Your customer clicks “buy now,” and suddenly dozens of invisible decisions kick into gear — which warehouse ships it, how inventory gets allocated, when labels print, how exceptions get handled. When this orchestration works, customers get exactly what they ordered on time. When it doesn’t? You’re dealing with frustrated customers, operational chaos, and lost revenue.
This guide breaks down the 5 essential stages of order management, tackles common challenges head-on, and shows you how to build scalable processes that actually work. You’ll learn how to automate routine decisions, connect disconnected systems, and create an operational foundation that grows with your business.
Try monday work managementKey takeaways
- Document every step from order capture to delivery to identify bottlenecks and automation opportunities before implementing new systems.
- Focus on the 5 core stages: Master order capture, intelligent routing, fulfillment orchestration, shipping tracking, and returns management to create seamless customer experiences.
- Connect scattered systems, integrating existing e-commerce, inventory, and shipping platforms to eliminate manual data entry and reduce costly errors.
- Design visual order processes, automate routing decisions, and track performance through real-time dashboards without technical expertise.
- Give sales, operations, and customer service access to the same order data so everyone can make informed decisions quickly.
What is order management?
Order management transforms customer clicks into delivered packages, orchestrating everything that happens between “order confirmed” and “delivered to your door.” This means coordinating inventory, processing payments, managing fulfillment, and handling returns across your entire operation.
For growing businesses, effective order management makes the difference between delighted customers and disappointed ones, between streamlined operations and costly chaos, between predictable revenue and constant fire-fighting. When your order system hums, customers get exactly what they want, teams work without friction, and your business grows confidently. But when it falters? You’re facing angry customers, operational nightmares, and serious revenue problems.
Consider how an e-commerce retailer processing hundreds of daily orders manages the same core activities as a B2B manufacturer handling complex enterprise shipments. Both capture order information, allocate inventory, coordinate fulfillment, track shipments, and manage post-delivery service. The real challenge isn’t running separate systems — it’s getting your e-commerce platform, inventory database, and shipping software to actually talk to each other so everyone sees the same information at the same time.
Order management vs. order processing
Order processing is the hands-on work: Someone receives the order, checks it for accuracy, pulls the items from shelves, boxes everything up, and sends it out the door. Order management encompasses the broader strategic framework including order processing plus inventory management, customer communication, returns handling, and performance optimization.
Understanding this distinction helps you approach order operations strategically rather than just tactically.
| Aspect | Order processing | Order management |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Individual order fulfillment | Entire order lifecycle |
| Focus | Tactical execution | Strategic orchestration |
| Activities | Picking, packing, shipping | Demand planning, inventory positioning, fulfillment strategy |
| Ownership | Warehouse teams | Cross-functional leadership |
| Timeframe | Per-order basis | Ongoing optimization |
Picture order processing as your warehouse crew grabbing products and boxing them up. Order management is the strategy behind it: choosing the right warehouse for each order, making sure inventory sits where you’ll need it, setting realistic delivery promises, and constantly finding ways to do it all better.
Order management vs. order fulfillment
Order fulfillment is the physical work. Think storing products, picking items off shelves, packing boxes, and shipping packages. Order management, on the other hand, is the bigger picture, including the strategy, planning, and coordination that ensures those boxes contain the right stuff and arrive when promised.
Picture order fulfillment as the kitchen in a restaurant where food is prepared and plated. Order management is the restaurant’s entire operation: taking orders, coordinating kitchen timing, managing customer expectations, handling complaints, and continuously improving the dining experience. Organizations often coordinate multiple fulfillment centers or partners, which is where order management becomes crucial for maintaining consistency across all operations.
The 5 essential stages of order management
Every order travels a path from the moment a customer clicks ‘buy’ until they open their package. While specific processes vary across industries, these 5 fundamental stages apply universally. When you understand what happens at each step — and where things typically go wrong — you can build systems that actually work when orders start flooding in.
Stage 1: Order capture and validation
Order capture transforms customer intent into a formal order in your business system. Orders arrive through multiple channels including websites, phone calls, emails, sales teams, mobile apps, and marketplace platforms. Centralizing this information into a single system of record is your first critical step.
Validation confirms you can deliver what the customer wants before you promise it. This step is crucial for preventing overselling and setting accurate expectations. Key validation activities include:
- Customer verification: Confirming identity and payment method validity
- Inventory checks: Ensuring products are actually in stock
- Pricing confirmation: Verifying current pricing and applicable discounts
- Information completeness: Ensuring all required details are present
With live inventory data and clear decision rules, your system can automatically green-light most orders, flagging only the tricky ones for human eyes.
