Your team just wrapped another quarterly planning session with clear priorities and ambitious goals. Six weeks later, projects are scattered across platforms, deadlines keep shifting, and nobody knows who’s working on what — sound familiar?
This guide shows you what work management actually means in practice, how it differs from project management, and why organizations use intelligent platforms to transform scattered operations into coordinated execution. You’ll learn the essential components that make work management effective, implementation strategies that deliver results, and how AI is reshaping how teams coordinate work across departments and time zones.
Try monday work managementKey takeaways
- Work management aligns individual activities with organizational goals through structured frameworks, ensuring every team member understands how their work drives business outcomes.
- Cross-functional teams coordinate seamlessly when everyone can see project status, dependencies, and resource allocation in real time across all departments.
- Intelligent automation handles status updates, notifications, and routine handoffs, freeing teams to concentrate on creative problem-solving and strategic initiatives.
- Comprehensive dashboards and analytics provide instant visibility into progress, bottlenecks, and resource utilization without waiting for manual reports.
- With monday work management, visual workflows, predictive insights, and Digital Workers handle complex orchestration while integrating with 200+ existing business applications.
What is work management?
Work management is the systematic approach to organizing, coordinating, and optimizing all work activities across an organization to achieve strategic objectives. It spans from the activities on your to-do list to the complex handoffs between departments, making sure every piece of work drives real business results.
Unlike simple task tracking, work management takes a holistic view of how work flows through an organization, how resources are allocated, and how different initiatives align with strategic priorities. Organizations implement work management to transform fragmented, siloed operations into coordinated systems that deliver consistent results — particularly important when only 21% of organizations have fundamentally redesigned workflows despite workflow redesign having the strongest correlation with financial gains.
The defining characteristics of work management shape how organizations plan, execute, and optimize work at every level:
- Strategic alignment: Connect daily activities directly to business objectives through goal-setting frameworks and OKRs.
- Cross-functional coordination: Break down departmental silos by creating shared visibility and standardized processes.
- Process optimization: Standardize and continuously improve workflows through automation and templates.
- Resource management: Allocate people, time, and budget strategically to ensure optimal utilization.
- Performance visibility: Track progress and outcomes in real time for data-driven decision making.
How work management operates in the digital workplace
The digital transformation of work has fundamentally changed what organizations need from work management systems. Traditional approaches like spreadsheets and email chains cannot support the complexity and coordination requirements of distributed teams working across time zones, especially when roughly 13.3% of U.S. workers work from home.
Remember those quick hallway chats that solved problems in seconds? Remote work may have ruined those, but that’s where digital work management steps in. Digital work management platforms replace this with structured systems that make work visible, trackable, and manageable from anywhere.
Your team already uses dozens of specialized applications. Any work management system worth implementing needs to connect with them all. The average enterprise uses dozens of specialized applications. Effective work management connects these systems, creating unified workflows that span multiple platforms while maintaining a single source of truth — a critical need given that the federal government alone invests over $100 billion annually in IT, with about 80% typically spent on operations and maintenance of existing systems.
From individual activities to organizational strategy
Good work management connects every level of your company — from the daily activities of individual contributors all the way up to your executive strategy. Here’s how work flows up through your organization in 4 distinct steps:
- Individual activities: The atomic units of work that form the foundation
- Projects: Collections of activities with defined objectives and timelines
- Programs: Major initiatives that aggregate multiple related projects
- Strategic goals: Enterprise-level objectives that define organizational direction
Consider a product launch initiative. Individual activities might include writing product descriptions and creating marketing materials. These belong to projects like “Website Update” or “Sales Enablement.” Those projects roll into the broader “Q2 Product Launch” program, which supports the strategic goal of expanding into new market segments.
This structure creates clear connections between daily work and business outcomes. Team members understand how their activities contribute to larger objectives. Managers see how projects align with departmental goals. Executives track how initiatives deliver against strategic priorities.
