A sales rep spends 20 minutes researching what looks like a high-intent lead, only to discover it is a student completing a class assignment. At the same time, a short inquiry from the previous week quietly signs with a competitor.
This is what happens when teams treat every contact as equal.
Not every form fill is a real opportunity. Not every download signals buying intent. Understanding what actually qualifies someone as a sales lead changes how you prioritize outreach, allocate sales time, and forecast revenue. When the definition is clear, the pipeline becomes clearer too.
Sales leads are more than names in a CRM. They are identifiable contacts who have demonstrated measurable interest. The difference between casual curiosity and genuine buying intent determines whether your team builds momentum or wastes effort.
Ahead, you will see how sales leads fit into the broader pipeline, how they differ from prospects and opportunities, the seven types that matter most, and the qualification frameworks that separate real deals from distractions. You will also learn how AI and automation make lead management more accurate and scalable in 2026.
Key takeaways
- Sales leads are defined by interest: A sales lead is created when a potential customer shows measurable interest and shares usable contact information enabling structured follow-up.
- Different lead types require different engagement strategies: Cold warm hot and qualified lead categories demand tailored outreach timing content and sales involvement to maximize conversion efficiency.
- Clear pipeline stages improve focus and forecasting: Separating leads prospects and opportunities helps teams allocate effort correctly and build more predictable revenue forecasts.
- Structured qualification frameworks reduce wasted effort: Methods like BANT CHAMP and MEDDIC bring consistency to lead evaluation and help sales teams prioritize deals with real buying intent.
- Modern CRMs improve lead management through automation and visibility: Platforms like monday CRM support visual pipelines AI-powered scoring and centralized communication tracking that reduce manual work and improve decision-making.
Sales leads definition
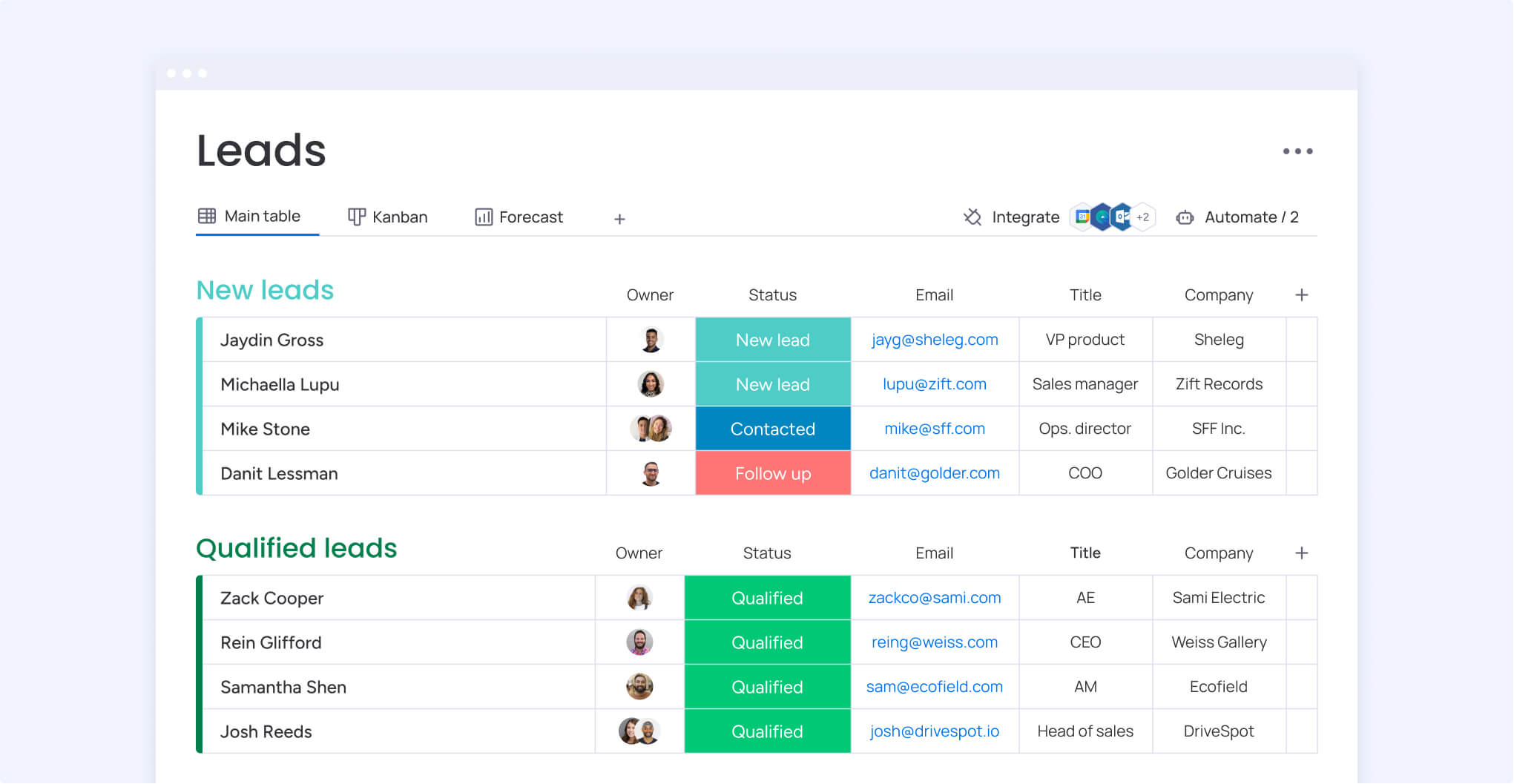
Sales leads are potential customers who have shown interest in a product or service and have shared their contact information. This makes them identifiable contacts that sales teams can reach, track, and nurture through a structured sales process over time.