Stage 2: Intelligent order routing
Order routing determines how and where each order gets fulfilled. Intelligent routing considers multiple factors simultaneously to optimize for cost, speed, and customer satisfaction.
Key routing considerations include:
- Geographic proximity: Reducing delivery time through strategic location selection
- Inventory availability: Preventing split shipments that increase costs and complexity
- Capacity constraints: Avoiding overloading specific locations during peak periods
- Special requirements: Accommodating items needing specific storage or packaging
Poor routing leads to delayed deliveries, higher costs, and customer dissatisfaction. A customer ordering 3 items might receive 3 separate shipments from different warehouses, increasing both shipping costs and frustration.
Stage 3: Fulfillment orchestration
Fulfillment orchestration coordinates all activities needed to get products to customers. Unlike simple execution, orchestration manages multiple moving parts simultaneously to ensure warehouse operations, quality control, and shipping coordination work together seamlessly.
Orchestration activities span several critical areas:
- Item reservation: Securing specific products for each order
- Workflow sequencing: Organizing warehouse activities for maximum efficiency
- Quality assurance: Ensuring accuracy and condition of shipped items
- Documentation creation: Generating shipping labels and tracking information automatically
- Carrier coordination: Scheduling pickups and managing delivery partnerships
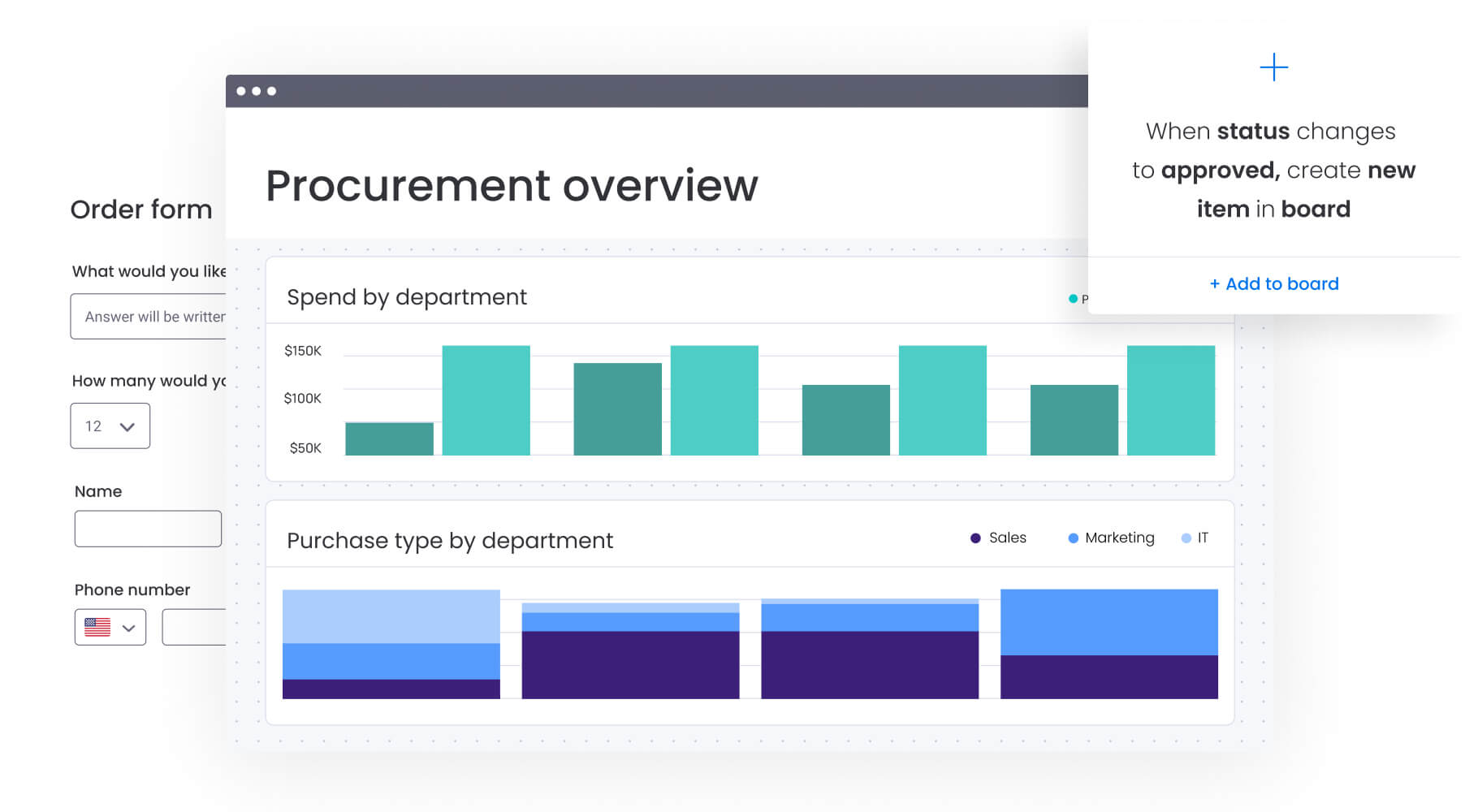
Teams using monday work management can automate these handoffs and track progress through customizable board views.
