Your team starts each day with good intentions, but by 3 p.m., priorities have shifted, new requests have landed, and half the team is scrambling to remember what they committed to yesterday. The difference between teams that consistently deliver and those that constantly react? How they organize and track their work using smart task lists.
This article covers 5 advanced task list strategies that address real work challenges, a 4-step implementation process for building systems that drive results, and how the right work platform helps teams move from individual productivity to coordinated execution. You’ll discover how to balance strategic work with urgent demands, optimize task organization for maximum efficiency, and create the transparency that keeps everyone aligned on what matters most.
Try monday work managementKey takeaways
- Use structured task lists with ownership, deadlines, and success criteria to move beyond personal reminders and create systems that drive real business results.
- Schedule 3 strategic tasks, 3 urgent items, and 3 maintenance activities each day to prevent overwhelm while advancing important work.
- Break large projects like “launch website” into concrete, actionable steps like “draft homepage copy” and “test mobile responsiveness” that can be completed in single work sessions.
- Use time-blocking and batch similar work together to reduce switching costs and protect focus time from meeting interruptions.
- Connect individual tasks to company objectives with monday work management’s flexible views, AI-powered prioritization, and automated workflows that eliminate coordination overhead.
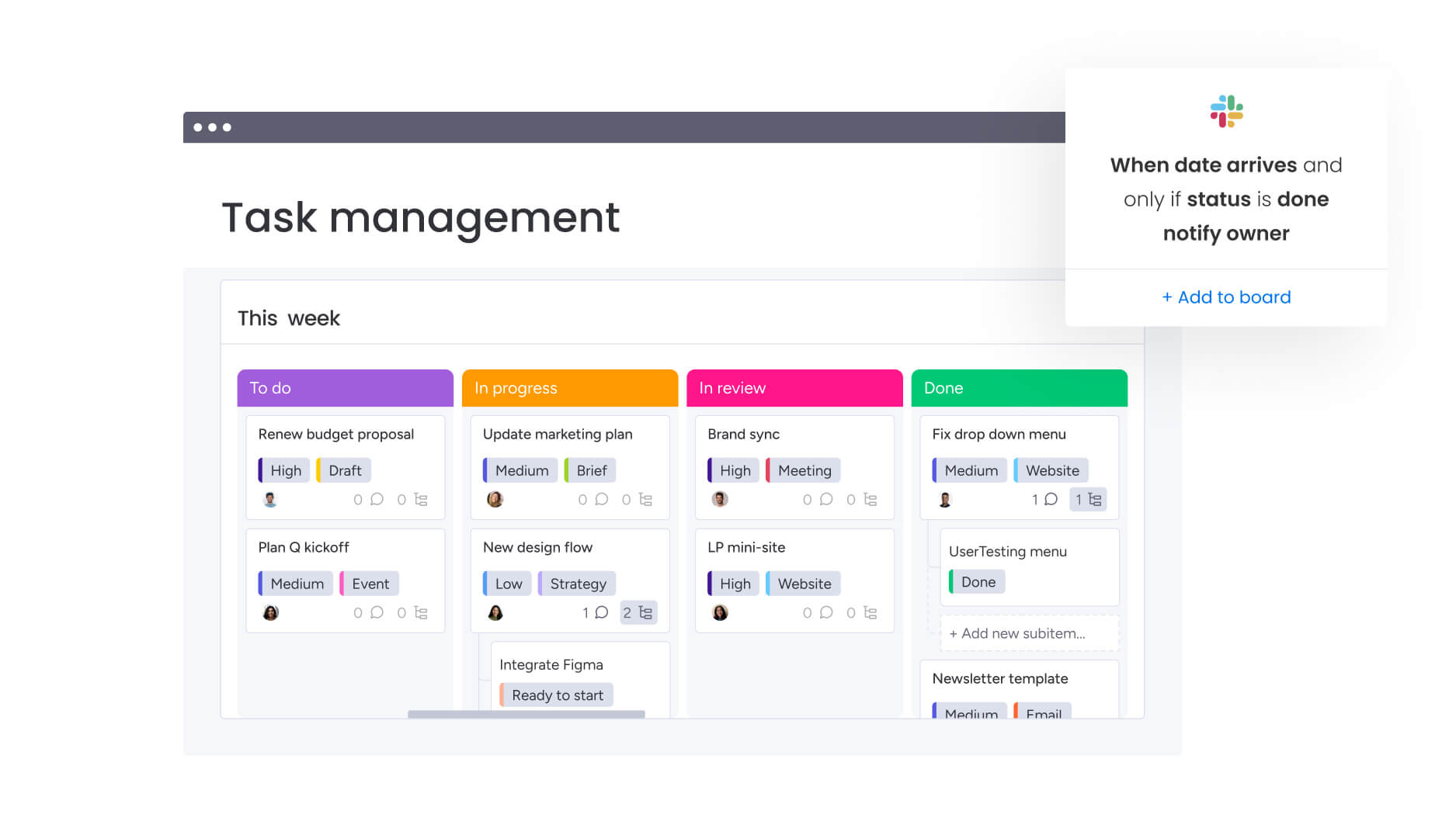
What makes task lists essential for modern work
A task list is an organized collection of work items that need completion, each with ownership, deadlines, and success criteria. Unlike simple checklists that capture personal reminders, task lists function as structured systems for managing complex work across individuals and teams.