In practical terms, a sales lead is created when interest meets identifiable data. When someone downloads a pricing guide and submits an email address, or completes a demo request form with company details, they move from an anonymous visitor to a known contact.
At that moment, they signal intent. They have taken an action that indicates curiosity or need, and they have provided information that allows follow-up. Without both demonstrated interest and usable contact details, teams are left with anonymous traffic or cold outreach lists.
This difference is what enables modern lead management. Once identified, leads can be tracked, scored, and routed based on engagement, fit, and behavior. Over time, these signals help teams prioritize outreach and guide contacts through the pipeline with consistency.
These real-world examples show how sales leads appear across different business models and industries:
- B2B software: A vice president of sales downloads an ROI calculator and shares a work email, company name, and team size, indicating interest tied to a measurable business outcome.
- Professional services: A startup founder submits a consultation form, outlining business challenges, goals, and a projected timeline, creating context for a tailored conversation.
- E-commerce: A shopper abandons a cart but provides an email address to receive a discount code, turning a missed purchase into a follow-up opportunity.
High-performing revenue teams treat lead capture as a deliberate process. Every interaction, from the first website visit to a demo request, is tracked and evaluated.
This approach turns lead management guesswork into a measurable system that supports predictable revenue growth.
Once identified, leads can be tracked, scored, and routed based on engagement, fit, and behavior. Over time, these signals help teams prioritize outreach and guide contacts through the pipeline with consistency.
Understanding the sales pipeline: lead vs prospect and opportunity
Clarity across pipeline stages removes guesswork from forecasting. When teams use consistent definitions, they know exactly where each contact stands and how much attention it deserves.
Leads, prospects, and opportunities are not interchangeable labels. They reflect increasing levels of qualification, engagement, and buying intent. The table below outlines how contact information, qualification depth, and sales involvement evolve at each stage.
| Stage | Contact information | Qualification level | Sales engagement | Key characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | Basic details (name, email) | Unqualified | Minimal or automated | Initial interest shown, fit unverified |
| Prospect | Complete profile with company data | Qualified against ICP | Active discovery conversations | Budget and authority confirmed |
| Opportunity | Full contact data plus stakeholder map | Highly qualified with validated need | Intensive with multiple touchpoints | Active evaluation, defined timeline |
- Lead characteristics and approach: A lead has shown initial interest and shared basic contact details, but fit and intent are still unverified. Engagement at this stage is often automated or light-touch while qualification begins.
- Prospect characteristics and approach: A prospect is a lead that aligns with your ideal customer profile and has demonstrated credible buying intent. Sales has validated key factors such as authority and organizational fit, making discovery conversations more focused and productive.
- Opportunity characteristics and approach: An opportunity represents an active deal. Budget, need, timeline, and decision process are defined. Engagement shifts from exploration to evaluation, proposal, and stakeholder alignment.
Clear stage definitions ensure sales effort matches buyer readiness, keeping the pipeline efficient and forecasts more reliable.
How understanding lead types accelerates revenue growth
Understanding lead types creates a strong foundation for predictable revenue growth and more efficient sales operations. When revenue teams accurately categorize and prioritize leads, they gain clearer visibility into pipeline health and performance.
That visibility supports more accurate forecasting and more strategic resource allocation across the organization.