Stage 4: Shipping and delivery tracking
The transition from internal fulfillment to customer delivery involves both physical transportation and information management. This stage keeps customers informed and enables proactive exception handling when delivery issues arise.
Tracking encompasses the complete delivery journey:
- Package transfer: Moving items to shipping providers with proper documentation
- Network monitoring: Tracking packages through the delivery network
- Proactive updates: Providing delivery progress notifications
- Exception management: Managing delays or delivery failures
- Completion verification: Confirming successful delivery
Customers who receive advance notice of delays are significantly more understanding than those who discover problems only when expected deliveries don’t arrive. Proactive communication maintains customer relationships even when delivery problems occur.
Stage 5: Returns and customer service
Returns and customer service are integral parts of order management, not afterthoughts. How you handle post-delivery issues significantly impacts customer loyalty and operational costs. A smooth returns process actually increases customer confidence and repeat purchases by reducing perceived risk.
Return management requires:
- Clear policies: Establishing what can be returned and under what conditions
- Physical coordination: Managing return shipments and processing
- Product assessment: Determining condition and resale potential
- Financial processing: Handling refunds and exchanges promptly
- Inventory reintegration: Returning sellable items to available stock quickly
Customer service teams need access to complete order history, shipping status, and return information to resolve issues effectively.
Try monday work managementWhy order management drives business success
Investing in optimized order management delivers results executives actually care about: faster fulfillment, lower costs, and happier customers. The payoff goes way beyond efficient operations—you’ll strengthen customer loyalty, pull ahead of competitors, and boost your bottom line. Companies that get order management right see the results everywhere—from warehouse efficiency to customer reviews to quarterly profits.
Create exceptional customer experiences
Order management directly impacts satisfaction through reliability, transparency, and responsiveness. Customers judge businesses not just on products but on the entire purchase experience from order placement through delivery and potential returns.
Specific experience improvements include:
- Accurate delivery promises: Using real-time inventory data to set realistic expectations
- Proactive communication: Providing order status and shipping updates automatically
- Consistent service quality: Maintaining standards across all channels and touchpoints
- Quick issue resolution: Enabling service teams with complete order visibility
These improvements build trust and reduce anxiety about purchase decisions while enabling service teams to resolve problems rapidly.
Reduce operational costs through automation
Automation cuts real costs, and these savings multiply as you grow. For example, automation that saves you an estimated $1,000 per month for 500 orders might save $10,000 monthly when you hit 5,000 orders.
Priority areas for cost reduction include:
- Labor efficiency: Automating order routing, status updates, and exception flagging reduces staff time per order
- Inventory optimization: Improved demand visibility and allocation decisions minimize carrying costs
- Shipping management: Optimizing carrier selection and routing based on real-time rates reduces transportation expenses
- Error reduction: Preventing mistakes that cost real money, service time, and customer goodwill
Scale operations without adding headcount
Growing businesses face a critical challenge: order volumes increase faster than the ability to hire and train staff. Effective order management systems enable handling increasing volumes without proportionally increasing headcount while maintaining or improving service quality.
Scalability comes from:
- Process standardization: Creating repeatable workflows that reduce training time
- Exception management: Automatically handling routine decisions without human intervention
- Cross-training support: Providing visibility across functions for flexible staffing
- Performance monitoring: Identifying bottlenecks before they impact service
Organizations achieve this scale using platforms like monday work management to coordinate work across departments without adding complexity.
Enable cross-department visibility
Order management breaks down information silos and enables coordination across business functions. When sales, operations, finance, and customer service access the same real-time order information, collaboration improves and problems get resolved faster.
With real visibility, you solve problems before customers notice them—not after they’ve already called to complain. Operations teams seeing upcoming order volumes can adjust staffing in advance. Customer service can reach out proactively when they spot delivery delays. monday work management’s dashboards and reporting capabilities support this cross-departmental transparency through customizable views showing each stakeholder their most relevant information.
Key order management metrics to monitor
High-performing teams track a small set of operational metrics to spot issues early:
- Order cycle time: Time from order placement to delivery
- Fulfillment accuracy: Percentage of orders shipped without errors
- On-time delivery rate: Orders delivered within promised windows
- Exception rate: Percentage of orders requiring manual intervention
- Return processing time: Average time to complete refunds or exchanges
Monitoring these metrics consistently helps teams prioritize automation and process improvements where they’ll have the biggest impact.