Work management vs. project management
Organizations frequently confuse work management with project management, but these disciplines serve different purposes and operate at different scales. Understanding this distinction helps organizations choose the right approach for their needs and avoid implementing solutions that don’t match their requirements.
| Work management | Project management | |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Enterprise-wide coordination across departments | Specific projects with defined deliverables |
| Timeline | Continuous, ongoing processes | Time-bound initiatives with clear start and end dates |
| Focus | Strategic alignment and organizational coordination | Tactical execution within defined constraints |
| Teams | Cross-functional groups spanning departments | Project-specific teams assembled for particular initiatives |
| Outcomes | Organizational efficiency and operational excellence | Project deliverables and defined success criteria |
| Metrics | Business KPIs, throughput, and resource utilization | Schedule variance, scope delivery, and budget adherence |
Ongoing processes vs. time-bound projects
The timeline difference is one of the clearest ways to tell these approaches apart. Work management handles continuous business operations that don’t have defined endpoints. These ongoing processes include:
- Customer service workflows: Handling support requests and maintaining satisfaction
- Marketing campaign management: Coordinating content creation and channel execution
- HR processes: Managing recruitment, onboarding, and employee development
- Financial operations: Processing invoices, managing budgets, and financial reporting
Project management focuses on discrete initiatives with specific start and end dates. These time-bound efforts include launching new products, implementing software systems, or conducting market research. They have defined objectives, timelines, and completion criteria.
Organizations need both approaches working together. monday work management handles both within a unified system, allowing teams to manage business operations alongside specific initiatives without switching between different platforms or methodologies.
Enterprise-wide vs. team-specific focus
Work management takes a holistic view of organizational operations, coordinating activities across departments and business units. The system considers how work flows between teams, how resources are allocated across the enterprise, and how different initiatives compete for attention and budget.
Project management typically operates at the team level, focusing on specific objectives and deliverables of individual projects. Project managers optimize within their project boundaries, managing assigned team members and resources to deliver specific outcomes.
This difference in scope affects how systems are designed and implemented. Work management platforms provide enterprise-wide visibility, allowing leaders to see all work across the organization, identify resource constraints, and make strategic trade-offs between competing priorities.
Try monday work management7 essential components of work management systems
Effective work management systems share common components that enable organizations to coordinate work at scale. These components work together to create comprehensive infrastructure for planning, executing, and optimizing work across the enterprise. Understanding these elements helps organizations evaluate platforms and design implementations that deliver maximum value.
Component 1: Goal and strategy management
Work management systems connect individual work to organizational objectives through structured goal-setting frameworks. These systems implement methodologies like OKRs, SMART goals, or custom strategic planning approaches that cascade from enterprise strategy down to team objectives.
Effective goal management capabilities enable leaders to:
- Define strategic objectives: Establishing clear, measurable enterprise goals
- Break down key results: Translating objectives into specific, trackable outcomes
- Assign ownership: Distributing responsibility across teams and individuals
- Track progress: Monitoring advancement toward strategic targets in real time
Teams see how their work contributes to higher-level goals, creating alignment and shared purpose across the organization.
Component 2: Resource allocation and skills matching
Intelligent resource management considers skills, availability, workload, and capacity when allocating people to work. The system maintains visibility into who is working on what, when team members have capacity for additional work, and which skills are available across the organization.