Checking off a completed task feels good for a reason. Your brain releases dopamine when you finish something, creating a natural reward that builds momentum. This neurological feedback loop is a powerful motivator, keeping you moving through your day.
Effective task organizers share these core components that separate strategic systems from basic checklists:
- Descriptions: Define exactly what “done” looks like for each task, eliminating ambiguity that causes rework
- Deadlines: Create temporal boundaries that drive prioritization and prevent work from expanding indefinitely
- Priority indicators: Help teams distinguish between urgent firefighting and important strategic work
- Ownership assignment: Establishes accountability and prevents tasks from falling into gaps between team members
Digital platforms enhance these core components by adding real-time collaboration, automated workflows, and visual management capabilities. Teams see how individual tasks connect to project milestones, identify bottlenecks before they cause delays, and rebalance workloads based on actual capacity rather than assumptions.
Task lists vs. to-do lists: understanding the difference
The distinction between task lists and to-do lists reflects fundamental differences in complexity, collaboration, and strategic alignment. Understanding these differences helps organizations choose the right approach for their work management needs.
| Dimension | Task lists | To-do lists |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Multi-step workflows with dependencies and subtasks | Single-action items without structure |
| Collaboration | Shared visibility, delegation, and workload balancing | Individual-focused with limited sharing |
| Tracking | Progress metrics, time estimates, and completion analytics | Simple checked/unchecked status |
| Integration | Connected to calendars, communications, and workflows | Standalone lists without context |
| Strategic alignment | Linked to projects, objectives, and organizational goals | Personal reminders without broader connection |
The science of task lists and achieving peak performance
Task lists function as external memory systems that reduce cognitive load by offloading mental tracking to a reliable structure. Your brain is great at solving problems but terrible at juggling dozens of commitments at once. Relying on memory alone can quickly burn through mental energy, leading to increased stress and reduced capacity for creative thinking.
The 3-3-3 rule provides a framework for daily task allocation that balances different work types without overwhelming capacity, and you can adapt the categories to your role. Each day should include 3 important tasks that advance strategic objectives, 3 urgent tasks that address immediate needs, and 3 maintenance tasks that keep systems running smoothly.
Mental health benefits extend beyond simple stress reduction. Task lists create psychological safety by making workload visible and manageable rather than overwhelming and uncertain. Writing down tasks reduces the anxiety loop where unfinished work creates intrusive thoughts that disrupt concentration.
These psychological principles are not just theoretical; they have a direct impact on performance. By implementing a structured task management system, you can improve both individual focus and organizational outcomes in several key ways:
- Reduced decision fatigue: Task lists eliminate the constant mental question of “what should I work on next” by establishing priorities ahead of time.
- Improved time estimation: Regular task completion builds calibration between estimated and actual time requirements.
- Enhanced focus: Task boundaries create natural work sessions where attention can fully engage with one objective.
- Momentum building: Small task completions create psychological wins that build confidence and motivation.
- Anxiety reduction: Externalizing commitments to a trusted system reduces the mental burden of trying to remember everything.
5 advanced task list strategies for working smarter
Today’s complex work environment demands strategies that go beyond simple task capture to create systems for prioritization, scheduling, and optimization. These approaches address the reality that professionals face competing demands, limited time, and the need to balance reactive work with strategic initiatives. Each strategy targets specific challenges that traditional task management approaches struggle to address.
