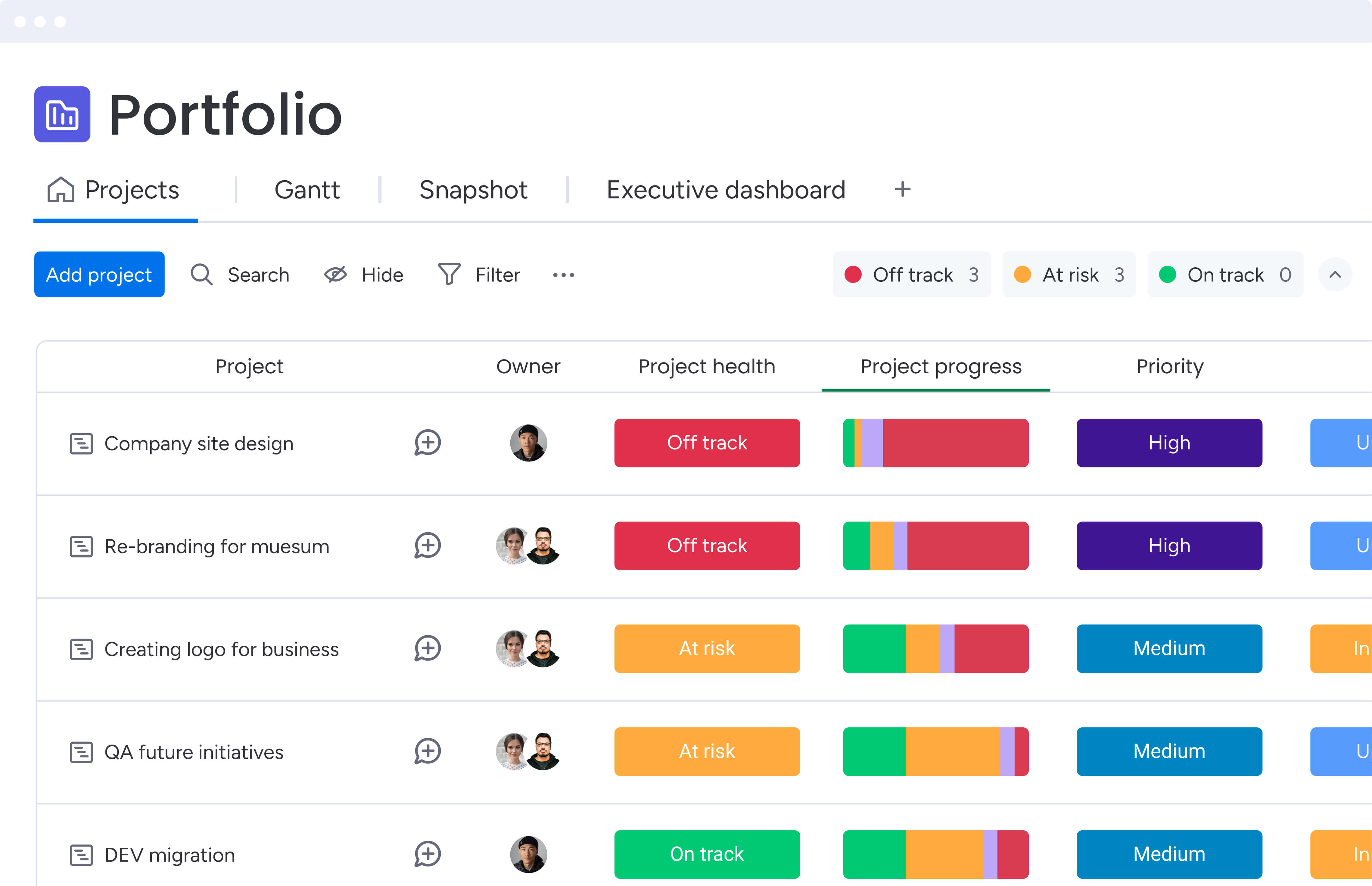
- Real-time portfolio visibility: Executives see portfolio health instantly — which projects are on track, at risk, or in trouble — without waiting for manual status reports or time-consuming review meetings.
- Optimized resource utilization: Prevent overallocation and burnout by seeing current workload across all projects, enabling teams to adapt quickly to changing priorities.
- Automated compliance and reporting: Generate status updates from actual project data rather than compiling reports manually. This automation frees project managers to focus on execution rather than documentation.
- Enhanced cross-functional collaboration: Break down silos with a shared platform where marketing sees development timelines, sales tracks implementations, and operations coordinates with customer success.