Advanced systems incorporate AI-powered optimization that analyzes historical patterns, current workload, and project requirements to recommend optimal resource allocation. This approach delivers several key benefits:
- Prevents overallocation: Identifies capacity constraints before they impact delivery
- Optimizes skill utilization: Matches expertise to requirements effectively
- Identifies bottlenecks: Spots resource constraints that could delay initiatives
- Improves satisfaction: Ensures team members work on appropriate assignments
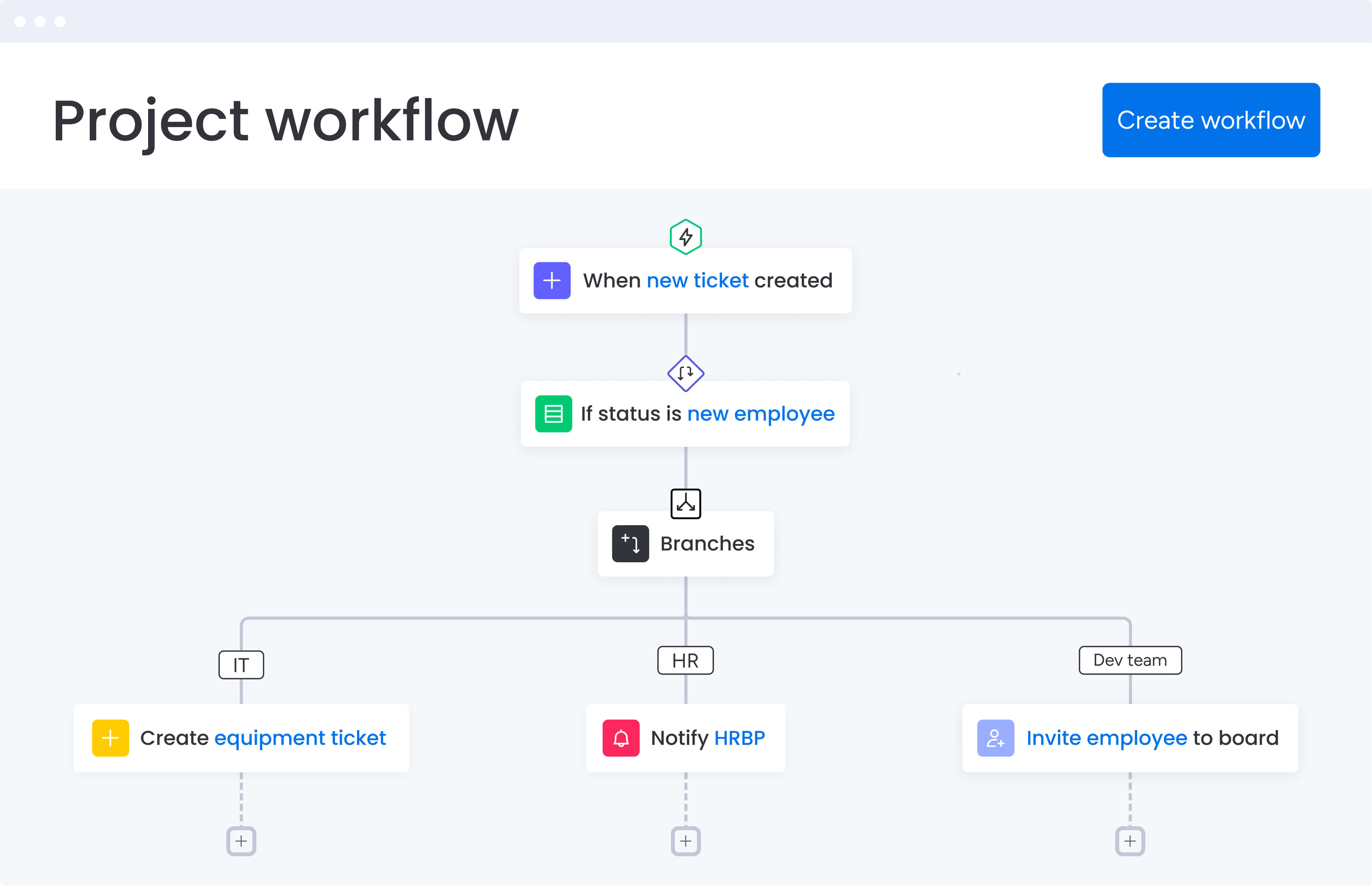
Component 3: Workflow automation
Automation reduces manual work and ensures consistent processes across the organization. Work management systems automate repetitive activities, standardize workflows, and eliminate administrative overhead that consumes team capacity.