Core components of order management systems
Understanding what capabilities to look for in order management solutions helps you evaluate options and make informed decisions. These core components represent the technical foundation enabling effective order management. Each component addresses specific operational challenges while contributing to overall system effectiveness.
Real-time inventory visibility
Real-time inventory visibility means seeing current stock levels, locations, and availability across all channels instantly. This capability is essential for effective inventory management and accurate order promising.
Key visibility requirements include:
- Multi-location tracking: Monitoring inventory across warehouses and stores,
- Channel synchronization: Ensuring consistent availability across all sales channels,
- Reserved inventory management: Tracking allocated items separately from available stock,
- Inbound inventory tracking: Providing visibility into incoming shipments and expected availability
Without these capabilities, you’re essentially flying blind when making fulfillment decisions.
Omnichannel order orchestration
Omnichannel orchestration manages orders consistently regardless of how or where customers place them. Customers expect seamless experiences whether ordering online, in-store, through mobile apps, or via phone, and they expect flexibility in fulfillment and returns.
Essential orchestration capabilities:
- Unified processing: Handling all orders through consistent workflows
- Cross-channel fulfillment: Enabling buy-online-pickup-in-store or ship-from-store options
- Consistent communication: Providing the same service quality across touchpoints
- Integrated returns: Allowing returns through any channel regardless of purchase origin
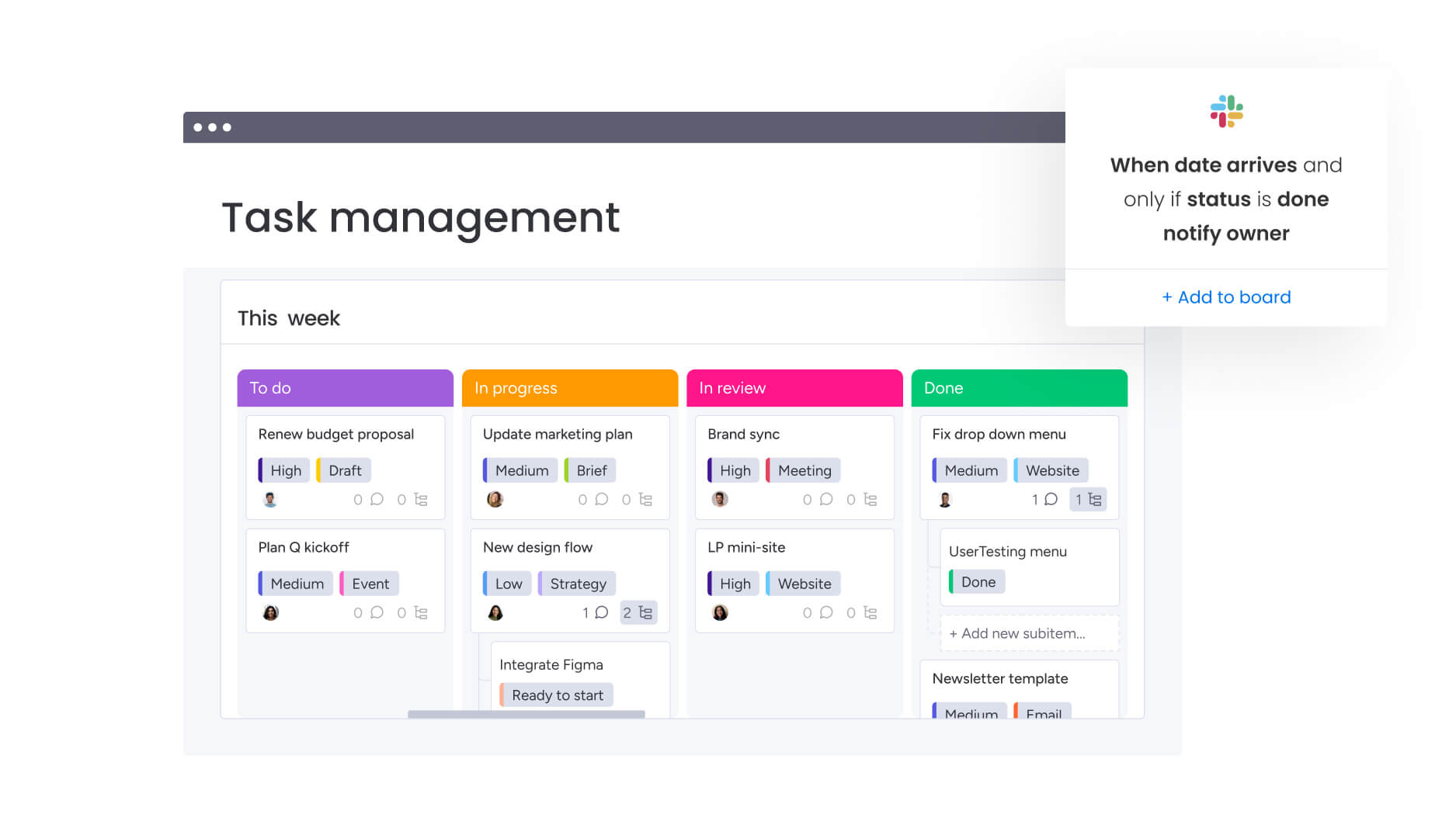
Workflow automation engine

Workflow automation executes routine order management activities without manual intervention. Automation reduces errors, improves consistency, and frees staff to focus on complex issues requiring human judgment.