- Data-driven decision making: Comprehensive analytics transform project data into strategic insights. Project managers identify which items consume more effort than planned, while portfolio managers analyze which project types consistently deliver on time and budget.
- Accelerated project delivery: Standardized processes, automated workflows, and proactive issue identification reduce project timelines without sacrificing quality.
Essential PMIS features that drive success
Effective PMIS implementations depend on specific capabilities that distinguish platforms that transform operations from those that simply digitize existing processes. The right feature set determines whether teams embrace the system or resist its adoption.
- Visual project dashboards: At-a-glance project health indicators and portfolio overviews make complex information accessible through color coding, progress indicators, and data visualization that everyone can understand.
- Workflow automation capabilities: Reduce manual work and accelerate project delivery through intelligent routing and notifications. Look for no-code automation configuration that lets business users create workflows without IT resources.
- Business system integration: Project data flows automatically between platforms, connecting project management to procurement, inventory, manufacturing, and customer information without manual data entry or duplicate records.
- Mobile accessibility: Full functionality from anywhere enables team members to update status, approve deliverables, and respond to issues from their phones — particularly critical for organizations with field operations or remote teams.
- Predictive risk analytics: AI analyzes historical project data, current performance indicators, and external factors to predict potential risks before they materialize, enabling proactive mitigation rather than reactive crisis management.
- Intelligent resource recommendations: AI optimizes resource allocation by analyzing skills, availability, workload, and project requirements to suggest optimal team assignments based on past performance and working relationships.
- Automated status reporting: AI generates intelligent project reports, identifies key insights, and provides executive summaries without manual intervention — analyzing project data to explain what happened and why it matters.
These AI capabilities represent a fundamental shift from reactive to proactive project management. Traditional PMIS platforms tell you what happened; AI-powered systems predict what will happen and recommend actions to optimize outcomes.
Try monday work management7 steps to implement your PMIS successfully
Successful PMIS implementation requires a structured approach that addresses technical, organizational, and change management dimensions. Teams that follow a clear implementation roadmap see faster user adoption and get more value from their investment — often months sooner than those who wing it. These steps provide a proven roadmap for transforming project management capabilities across the enterprise.
Step 1: Evaluate current project management maturity
Assessment begins with understanding the organization’s current project management capabilities, existing systems and processes, and readiness for change. Maturity assessment frameworks evaluate whether the organization operates at ad hoc, defined, managed, or optimized levels across key dimensions.
Key evaluation areas include:
- Process standardization: How consistent are project management approaches across teams
- Technology adoption: What systems currently support project work
- Change readiness: How receptive is the organization to new processes and technology
Step 2: Define PMIS requirements and goals
Requirements definition translates business needs into specific PMIS capabilities and success criteria. This step involves identifying must-have features versus nice-to-have capabilities, defining integration requirements with existing systems, and establishing success metrics.
Critical requirements include:
- Functional capabilities: What the system must do to support business objectives
- Integration needs: Which existing systems require connection
- Success metrics: How the organization will measure implementation success
Step 3: Select your PMIS platform
Platform evaluation assesses available solutions against defined requirements using structured decision frameworks. Evaluation criteria should include functional capabilities, integration depth, usability, scalability, vendor stability, implementation support, and total cost of ownership.
Step 4: Design your implementation roadmap
Implementation planning develops a phased rollout approach that manages risk while delivering value incrementally. Most successful PMIS implementations follow a pilot-first approach rather than attempting organization-wide deployment immediately.
Step 5: Configure workflows and integrations
System configuration translates organizational processes into PMIS workflows while establishing integrations with business systems. Organizations implementing platforms like monday work management benefit from no-code configuration capabilities that enable business users to design workflows without requiring IT development resources.
Step 6: Launch pilot program
Pilot launch tests the PMIS with a limited user group, gathering feedback and refining the implementation before organization-wide rollout. The pilot period typically runs 6-8 weeks, long enough to experience complete project workflows from initiation through closure.
Step 7: Scale across the organization
Organization-wide rollout extends PMIS access to all relevant teams and departments, supported by comprehensive training, change management, and ongoing optimization.
Common PMIS implementation challenges and solutions
Organizations implementing PMIS capabilities encounter predictable challenges that can derail implementations if not addressed proactively. Understanding these common obstacles and proven solutions increases implementation success rates. Preparation for these challenges enables organizations to maintain momentum and achieve successful adoption.
Change resistance and adoption challenges
Change resistance typically stems from comfort with existing processes, concern about learning new systems, fear that increased visibility will expose performance issues, and skepticism about whether the new system will actually improve work. Effective adoption strategies address these concerns through:
- Executive sponsorship: Visible leadership support
- Early engagement: Involve skeptics in the selection process
- Quick wins: Demonstrate tangible benefits early
- Tailored training: Role-specific programs that show relevance
Data migration complexity
Moving historical project data from existing systems into the new PMIS presents both technical and strategic challenges. Data quality assessment often reveals that existing data is incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate.