Common automation scenarios include:
- Status-based routing: Automatically moving work between stages
- Notification triggers: Alerting stakeholders when conditions are met
- Data synchronization: Keeping information consistent across systems
- Approval workflows: Routing decisions through proper channels
These automations free teams to focus on work requiring human judgment and creativity while ensuring consistent process execution.
Component 4: Real-time analytics and reporting
To make smart decisions based on real data, leaders need to see exactly how work is progressing, who’s overloaded, and which metrics are trending in the right direction. Work management systems provide dashboards and analytics that answer critical questions about organizational performance without waiting for manual report compilation.
Real-time analytics capabilities include:
- Progress tracking: Monitoring advancement across all initiatives
- Resource utilization: Understanding capacity allocation and availability
- Performance metrics: Measuring outcomes against established KPIs
- Trend analysis: Identifying patterns that inform future planning
Component 5: Cross-functional integration
Work management systems enable collaboration across departments by providing shared visibility into work that spans multiple functions. The platform standardizes processes that coordinate cross-functional activities and maintains communication that keeps stakeholders aligned.
Integration capabilities include:
- Pre-built connectors: Linking to common business applications automatically
- APIs for custom integrations: Connecting specialized systems and workflows
- Data synchronization: Maintaining consistency across the technology ecosystem
- Unified communication: Coordinating stakeholders through shared interfaces
Component 6: AI and predictive insights
AI transforms work management from reactive to proactive — spotting potential problems before they happen, predicting when projects will actually finish, and suggesting smarter ways to allocate your team’s time. AI analyzes patterns in historical data to forecast project completion dates, identify initiatives at risk of delay, and suggest optimal resource allocation.
These capabilities transform reactive coordination into proactive management:
- Predictive forecasting: Anticipating completion dates and resource needs
- Risk identification: Surfacing potential issues before they become critical
- Intelligent recommendations: Suggesting optimizations based on data analysis
- Pattern recognition: Identifying trends that inform strategic decisions
Component 7: Security and compliance
Enterprise-grade security features protect sensitive data and ensure work management systems meet regulatory requirements. Organizations handling customer data or operating in regulated industries require robust security controls, audit capabilities, and compliance certifications.
Security extends beyond technical controls to include governance capabilities:
- Role-based access control: Restricting information based on organizational roles
- Data encryption: Protecting sensitive information in transit and at rest
- Audit logging: Tracking system usage for compliance and security monitoring
- Compliance certifications: Meeting standards like SOC 2 and GDPR requirements
Key benefits of implementing work management
Organizations implement work management to achieve specific business outcomes that directly impact competitive advantage and financial performance. These benefits extend beyond general efficiency improvements to deliver measurable value across multiple dimensions of organizational performance.
Boost productivity through intelligent automation
Work management systems eliminate manual, repetitive activities that consume significant team capacity without adding value. Automation handles routine activities like status updates, data entry, and notification management, freeing teams to focus on work requiring human judgment and creativity.
The productivity impact extends beyond time savings:
- Consistency improvement: Automation ensures standardized process execution.
- Error reduction: Eliminates mistakes from manual data handling.
- Coordination efficiency: Reduces time spent on handoffs between functions.
- Focus enhancement: Allows teams to concentrate on high-value activities.
Enable seamless cross-department collaboration
Work management breaks down organizational silos by creating shared visibility and standardized processes across departments. Marketing, IT, operations, and finance coordinate through unified workflows rather than disconnected email chains and spreadsheets.
Shared visibility into cross-functional work enables proactive coordination:
- Dependency management: Teams see how their work affects other departments.
- Handoff optimization: Smooth transitions between functional areas.
- Issue prevention: Identify blocking problems before they impact delivery.
- Alignment maintenance: Keep stakeholders coordinated without constant meetings.