Common applications include:
- Order routing rules: Directing orders to optimal locations automatically
- Status notifications: Sending customer updates when order status changes
- Exception alerts: Flagging orders needing attention based on predefined criteria
- Approval workflows: Routing special requests through authorization processes
Did you know? Organizations using monday work management can customize automation capabilities through visual workflow builders without coding expertise.
System integration framework
System integration connects order management with other business systems. Organizations use multiple specialized systems that must work together seamlessly to provide unified order management.
Critical integration points include:
- ERP connectivity: Synchronizing financial and inventory systems
- E-commerce platform integration: Importing orders automatically from online stores
- Shipping carrier APIs: Automating label generation and tracking updates
- Customer service system links: Providing complete order context for support teams
Poor integration creates data silos where information exists in multiple places with potential inconsistencies.
Performance analytics dashboard
Performance analytics transform operational data into actionable insights for continuous improvement. Analytics measure, monitor, and improve order management effectiveness by revealing patterns, identifying problems, and demonstrating business value.
Essential analytics capabilities include:
- Order cycle time tracking: Measuring time from placement to delivery
- Fulfillment accuracy metrics: Monitoring error rates and quality indicators
- Customer satisfaction indicators: Tracking delivery performance and service quality
- Cost analysis: Understanding true processing and fulfillment expenses
Effective dashboards present information in formats that different stakeholders can easily understand and act upon.
7 order management challenges every business faces
Growing businesses encounter predictable problems as they scale operations. Recognizing these challenges helps you diagnose your current situation and understand what to address first. Each challenge represents a common growth pain point that can significantly impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
1. Scattered data across disconnected systems
Organizations typically start with separate systems for different functions: e-commerce platforms for online orders, accounting software for finances, inventory management for stock tracking, and shipping applications for fulfillment. These systems often don’t communicate effectively, creating information silos.
This fragmentation causes:
- Inventory discrepancies: Different systems showing conflicting stock levels
- Order status confusion: Inability to provide accurate customer updates
- Manual data entry: Staff spending hours weekly transferring information between systems
- Delayed decision-making: Waiting for compiled reports instead of accessing real-time data
With monday work management, you can address this challenge by centralizing order data and connecting systems through integrations.
2. Manual processing bottlenecks
Manual processes that work at small scale become bottlenecks as businesses grow. Staff manually checking order details creates delays and introduces errors. Manually deciding fulfillment locations becomes time-consuming and inconsistent as volumes increase.
A business processing 100 orders daily might handle manual processes adequately, but at 500 orders daily, those same processes become unsustainable without automation. Manual processes create:
- Error susceptibility: Human mistakes in data entry and decision-making
- Inconsistent execution: Different staff members following different procedures
- Capacity constraints: Physical limits on how many orders staff can process
3. Limited order tracking visibility
Many businesses track orders internally but struggle to provide customers with accurate delivery information or proactively manage exceptions. Visibility gaps occur between internal systems and carrier networks, creating blind spots during critical last-mile delivery.
Poor visibility creates:
- Customer service burden: Representatives spending time researching status instead of resolving issues
- Reactive problem-solving: Discovering delivery problems only after customer complaints
- Reduced satisfaction: Customers feeling uninformed about their order progress
Organizations providing proactive delivery updates see significantly fewer service inquiries and higher satisfaction ratings.
4. Inventory accuracy issues
Inventory management accuracy problems compound throughout the order management process. Common causes include manual counting errors, system update delays, unrecorded theft or damage, and integration gaps between systems.
These issues cascade into:
- Overselling: Accepting orders for unavailable products, forcing cancellations
- Stockouts: Missing sales opportunities due to inaccurate availability data
- Inefficient allocation: Requiring order splitting when consolidated shipments were possible
- Customer disappointment: Inventory surprises discovered after purchase confirmation
5. Complex return processing
Return processing often becomes an afterthought creating operational headaches and customer frustration. Returns are increasingly important for customer satisfaction and competitive advantage as customers expect easy, flexible return policies.