Predictability benefits
Lad classification directly addresses the predictability challenges many mid-market organizations face. When leads are categorized by temperature and qualification level, sales leaders can forecast conversion rates with greater confidence. Knowing that hot leads convert at 40% while cold leads convert at 5% allows teams to build forecasts based on an actual lead mix rather than assumptions.
Efficiency improvements
Proper lead typing delivers meaningful efficiency gains across the sales process. Sales representatives who understand which leads deserve immediate attention can focus their time on the most promising opportunities first.
Instead of treating every inquiry the same, they engage hot leads quickly while nurturing warm leads with targeted content and sales prospecting until they’re ready for direct sales contact.
Team collaboration enhancement
Lead typing also strengthens collaboration between marketing and sales teams. When both teams share a consistent framework for lead classification, handoffs become smoother and more reliable. Marketing teams clearly understand what qualifies a lead for sales follow-up, while sales teams receive leads with clear context, engagement history, and expectations already defined.
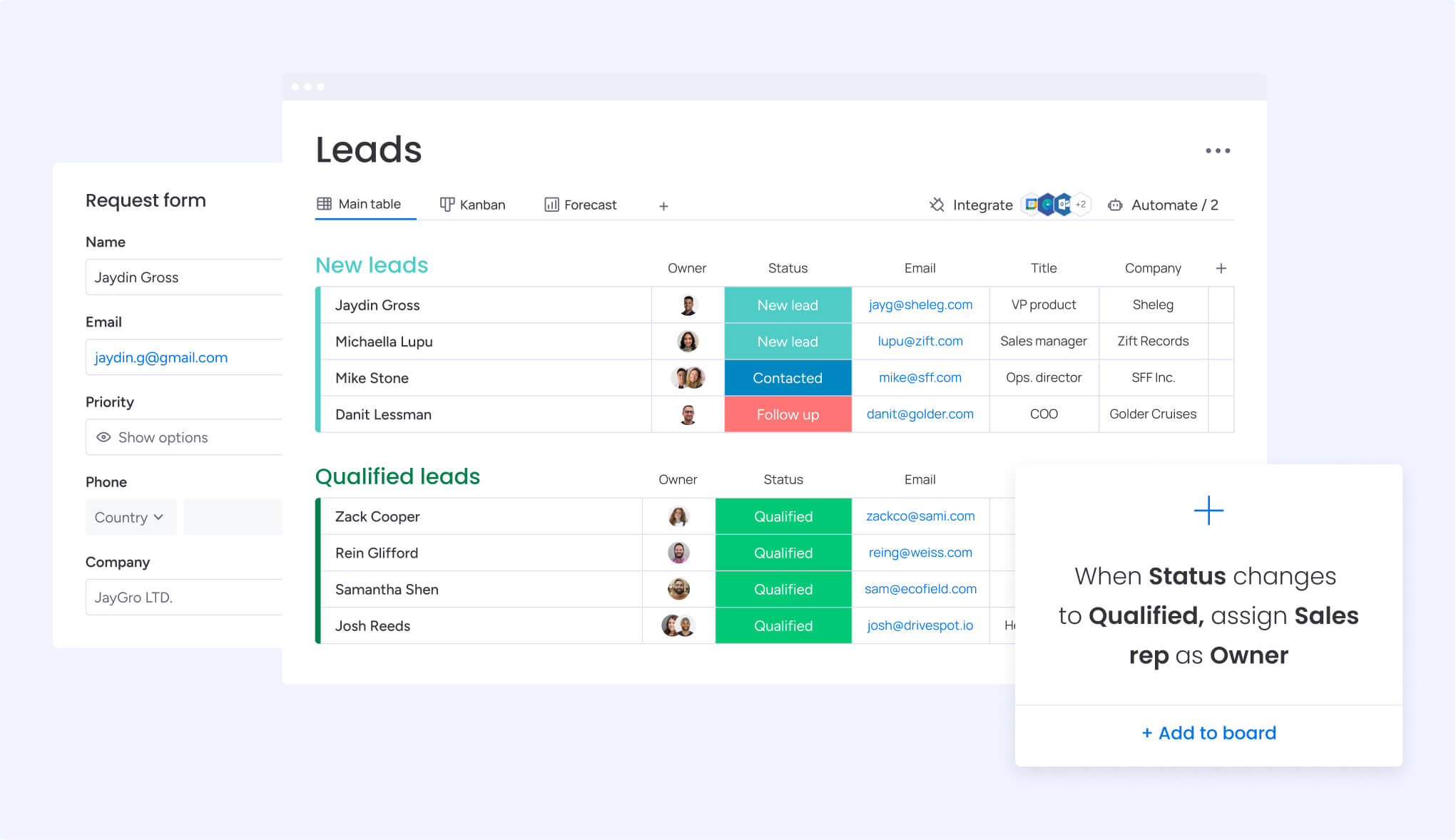
Modern and intelligent solutions like monday CRM support this process through automated lead scoring and categorization based on demographic and behavioral data. These clever platforms evaluate factors such as company size, industry, website activity, and email engagement to assign scores automatically.