Effective data migration strategies include:
- Data quality assessment: Identify which information is accurate and valuable enough to migrate
- Prioritization: Focus migration effort on active projects and recent historical data that will inform future planning
- Phased approach: Migrate critical data first, then historical information as resources allow
Integration difficulties
Connecting PMIS to existing business systems often proves more complex than anticipated due to technical constraints, data format incompatibilities, and organizational policies. Effective integration management begins with realistic assessment of integration feasibility and value. Not all integrations deliver equal business value.
Transform project chaos into strategic execution with monday work management
Organizations seeking PMIS capabilities increasingly turn to platforms that combine enterprise functionality with intuitive usability. With monday work management, you gain comprehensive PMIS capabilities through a visual, flexible platform that teams actually enjoy using.
- Visual portfolio management: Switch between Gantt charts, Kanban boards, calendar views, and executive dashboards to visualize project data the way that makes sense for each stakeholder. Customizable boards adapt to your workflows rather than forcing you into rigid templates.
- AI-powered intelligence: Portfolio Risk Insights scan project boards to identify potential risks and flag concerning trends before they derail delivery. Resource management AI recommends optimal team assignments based on skills, availability, workload, and past performance.
- Strategic alignment: Link projects directly to strategic goals and OKRs so teams see how their work contributes to organizational priorities. Portfolio management capabilities reveal dependencies, resource conflicts, and trends across all initiatives.
- Enterprise-grade security: Multi-level permissions ensure users see only what’s relevant to their role, while 200+ native integrations connect your PMIS to existing ERP, CRM, financial, and HR systems.
Build your enterprise PMIS in weeks, not months
Organizations implementing PMIS capabilities through cloud platforms achieve operational value in weeks rather than waiting months for traditional enterprise systems to become functional. A realistic timeline for monday work management PMIS implementation follows this pattern:
- Weeks 1-2: Define requirements, configure initial boards and workflows, establish integrations with highest-priority business systems
- Weeks 3-4: Deploy to pilot group of 3-5 projects and 20-50 users, provide intensive support and gather feedback
- Weeks 5-8: Address feedback from pilot, complete additional integrations, develop training materials and documentation
- Weeks 9-12: Deploy to all relevant teams and departments in waves, provide training and support, establish governance processes
This timeline delivers operational PMIS capabilities in 3 months with ongoing enhancement, compared to 6-12 months for traditional enterprise PMIS implementations. The platform’s ability to grow with organizational needs eliminates the need for major reconfigurations as requirements evolve.
Start building your enterprise PMIS today
Implementing a PMIS fundamentally changes how your teams deliver the work that matters most. The shift from fragmented project management to integrated portfolio intelligence enables more informed decisions, faster execution, and stronger alignment between daily work and strategic objectives, giving organizations competitive advantages through improved resource utilization, accelerated project delivery, and data-driven decision making.
With monday work management, you get the enterprise-grade capabilities organizations need with the intuitive design that ensures adoption. The platform’s combination of visual interfaces, AI-powered intelligence, and extensive integration capabilities delivers PMIS value without the complexity and lengthy implementation timelines of traditional enterprise solutions.
Try monday work managementFAQs
What is the difference between PMS and PMIS?
PMS (Project Management System) refers to systems focused on managing individual projects, while PMIS (Project Management Information System) encompasses enterprise-wide portfolio management, strategic alignment, and business intelligence capabilities across all projects.
How long does PMIS implementation typically take?
Implementation timelines range from 2-4 months for cloud platforms like monday work management to 6-12 months for traditional enterprise PMIS solutions, depending on organizational complexity and integration requirements.
Can a PMIS integrate with existing ERP and CRM systems?
Yes, PMIS platforms provide native integrations with major ERP and CRM systems, enabling automated data flow between project management and business systems without requiring custom development.
Which industries benefit most from PMIS implementation?
Industries with complex project portfolios including construction, consulting, technology, healthcare, manufacturing, and professional services gain the greatest value from PMIS capabilities.
Is PMIS suitable for small and medium businesses?
Cloud-based PMIS solutions have made enterprise-level capabilities accessible to organizations of all sizes through flexible pricing, rapid implementation, and scalable architectures that grow with business needs.
How does cloud-based PMIS enhance collaboration?
Cloud deployment enables real-time access from any location, full mobile functionality, seamless external stakeholder inclusion, and automatic updates that keep all users on the same platform version.