Return challenges include:
- Unclear policies: Leading to inconsistent decisions and customer confusion
- Manual authorization: Creating slow approval processes that frustrate customers
- Reverse logistics complexity: Orchestrating return shipments and processing
- Inventory management: Determining what returned items can be resold and when
6. Peak season capacity constraints
Seasonal demand spikes during holidays, sales events, or product launches expose weaknesses in order management processes. Systems and processes working adequately during normal periods often break down under peak loads.
Peak season brings:
- Processing delays: Overwhelming staff and systems, frustrating customers
- Inventory allocation conflicts: Requiring rapid decisions about limited stock
- Shipping capacity constraints: Affecting delivery promises and customer expectations
- Staff overwhelm: Leading to errors and service quality degradation
7. Compliance documentation gaps
Regulatory and business compliance requirements affect order management, particularly for organizations in regulated industries or international markets. Compliance gaps create legal risks, business disruptions, and financial penalties.
Key compliance areas include:
- Tax documentation: Meeting requirements for different jurisdictions
- Shipping regulations: Handling international and customs requirements properly
- Industry standards: Following specific rules for healthcare, food, or other regulated products
- Audit trails: Maintaining complete records of processing decisions and changes
Building order management without system replacement
You can improve order management capabilities without the cost and disruption of replacing existing systems. Incremental improvements deliver immediate value while building toward more comprehensive solutions. This approach allows organizations to enhance operations gradually while maintaining business continuity.
Step 1: Map your current order workflow

Workflow mapping reveals inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for automation that aren’t obvious from day-to-day operations. This essential first step helps you understand current processes and identify improvement opportunities.
Document your complete process by following these activities:
- Track every action: Record each step from order receipt to delivery completion
- Identify handoffs: Note where orders move between people or systems
- Map data flow: Track how order information moves through the process
- Document decision points: Note where manual decisions or approvals are required
- Measure timing: Record how long each step typically takes
Teams using monday work management’s visual workflow builder can document and optimize these processes through visual representations that teams easily understand and improve collaboratively.
Step 2: Identify automation opportunities
High-volume, routine activities following predictable rules represent the best automation candidates because they deliver measurable time savings and error reduction. Recognizing which manual activities can be automated delivers immediate impact.
Prime automation candidates:
- Order routing: Automatically directing orders based on inventory location and shipping costs
- Status notifications: Sending customer updates when order status changes
- Inventory alerts: Notifying teams when stock levels reach reorder points
- Exception flagging: Automatically identifying orders needing special attention
Prioritize automation opportunities based on volume, error rates, and staff time consumption.
Step 3: Connect systems through integration
Improving system connectivity delivers immediate value without major IT projects. Integration reduces manual data entry, improves accuracy by eliminating transcription errors, and provides visibility by consolidating information from multiple sources.
Integration approaches include:
- API connections: Using existing system APIs for real-time data exchange
- File-based integration: Setting up automated exports and imports between systems
- Webhook notifications: Receiving real-time updates when events occur
- Third-party integration platforms: Connecting multiple systems without custom development
Step 4: Design custom order forms
Custom forms standardize order capture and improve data quality without changing existing systems. Well-designed forms improve both customer experience and internal processing by collecting complete, accurate information upfront.
Form design should:
- Collect necessary data upfront: Preventing processing delays from missing information
- Ensure data accuracy: Validating information before submission
- Show relevant fields: Displaying appropriate options based on customer selections
- Route data automatically: Sending form information to appropriate systems
The benefits of AI-powered order management
Artificial intelligence transforms order management through practical applications already available or emerging. AI enhances human decision-making rather than replacing people entirely, handling routine decisions at scale while escalating complex situations requiring human judgment. Organizations implementing AI capabilities see immediate improvements in processing speed and accuracy.
Automated order classification
AI automatically categorizes and prioritizes orders based on multiple factors, reducing manual review time and improving processing consistency. This pattern recognition learns from historical data and business rules to make classification decisions that would require significant human time.
Classification capabilities include:
- Priority assignment: Identifying urgent orders requiring expedited processing
- Routing optimization: Classifying orders by optimal fulfillment location
- Risk assessment: Flagging payment or fraud indicators for review
- Special handling identification: Recognizing custom processing requirements automatically
Organizations using monday work management’s AI Assistant can categorize orders automatically based on custom business rules, learning from corrections to improve accuracy over time.
Predictive demand planning
AI analyzes historical patterns, seasonal trends, and external factors to forecast future demand more accurately than traditional methods. These predictions enable better inventory positioning, capacity planning, and resource allocation.