7 types of sales leads that drive pipeline success
Revenue teams that understand lead types can also tailor outreach strategies to maximize conversion efficiency. These seven classifications reflect the full spectrum of buyer readiness, from early awareness to sales-ready engagement.
1. Cold leads
Cold leads show minimal engagement with your organization and sit at the earliest stage of the buying journey. These contacts may come from trade show lists, purchased databases that match your ideal customer profile, or outbound prospecting efforts without prior brand interaction.
Because cold leads are unfamiliar with your solution, they require education and trust-building before meaningful sales conversations can occur. Conversion timelines are typically longer, often stretching across several months, which makes cold leads a longer-term pipeline investment.
Effective strategies for cold leads emphasize value and credibility before selling:
- Educational content: Share industry insights and resources that address common challenges.
- Multi-touch sequences: Combine email, social outreach, and content distribution to build familiarity.
- Value-first outreach: Lead with helpful resources rather than direct product pitches.
2. Warm leads
Warm leads demonstrate moderate interest through multiple touchpoints and clear brand awareness. They may have engaged with blog content, attended webinars, or arrived through customer referrals. While they have not declared immediate buying intent, their actions show meaningful curiosity.
Because warm leads have already invested time learning about your solution, they tend to convert faster than cold leads. Effective engagement focuses on relevance and continuity:
- Targeted follow-up: Reference prior interactions to show awareness and context.
- Relevant content: Share case studies, examples, and comparison guides.
- Personalized demos: Invite them to tailored demonstrations aligned with their interests.
3. Hot leads
Hot leads display strong buying signals and represent the highest-priority opportunities in the pipeline. They may request demos, ask for pricing, or contact sales directly with implementation questions. These leads are actively evaluating options and often operate within defined timelines.
Hot leads require immediate, personalized engagement from sales teams:
- Same-day follow-up: Respond within hours rather than days.
- Detailed information: Tailor answers to specific needs and constraints.
- Consultative focus: Validate requirements and demonstrate solution fit.
4. Information qualified leads (IQLs)
Information qualified leads engage with educational materials but show no clear purchase intent. They are typically in early research stages, focused on understanding problems rather than selecting solutions. Common actions include subscribing to blogs, downloading e-books, or attending thought leadership webinars.
Because IQLs prioritize learning, they benefit from a nurturing approach:
- Continued education: Deliver consistent, high-value content.
- Trust building: Position your organization as a credible authority.
- Patient progression: Allow readiness to develop naturally over time.
5. Marketing qualified leads (MQLs)
Marketing qualified leads meet defined criteria that signal readiness for sales engagement. They align with ideal customer profiles and demonstrate consistent behavioral engagement, such as repeated content interactions and visits to high-intent pages.
Sales teams should engage MQLs with structured follow-up:
- Prompt outreach: Connect within twenty-four hours of qualification.
- Focused qualification: Confirm interest, fit, and readiness.
- Clear next steps: Propose discovery calls or demonstrations.
6. Product qualified leads (PQLs)
Product qualified leads have first-hand experience with your product through trials, freemium access, or interactive demos. Their usage data offers concrete insights into adoption patterns and potential barriers.
Successful PQL engagement relies on contextual, data-driven outreach:
- Usage-based conversations: Reference specific actions within the product.
- Feature guidance: Highlight capabilities aligned with their behavior.
- Conversion support: Remove obstacles preventing full adoption.
7. Sales qualified leads (SQLs)
Sales qualified leads have been fully vetted by sales teams and meet all criteria for active pursuit. Discovery conversations confirm budget, authority, need, and timeline, making SQLs the most valuable leads in the pipeline.
SQL engagement includes comprehensive sales execution:
- In-depth discovery: Conduct detailed needs assessments.
- Customized proposals: Align solutions to business requirements.
- Targeted demonstrations: Focus on relevant stakeholders and scenarios.
Lead qualification strategies that actually work
Not every lead deserves the same level of attention. The challenge is knowing which conversations to prioritize and which to nurture.