Make data-driven decisions with confidence
Comprehensive visibility and analytics enable leaders to make informed decisions quickly based on current information. Work management systems provide real-time insights into organizational performance, resource utilization, and strategic progress.
The competitive advantage of data-driven decision-making manifests in several ways:
- Faster market response: Identify trends and adapt quickly to changes.
- Bottleneck identification: Spot constraints before they become critical.
- Resource optimization: Reallocate capacity toward high-priority initiatives.
- Strategic agility: Adjust direction without waiting for quarterly planning cycles.
Accelerate time to value and ROI
Effective work management reduces time-to-market through coordination, resource optimization, and process efficiency. Organizations deliver projects faster, launch products sooner, and implement changes more quickly when work management eliminates coordination overhead.
Return on investment improves through multiple mechanisms:
- Reduced operational costs: Lower administrative overhead.
- Improved resource utilization: Focus capacity on high-value activities.
- Faster delivery: Earlier revenue realization from new capabilities.
- Quality enhancement: Fewer errors and rework cycles.
The work management implementation process step-by-step
Implementing work management is about more than buying software — it’s about thoughtfully connecting your tech, processes, and people to create a system that actually works. This structured methodology ensures implementations deliver intended value while minimizing disruption to ongoing operations.
Step 1: Define business objectives and KPIs
Start by answering one question: What exactly are you trying to fix? Your leadership team needs to set clear, measurable goals that will guide your implementation and tell you whether it’s working.
This foundational step involves several critical activities:
- Strategic alignment: Connect work management goals to business strategy.
- Success metrics: Establish KPIs that track both leading and lagging indicators.
- Stakeholder engagement: Involve key leaders in defining objectives.
- Value measurement: Determine how success will be quantified and reported.
Establishing success metrics upfront ensures implementation efforts focus on measurable value rather than technology deployment alone.
Step 2: Map and analyze current workflows
Before you can improve anything, map out how work actually happens today. Get into the trenches and document each step, handoff, and decision point — especially the messy parts that cause the most headaches.
The analysis phase examines several dimensions of current operations:
- Process documentation: Map existing workflows and identify inefficiencies.
- Resource allocation patterns: Understand capacity utilization across teams.
- System inventory: Catalog current applications and integration points.
- Pain point identification: Document specific challenges and bottlenecks.
This comprehensive analysis reveals opportunities for improvement and informs process redesign efforts.
Step 3: Design optimized processes
Now comes the fun part: redesigning your processes. Look for manual steps you can automate, complicated handoffs you can simplify, and inconsistent decisions you can standardize with clear rules.
Effective process design balances several considerations:
- Standardization benefits: Consistent execution improves quality and efficiency.
- Flexibility requirements: Teams need ability to adapt workflows to specific contexts.
- Automation opportunities: Identify repetitive activities suitable for automation.
- Integration needs: Design processes that work across existing systems.
Step 4: Implement automation and integration
Technical implementation translates process designs into configured systems. Organizations set up their work management platform, configure automation rules, establish integrations, and build dashboards.
Implementation follows an iterative approach:
- Pilot deployment: Start with core workflows and limited user groups.
- Configuration setup: Build automation rules and integration connections.
- Dashboard creation: Design analytics and reporting interfaces.
- User training: Prepare teams for new processes and systems.
Organizations start with core workflows and gradually expand to additional processes and teams, allowing learning and adjustment based on real usage.
Step 5: Monitor performance metrics
Ongoing measurement tracks progress against defined KPIs and identifies areas for improvement. Organizations establish regular cadences for reviewing metrics and assessing whether work management delivers intended value.
Performance monitoring activities include:
- KPI tracking: Measure progress against established success criteria.
- User adoption: Monitor platform usage and engagement levels.
- Process efficiency: Analyze workflow performance and identify bottlenecks.
- Value realization: Assess business impact and return on investment.
Performance monitoring reveals opportunities for optimization and guides continuous improvement efforts.