Predictive planning enables:
- Inventory optimization: Predicting which products to stock and where
- Capacity planning: Forecasting staffing and resource needs accurately
- Supplier coordination: Providing more accurate demand forecasts to partners
- Pricing optimization: Understanding demand sensitivity to price changes
Digital workers for order processing
Digital workers are AI-powered assistants handling routine order management activities autonomously. These are more sophisticated than simple automation: they learn, adapt, and handle complex scenarios typically requiring human intervention.
Digital worker capabilities include:
- Order monitoring: Continuously tracking progress and identifying issues
- Exception handling: Researching and resolving common problems autonomously
- Customer communication: Providing proactive updates and answering routine questions
- Performance analysis: Generating insights and recommendations for improvement
Organizations using monday work management’s Digital Workforce can train specialists for specific order management activities, handling routine work while escalating complex situations requiring human judgment.
Try monday work managementTransform your order management with monday work management

Address order management challenges head-on with monday work management‘s flexible platform approach rather than rigid pre-built processes. The platform allows teams to design custom solutions matching their specific requirements instead of forcing businesses to adapt to pre-configured workflows. This flexibility enables organizations to maintain their unique competitive advantages while gaining operational efficiency.
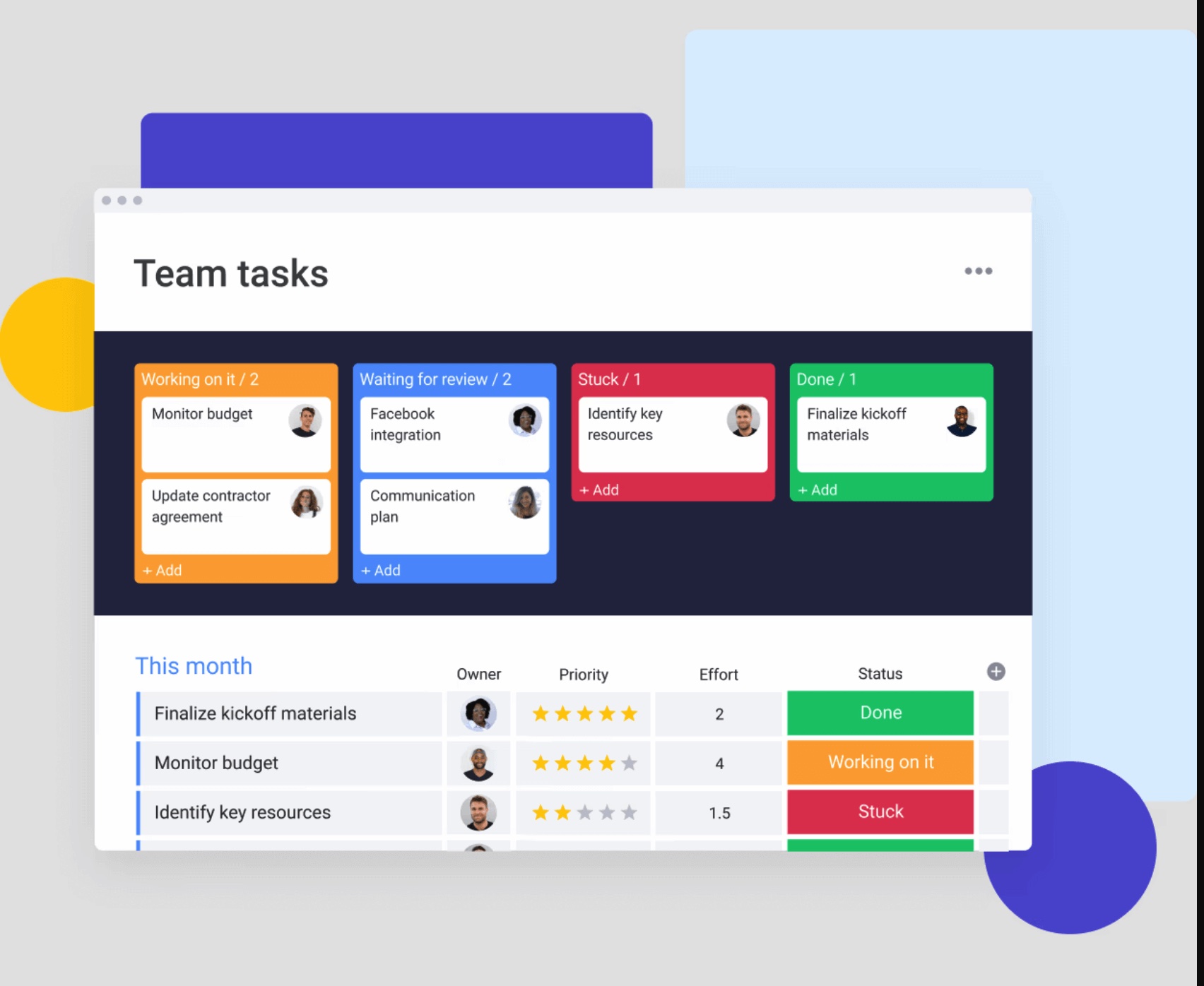
Visual order workflow builder
The visual workflow builder enables businesses to design and optimize order management processes without technical expertise. Drag-and-drop design creates order processes visually, making workflow creation accessible to operations teams rather than requiring IT involvement.