That is where structured qualification frameworks make a real difference. Instead of relying on instinct or inconsistent judgment, these models give sales teams a shared language for evaluating fit, intent, and timing. They turn “this feels promising” into clear criteria that support better forecasting and smarter pipeline decisions.
The right framework depends on how you sell. Simpler deal cycles may benefit from lightweight qualification. Larger, multi-stakeholder enterprise sales require deeper validation.
Below are the most widely used approaches, each designed for different levels of complexity and deal size.
BANT framework implementation
The BANT framework evaluates leads across four essential buying criteria, helping teams focus on prospects most likely to convert within a reasonable timeframe.
Budget assessment:
- Purpose: Determine whether the lead has financial resources allocated for your solution.
- Approach: Explore expected investment ranges and funding approval processes.
- Benefit: Focuses sales efforts on leads with the financial capacity to buy.
Authority identification:
- Purpose: Reveal who makes the final purchasing decision and influences that decision.
- Approach: Map the decision-making structure and key stakeholders.
- Benefit: Ensures engagement with contacts who have purchasing power.
Need validation:
- Purpose: Confirm the lead has a genuine business problem your solution addresses.
- Approach: Explore current challenges and consequences of not solving them.
- Benefit: Qualifies leads with compelling reasons to buy versus casual interest.
Timeline establishment:
- Purpose: Determine when the lead intends to make a decision and implement.
- Approach: Understand what’s driving their timeline and urgency factors.
- Benefit: Prioritizes leads with near-term buying intent.
CHAMP for consultative selling
CHAMP reorders traditional qualification priorities to focus first on customer challenges, creating more natural and consultative conversations.
Challenges exploration:
- Priority: First qualification step.
- Benefit: Builds rapport by demonstrating genuine interest in customer situation.
- Approach: Understand pain points before discussing solutions or pricing.
Authority identification:
- Priority: Second qualification step.
- Benefit: Natural sequencing after establishing context.
- Approach: Determine who has power to allocate resources toward solving problems.
Money discussions:
- Priority: Third qualification step.
- Benefit: Frame pricing relative to identified pain points.
- Approach: Make budget conversations more productive through context.
Prioritization assessment:
- Priority: Final qualification step.
- Benefit: Gauge urgency and likelihood of near-term action.
- Approach: Understand where solving this challenge ranks among competing priorities.
MEDDIC for complex enterprise deals
MEDDIC offers comprehensive qualification for enterprise sales with long cycles and multiple stakeholders.
Metrics quantification:
- Focus: Establish measurable business impact of both problem and solution.
- Approach: Identify specific numbers like cost savings or efficiency gains.
- Value: Justifies investment with concrete business case.
Economic Buyer identification:
- Focus: Pinpoint the person with budget authority and final approval power.
- Approach: Engage the economic buyer directly.
- Value: Improves win rates and shortens sales cycles.
Decision Criteria discovery:
- Focus: Reveal specific requirements for solution selection.
- Approach: Understand evaluation criteria and weighting.
- Value: Enables effective positioning and objection handling.
Decision Process mapping:
- Focus: Document steps, stakeholders, and timeline for purchasing decisions.
- Approach: Map organizational complexity and approval workflows.
- Value: Helps sales teams navigate enterprise buying processes.
Identify Pain exploration:
- Focus: Uncover business consequences of not solving the problem.
- Approach: Go beyond surface challenges to understand impact.
- Value: Creates urgency and justifies investment.
Champion development:
- Focus: Identify and cultivate internal advocates.
- Approach: Build relationships with stakeholders who sell internally.
- Value: Provides ongoing support throughout the sales process.
AI-powered scoring implementation
Artificial intelligence transforms lead qualification from manual evaluation to automated, data-driven scoring that scales across thousands of leads. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns in historical conversion data, revealing which combinations of behaviors and characteristics correlate with closed deals.
AI-powered scoring evaluates factors human teams might overlook or weight inconsistently. For example, the system might find that leads who visit pricing pages three times, download multiple case studies, and engage with emails within 48 hours convert at 60%.
These systems continuously learn and improve as they process more data. Modern platforms like monday CRM can automatically detect sentiment in communications, extract key information from emails and documents, and assign leads to the most relevant team members.

“With monday CRM, we’re finally able to adapt the platform to our needs — not the other way around. It gives us the flexibility to work smarter, cut costs, save time, and scale with confidence.”
Samuel Lobao | Contract Administrator & Special Projects, Strategix
“Now we have a lot less data, but it’s quality data. That change allows us to use AI confidently, without second-guessing the outputs.”