Step 6: Scale and continuously improve
Successful pilot implementations expand across the organization through deliberate scaling strategies. Organizations document lessons learned, refine processes based on experience, and develop rollout plans for additional teams.
Scaling considerations include:
- Change management: Prepare additional teams for new processes.
- Process refinement: Improve workflows based on pilot experience.
- Training expansion: Develop comprehensive user education programs.
- Governance establishment: Create ongoing management and optimization processes.
Continuous improvement becomes part of organizational culture as teams regularly assess and optimize their workflows.
Who benefits from work management
Work management creates value across all organizational functions by providing the coordination infrastructure that business operations require. Different departments leverage work management for their specific workflows while benefiting from cross-functional visibility and standardized processes.
Operations and business teams
Operations teams use work management to standardize processes, manage resources, and maintain business continuity across complex workflows. These teams coordinate activities like supply chain management, facility operations, and vendor management that require consistent execution and real-time visibility.
Key operational benefits include:
- Process standardization: Ensures consistent execution across locations and teams
- Resource optimization: Allocates capacity effectively across competing priorities
- Bottleneck identification: Spots constraints before they impact service delivery
- Compliance management: Maintains audit trails and regulatory requirements
monday work management helps operations teams build, scale, and streamline business projects and processes with timelines, workload visibility, and bottleneck identification.
Marketing and creative departments
Marketing teams coordinate campaigns involving content creation, design, approval workflows, and channel execution. Work management platforms organize these multi-step processes, ensuring creative assets move smoothly through production and publication.
Content workflows particularly benefit from work management capabilities:
- Editorial calendar management: Tracks planning and production schedules
- Creative brief coordination: Flows requirements from strategy to execution teams
- Review process optimization: Routes assets through stakeholders efficiently
- Campaign coordination: Synchronizes activities across multiple channels
HR and people teams
Human resources teams manage ongoing processes that touch every employee. Recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and employee relations all benefit from structured coordination and standardized workflows.
HR-specific advantages include:
- Recruitment coordination: Tracks candidates through evaluation stages
- Onboarding standardization: Ensures consistent new employee experiences
- Performance management: Coordinates reviews and development planning
- Compliance tracking: Maintains records for regulatory requirements
Finance and accounting
Finance teams use work management for budgeting processes, financial reporting, and compliance management. The platform structures complex workflows like budget planning cycles requiring input from multiple departments.
Financial process benefits include:
- Budget planning coordination: Collects input from stakeholders efficiently
- Reporting automation: Streamlines financial statement preparation
- Approval workflow management: Routes financial decisions through proper channels
- Audit preparation: Maintains documentation and process records
IT and technology teams
IT teams manage service delivery, infrastructure operations, and coordination with business stakeholders through work management platforms. Service request workflows route tickets to appropriate teams and maintain SLA compliance.
Technology team advantages include:
- Service request management: Routes tickets efficiently to appropriate teams
- Project coordination: Manages development and infrastructure initiatives
- Change management: Coordinates system updates and deployments
- Stakeholder communication: Keeps business users informed of progress
Executive leadership and strategy
Executives use work management for strategic planning, portfolio oversight, and organizational performance monitoring. The platform provides visibility into resource allocation across strategic priorities and progress toward goals.
Leadership benefits include:
- Portfolio visibility: Monitors all initiatives and resource allocation
- Strategic alignment: Ensures activities support business objectives
- Performance tracking: Measures progress against strategic goals
- Decision support: Accesses real-time data for informed choices
How AI is revolutionizing work management
AI is changing work management from constantly putting out fires to preventing them in the first place. It spots patterns humans miss and makes smart predictions about what’s coming next. AI digs through mountains of work data to predict which projects will miss deadlines, flag team members who are about to burn out, and make decisions that would take humans hours of spreadsheet analysis.
AI-powered resource optimization
AI analyzes skills, availability, workload, and historical performance to optimize resource allocation automatically. The system considers factors that human managers struggle to balance simultaneously, improving both delivery outcomes and team satisfaction.