Strategy 1: Priority matrix for strategic alignment
The Eisenhower Matrix adapted for task lists creates a 4-quadrant system that categorizes work by urgency and importance. Important-and-urgent tasks require immediate attention and directly impact key objectives. Important-but-not-urgent tasks represent strategic work that builds long-term value but lacks artificial deadlines.
Urgent-but-not-important tasks create time pressure without advancing core goals and often represent opportunities for delegation or automation. Neither-urgent-nor-important tasks should be eliminated or deferred indefinitely.
Strategy 2: Time-blocked task scheduling
Time-blocked scheduling assigns specific calendar slots to tasks based on realistic duration estimates and energy levels throughout the day. Rather than maintaining an undifferentiated list of tasks, this approach treats task completion as appointments that protect focus time from meeting creep and interruptions.
High-cognitive-load tasks get scheduled during peak energy hours, while administrative work fills lower-energy periods.
Strategy 3: Context-based task grouping
Context-based grouping organizes tasks by the mental mode, tools, or location they require rather than by project or deadline. All phone calls get batched together to minimize the switching cost between communication and deep work.
Email-related tasks form another group that gets processed in dedicated sessions rather than continuously throughout the day. Creative work requiring uninterrupted focus gets protected in separate blocks from collaborative tasks that benefit from real-time interaction.
Strategy 4: Weekly-daily cascade planning
Weekly-daily cascade planning establishes a 3-tier system where weekly objectives cascade into daily actionable tasks. Each week begins with identifying the 3-5 most important outcomes that need achievement by week’s end.
These weekly objectives then break down into specific daily tasks that represent concrete progress toward those outcomes. Daily planning sessions review yesterday’s completion, adjust today’s priorities based on new information, and ensure that daily work ladders up to weekly goals.
Strategy 5: AI-powered task optimization
AI-powered optimization uses machine learning to categorize tasks, suggest priorities, and identify optimal task sequences based on dependencies and resource availability. AI capabilities automatically categorize incoming tasks by type, urgency, and strategic alignment, reducing the manual overhead of task organization.
Prioritization algorithms consider multiple factors including deadlines, dependencies, resource availability, and strategic importance to surface the highest-value work at any given moment.
Quick comparison: Strategy implementation strategies
These strategies work together to create comprehensive task management systems. Each addresses different aspects of work complexity:
| Strategy | Implementation difficulty | Time investment | Impact level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Priority matrix | Low | 15–30 min weekly | High — transforms decision-making |
| Time-blocked scheduling | Medium | 30–45 min daily | High — protects focus time |
| Context-based grouping | Low | 20–30 min weekly | Medium — reduces switching costs |
| Weekly-daily cascade | Medium | 45–60 min weekly | High — ensures strategic alignment |
| AI-powered optimization | Low (with platform) | 5–10 min daily | Medium-high — scales with usage |
4 steps to build task lists that actually work
Moving from scattered commitments to structured execution requires a systematic approach. These 4 steps transform how your team captures, organizes, and executes work — from initial brain dump to enterprise-wide coordination.
Step 1: Capture and break down your work
Start with a brain dump. Write down every commitment, idea, and responsibility currently occupying mental space — no filtering, no organizing, just capture. You’ll likely uncover dozens of items you’ve been trying to remember, far more than the 5-9 items working memory can typically handle.
Next, break large projects into specific, actionable tasks that can be completed in a single work session. “Launch new website” becomes “draft homepage copy,” “review design mockups with team,” “configure hosting environment,” and “test mobile responsiveness.”
For each task, establish clear ownership, realistic deadlines with buffer time, and specific success criteria that define what “done” looks like. Optimal task size falls between 15 minutes and 2 hours of focused work — short enough to feel achievable, substantial enough to matter.
Step 2: Choose an organizational structure that matches how work flows
Once tasks are clearly defined, the next decision is how to organize and visualize them so people can execute in the right order.
Start by identifying task dependencies: Which work must happen before something else can begin? You don’t need complex project math here. The goal is simply to answer: “What can’t move forward until something else is done?”Mapping these relationships early prevents hidden bottlenecks and last-minute scrambling.
Next, choose a task structure, or how work is grouped and nested:
- Flat structures work best for personal productivity and simple workflows, where tasks can live at the same level without losing context.