Elizabeth Gerbel | CEO
“Without monday CRM, we’d be chasing updates and fixing errors. Now we’re focused on growing the program — not just keeping up with it."
Quentin Williams | Head of Dropship, Freedom Furniture
“There’s probably about a 70% increase in efficiency in regards to the admin tasks that were removed and automated, which is a huge win for us.“
Kyle Dorman | Department Manager - Operations, Ray White
"monday CRM helps us make sure the right people have immediate visibility into the information they need so we're not wasting time."
Luca Pope | Global Client Solutions Manager at Black Mountain
“In a couple of weeks, all of the team members were using monday CRM fully. The automations and the many integrations, make monday CRM the best CRM in the market right now.”
Nuno Godinho | CIO at VelvHow AI and automation transform lead management
Qualification frameworks bring discipline to sales conversations. They help reps ask better questions, validate fit, and prioritize real opportunities.
But as lead volume grows, applying that same rigor manually becomes difficult. Research takes time. Scoring becomes inconsistent. Follow-ups slip. Even the best frameworks break down under scale.
This is where AI and automation step in. Not to replace judgment, but to support it. By handling enrichment, prioritization, and real-time alerts automatically, these systems allow sales teams to focus on conversations instead of administration.
Instant lead enrichment and data quality
AI-powered enrichment automatically fills missing lead information using external sources, eliminating hours of manual research. When a lead provides only a name and email, enrichment systems append company details, job title, social profiles, and technology stack information in seconds.
Data quality improvements:
- Ongoing maintenance: Automation detects when contact information becomes outdated.
- Record flagging: Systems identify records that require updates.
- Time savings: Prevents sales teams from wasting time on obsolete contacts.
Sales representatives who previously spent 30 minutes researching each lead can now access complete profiles instantly. Platforms like monday CRM can pull data directly from uploaded documents, emails, and images, automatically populating lead records with relevant details: this efficiency allows reps to contact more leads daily without sacrificing personalized engagement.
Predictive scoring that prioritizes revenue
Machine learning analyzes historical conversion data to predict which leads are most likely to close. These models evaluate hundreds of variables to generate conversion probability scores that guide daily prioritization.
Predictive advantages:
- Pattern recognition: Identifies non-obvious patterns in successful conversions.
- Dynamic scoring: Continuously updates based on new behavioral data.
- Revenue focus: Prioritizes leads most likely to generate revenue.
This approach outperforms rule-based scoring by uncovering patterns humans might miss. For instance, while traditional rules might focus on job title and company size, machine learning can reveal that leads who view pricing pages on mobile devices after downloading case studies convert at higher rates.
Predictive scoring also directly addresses the predictability challenge facing revenue leaders. When you can see that 40% of high-scoring leads typically convert within 60 days, you can forecast revenue with greater confidence and allocate resources strategically.
Multi-touch attribution across channels
AI-powered attribution tracks leads across multiple touchpoints, offering complete visibility into the buyer journey. This holistic perspective identifies which marketing activities generate the highest-quality leads and how each interaction contributes to conversions.
Multi-touch attribution uses machine learning to assign weight to each engagement, recognizing the impact of blog posts, webinars, email sequences, and demo requests. This insight helps revenue teams understand true lead generation ROI and guide prospects toward interactions that accelerate pipeline progression.
Behavioral triggers for perfect timing
Automation detects behavioral signals that indicate buying intent, enabling sales teams to engage leads at the most effective moments. Intelligent triggers monitor activity across websites, emails, content platforms, and product trials.
Common behavioral triggers that warrant immediate follow-up include:
- Pricing page visits: Signal leads are evaluating costs and comparing options.
- Competitor research: Indicates active vendor evaluation.
- Repeated product page visits: Shows focused interest in particular features.
- Engagement spikes: Suggests renewed interest after dormancy.
- Trial requests: Represents explicit buying signals demanding immediate response.
Leads contacted within five minutes of showing high-intent behaviors convert at significantly higher rates than those reached hours or days later. Automated alerts ensure sales teams respond immediately when strong buying signals emerge, maximizing conversion opportunities.

6 proven methods to generate high-quality leads
Generating high-quality leads requires strategies that consistently attract prospects aligned with your ideal customer profile and demonstrate genuine interest in your solutions. The most successful approach combines multiple channels to maintain a steady lead flow while prioritizing lead quality.
Method 1: Social selling on the right platforms
Social selling leverages professional networks and industry communities to identify, engage, and nurture potential leads through relationship-building and value-sharing. Sales professionals use platforms like LinkedIn to establish credibility and connect with prospects in a natural, non-intrusive way.