Workflow capabilities include:
- Custom stages: Defining order statuses and transitions matching business needs
- Automated handoffs: Setting up automatic assignments and notifications when orders move between stages
- Approval workflows: Building multi-step approval processes for special orders or exceptions
Real-time order dashboards
Dashboard capabilities provide comprehensive visibility into order management performance. Customizable views show different stakeholders the information most relevant to their roles: operations managers see detailed process metrics, customer service sees order status and customer history, executives see high-level trends and financial impacts.
Dashboard features include:
- Order status tracking: Providing real-time visibility across all stages
- Performance metrics: Showing key indicators like processing time and fulfillment accuracy
- Exception monitoring: Providing immediate alerts for orders needing attention
- Trend analysis: Identifying seasonal variations and emerging issues
Automated order routing
Automation capabilities optimize order routing decisions based on business rules and real-time conditions. Automation ensures consistent decision-making while reducing manual work.
Routing automation includes:
- Rule-based routing: Automatically directing orders based on inventory availability and shipping costs
- Dynamic adjustments: Adapting routing decisions based on changing conditions
- Exception handling: Escalating complex routing decisions to appropriate team members
- Performance optimization: Learning from routing outcomes to improve future decisions
Seamless system integration
Integration capabilities connect with existing business systems to create a unified order management environment. Pre-built connectors and flexible APIs enable integration without extensive custom development.
Integration capabilities include:
- E-commerce platforms: Automatically importing orders from online stores
- ERP systems: Synchronizing inventory and financial data
- Shipping carriers: Generating labels and tracking updates automatically
- Customer service applications: Providing service teams with complete order context
Quick comparison: monday work management vs. traditional order management
| Traditional order management solutions | monday work management | |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation time | 6–18 months with significant IT involvement | Configurable in weeks, not months |
| Customization | Limited to predefined workflows and rigid configurations | Fully customizable workflows built with visual builders |
| Integration | Complex, expensive custom development required | Pre-built integrations with extensible API support |
| User adoption | Requires extensive training and change management | Intuitive interface with minimal training required |
| Scalability | Costly upgrades and reconfiguration as volumes grow | Scales through flexible plans and seat-based pricing |
| Visibility | Separate reporting tools and delayed insights | Centralized dashboards with near real-time status tracking |
| AI capabilities | Limited or available as paid add-ons | Built-in AI blocks with configurable AI-powered workflows |
| Automation | Rule-based automation requiring technical setup | Visual automation rules configurable without coding |
| Mobile access | Often limited or dependent on separate apps | Full mobile functionality with native mobile apps |
Streamline operations and accelerate growth
Effective order management creates the foundation for sustainable business growth by connecting customer expectations with operational capabilities. Organizations that invest in comprehensive order management see measurable improvements in customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and financial performance.
The key to success lies in choosing solutions that adapt to your business rather than forcing your business to adapt to rigid systems. monday work management provides the flexibility to design workflows matching your specific requirements while delivering the automation and visibility needed for scale.
Start by mapping your current processes, identifying automation opportunities, and gradually implementing improvements that deliver immediate value. Focus on connecting systems, standardizing workflows, and providing teams with the visibility they need to make informed decisions quickly.
Try monday work managementFAQs
What is order management?
Order management is the end-to-end process of capturing, tracking, and fulfilling customer orders from initial placement through delivery and returns.
What's the difference between order management and inventory management?
Order management orchestrates the entire process from customer order to delivery completion, while inventory management focuses specifically on tracking stock levels and optimizing storage costs.
Can small businesses benefit from order management systems?
Small businesses absolutely benefit from order management systems, especially as they grow beyond manual processes and need automated status updates and centralized order tracking.
How much does order management software cost?
Order management software costs vary widely, with cloud-based platforms typically using subscription pricing starting around $10-50 per user monthly, while traditional enterprise solutions often require significant upfront investments.
What order management metrics should teams track?
Essential order management metrics include order cycle time, fulfillment accuracy rates, on-time delivery performance, customer satisfaction scores, and order processing costs.