Resource optimization capabilities include:
- Skills matching: Connects expertise to project requirements automatically
- Capacity planning: Predicts resource needs based on historical patterns
- Workload balancing: Distributes assignments to prevent overallocation
- Performance optimization: Considers individual strengths in assignment decisions
With monday work management’s AI capabilities, you can assign the right people to the right projects, taking into account effort, level, availability, and skills.
Predictive risk management
AI identifies potential risks and bottlenecks before they impact delivery by analyzing patterns in current activities. The system recognizes early warning signs like schedule slippage or resource constraints that indicate projects may encounter problems.
Predictive capabilities include:
- Schedule forecasting: Predicts completion dates based on current progress
- Risk identification: Surfaces potential issues before they become critical
- Bottleneck detection: Identifies resource constraints that could delay delivery
- Mitigation recommendations: Suggests actions to address identified risks
Portfolio Risk Insights in monday work management scans project boards, flagging potential risks by severity so organizations can address critical issues proactively.
Intelligent process automation

AI-powered automation creates intelligent processes that adapt based on context and learning. Rather than following fixed logic, intelligent automation analyzes situations and determines appropriate actions based on patterns and outcomes.
Intelligent automation examples include:
- Content classification: Automatically classifies items based on content analysis
- Information summarization: Distills lengthy documents into concise summaries
- Data extraction: Identifies and pulls specific information from unstructured content
- Decision routing: Directs work to appropriate teams based on context
AI Blocks in monday work management demonstrate these capabilities through specialized functions that handle complex analysis and decision-making automatically.
Digital workers and agentic AI
Digital workers take automation to the next level — they’re AI assistants that don’t just perform tasks but manage entire processes from start to finish with reduced manual oversight. These AI-powered workers understand objectives, make decisions, coordinate with systems and people, and complete complex processes with a human in the loop.
Digital worker capabilities include:
- Autonomous monitoring: Continuously tracks project health and performance
- Proactive insights: Identifies opportunities and risks without prompting
- Workflow orchestration: Coordinates complex processes across systems
- Stakeholder communication: Provides updates and recommendations to teams
With monday work management’s Digital Workforce, you can implement specialized workers for common business functions, such as the Project Analyzer that monitors projects in real-time and the Campaign Manager that help optimize marketing decisions through intelligent analysis.

Transform your organization with intelligent work management
Work management transforms chaotic, disconnected workflows into a synchronized system where everyone knows exactly what’s happening and why it matters. Organizations that implement comprehensive work management gain competitive advantages through improved alignment, faster execution, and data-driven decision making, moving beyond efficiency improvements to enable entirely new capabilities.
With visual workflows that make complex work understandable, AI capabilities that automate routine coordination and provide predictive insights, and integrations with 200+ applications connects to your existing technology ecosystem, monday work management can help deliver the work management transformation you need.
Try monday work managementFAQs
What is the primary purpose of work management software?
The primary purpose of work management software is to coordinate work across organizations by connecting daily activities to strategic objectives, providing visibility into progress and resource utilization, and enabling cross-functional collaboration. It transforms fragmented operations into coordinated systems that deliver consistent results aligned with business goals.
How does work management improve team productivity?
Work management improves productivity through intelligent automation that eliminates manual coordination overhead, real-time visibility that reduces status meetings, standardized processes that reduce errors and rework, and optimized resource allocation that ensures teams focus on high-value activities.
Can work management handle both projects and ongoing processes?
Yes, work management platforms handle both time-bound projects with specific deliverables and ongoing operational processes that continue indefinitely. The same platform coordinates project execution, manages continuous workflows like customer service, and provides unified visibility across all work types.
How do work management systems integrate with existing applications?
Work management platforms integrate through pre-built connectors to common business applications, APIs for custom integrations, and webhooks for real-time connections. Data flows automatically between systems, and teams work in their preferred applications while the platform maintains unified visibility.