Implementation approach:
- Profile optimization: Communicate expertise and value proposition clearly.
- Content sharing: Position yourself as a knowledgeable resource.
- Gradual engagement: Move from profile views to direct conversations.
- Value-first interactions: Comment thoughtfully on industry discussions.
Method 2: Content that attracts your ideal customers
Educational content marketing draws qualified leads by addressing the specific challenges and information needs of your target audience. Whitepapers, case studies, webinars, and research reports offer value that attracts prospects actively seeking solutions.
Content strategy framework:
- Top-of-funnel: Explore industry challenges and trends.
- Middle-of-funnel: Provide solution frameworks and comparisons.
- Bottom-of-funnel: Offer implementation guides and ROI calculators.
- Quality focus: Deliver insights that appeal to serious prospects.
Method 3: Multi-channel campaigns that convert
Coordinated campaigns across email, social media, content marketing, and direct outreach create multiple touchpoints, building awareness and trust more effectively than single-channel approaches.
Campaign structure:
- Awareness building: Start with educational content and thought leadership.
- Direct outreach: Follow up with personalized communication.
- High-touch activities: Include demos and consultations.
- Consistent messaging: Mthe core message across formats.
Method 4: Strategic referral programs
Existing customers and partners become valuable lead sources through structured referral programs that incentivize and facilitate introductions to qualified prospects. Referral leads often convert faster due to pre-existing trust.
Program elements:
- Ideal customer profiles: Help customers identify good referral candidates.
- Referral templates: Simplify introductions with ready-to-use language.
- Incentive structures: Reward both successful referrals and attempts.
- Easy processes: Make referral submission simple and trackable.
Method 5: Partnership and co-marketing initiatives
Collaborating with complementary businesses extends lead generation reach by tapping into partner audiences through joint initiatives that provide mutual value.
Partnership activities:
- Joint webinars: Combine expertise on topics relevant to both audiences.
- Content partnerships: Produce co-branded resources.
- Cross-promotion: Leverage both partner networks for distribution.
- Mutual value: Ensure initiatives benefit all involved organizations.
Method 6: Event-based lead generation
Events create concentrated opportunities for lead generation through direct engagement, educational presentations, and networking interactions. Trade shows, conferences, and webinar series attract audiences actively interested in your industry and solution category.
Event strategy:
- Strategic participation: Select events matching your ideal customer profile.
- Compelling demonstrations: Showcase value through interactive experiences.
- Systematic capture: Implement consistent lead collection processes.
- Follow-up planning: Prepare immediate post-event engagement sequences.

Bring structure and visibility to your pipeline with monday CRM
Lead management becomes chaotic when information lives in different places. Updates sit in inboxes. Notes live in private docs. Forecasts depend on guesswork. Over time, even strong qualification systems lose impact without a clear way to track movement.
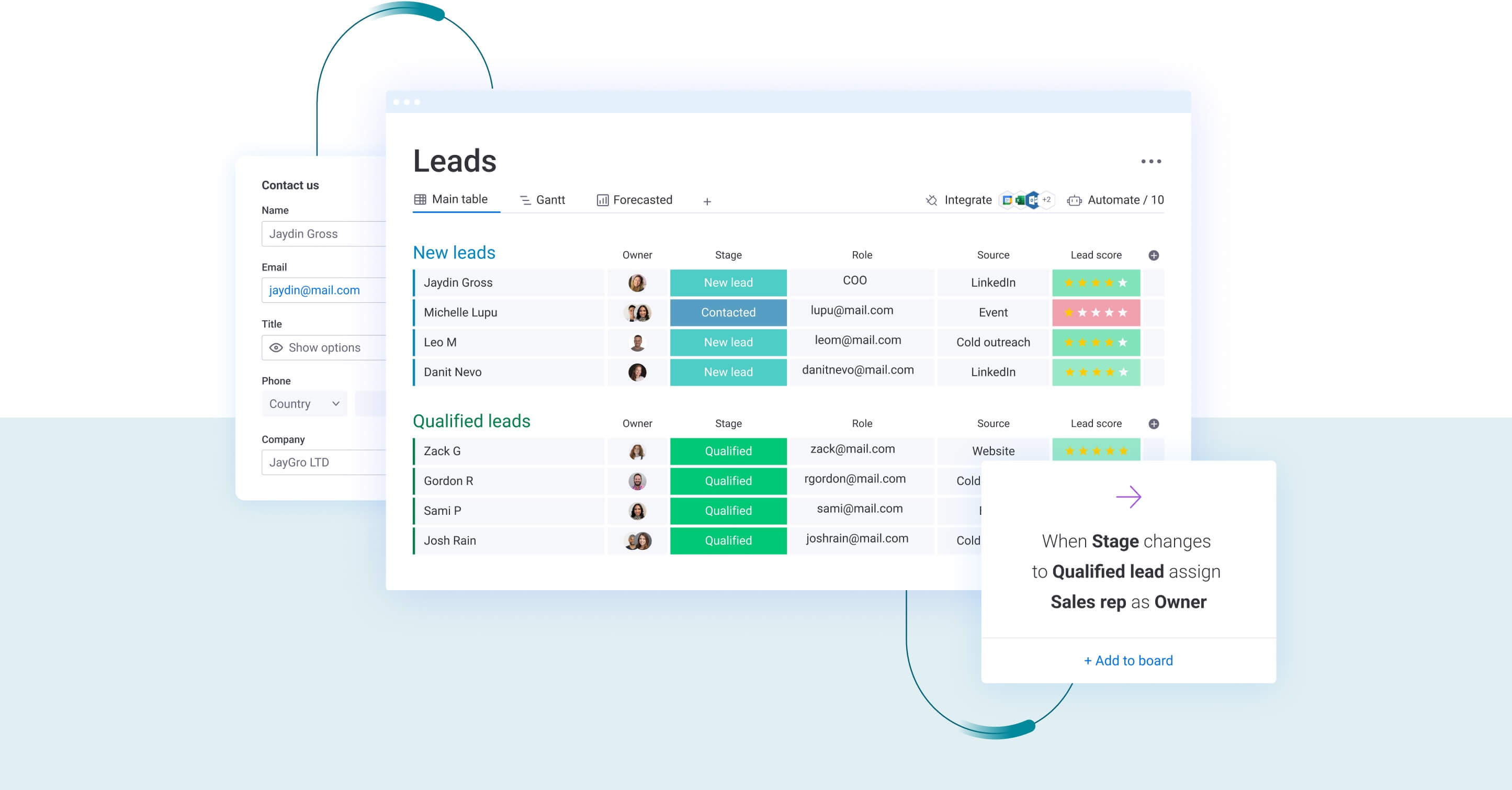
monday CRM brings everything into one visual workspace where progress is obvious and priorities are clear.
Instead of chasing status updates, teams can:
- Visualize every stage: Kanban-style boards show where each lead sits, how long it has been there, and what needs to happen next.
- Organize by what matters: Leads can be grouped by type, qualification stage, source, assigned representative, or custom categories that reflect your sales process.
- Prioritize with AI scoring: Demographic fit and engagement signals are evaluated automatically, helping teams focus on leads most likely to convert.
- Centralize every interaction: Emails, notes, documents, and activity history live in a single timeline, eliminating duplicate outreach and confusion.
- Forecast with live data: Real-time dashboards surface conversion rates, source performance, and bottlenecks before they impact revenue.
As leads move, scores adjust and workflows trigger automatically. Nothing relies on memory or manual follow-up. The result is a pipeline that feels controlled instead of reactive.
With monday CRM, visibility is no longer a reporting exercise. It becomes part of how revenue teams operate every day.
Frequently asked questions
What is an example of a sales lead?
A sales lead example is a marketing director who downloads your product pricing guide and provides their work email address, company name, and job title. This action indicates interest in your solution, creating an identifiable prospect your sales team can contact.
How do you get leads in sales?
You get sales leads through content marketing that attracts prospects researching solutions, social selling on professional networks, referral programs leveraging existing customers, events like webinars and trade shows, and multi-channel campaigns engaging potential customers across email and social media.
What sales leads actually do?
Sales leads represent potential customers who have shown interest in your product by taking specific actions, such as downloading content or requesting information. They serve as the starting point for your sales process, where teams qualify, nurture, and convert them into paying customers.
How many touchpoints does it take to convert a lead?
Converting a lead typically requires multiple touchpoints across different channels. B2B sales often need eight to twelve touchpoints, while simpler transactional sales may convert with fewer interactions, depending on industry and deal complexity.
What's the difference between inbound and outbound leads?
Inbound leads come to you through content marketing, search engines, or referrals, where prospects initiate contact. Outbound leads result from proactive outreach efforts like cold calling, email campaigns, or social selling, where your team initiates the relationship.
How do you calculate lead score?
Lead score is calculated by assigning point values to demographic characteristics, such as company size and job title, as well as behavioral actions like content downloads, webinar attendance, and website visits. AI-powered systems or manual processes then total these points to rank leads by conversion probability.