- Hierarchical structures are better for complex initiatives, where large outcomes break down into projects, phases, and subtasks.
- Hybrid structures combine both, allowing high-level projects with flexible task groupings underneath — ideal for teams juggling different work types.
Finally, select the view that makes work easiest to understand and act on:
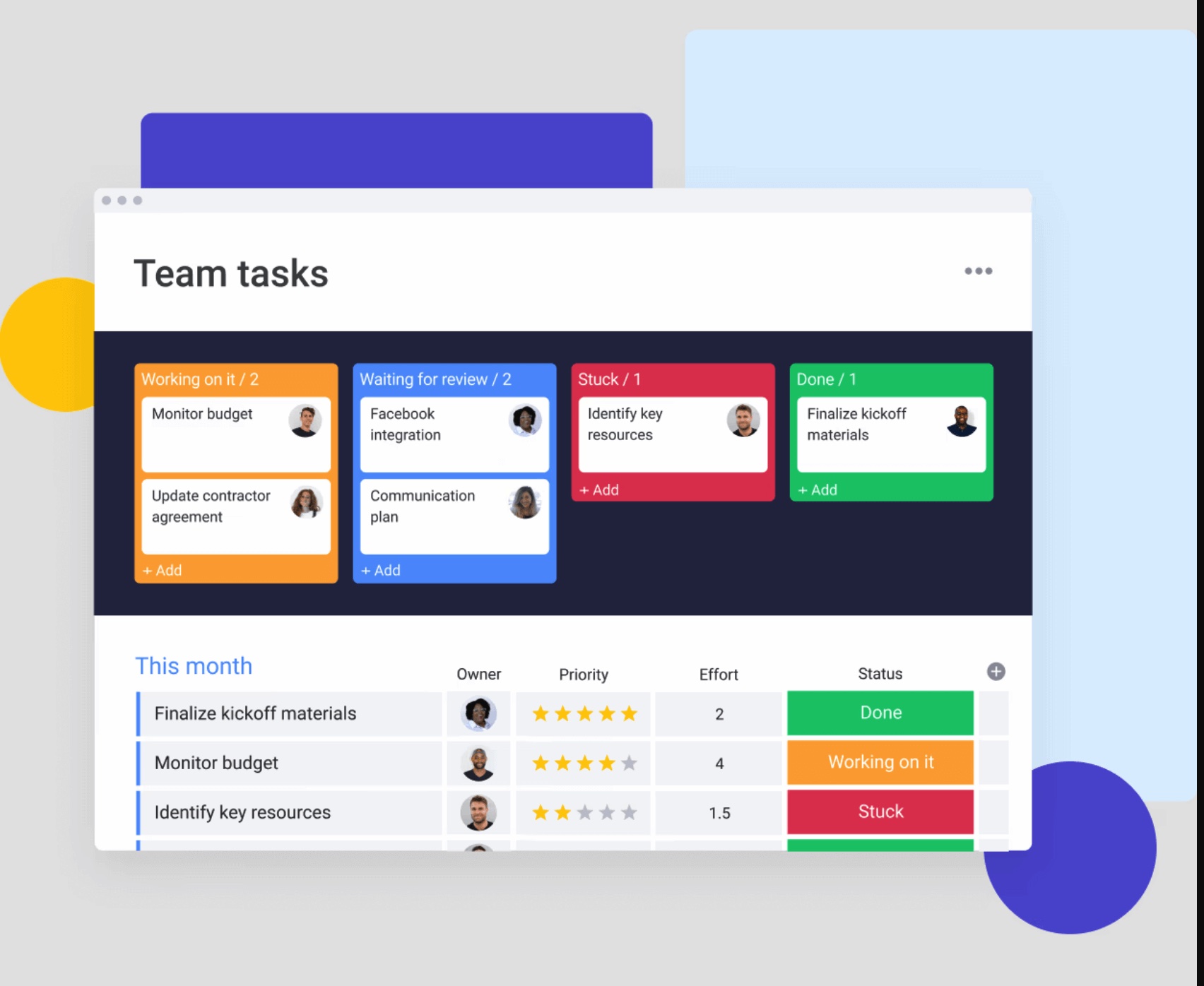
- Kanban boards show how tasks move through stages, making bottlenecks and work-in-progress limits visible.
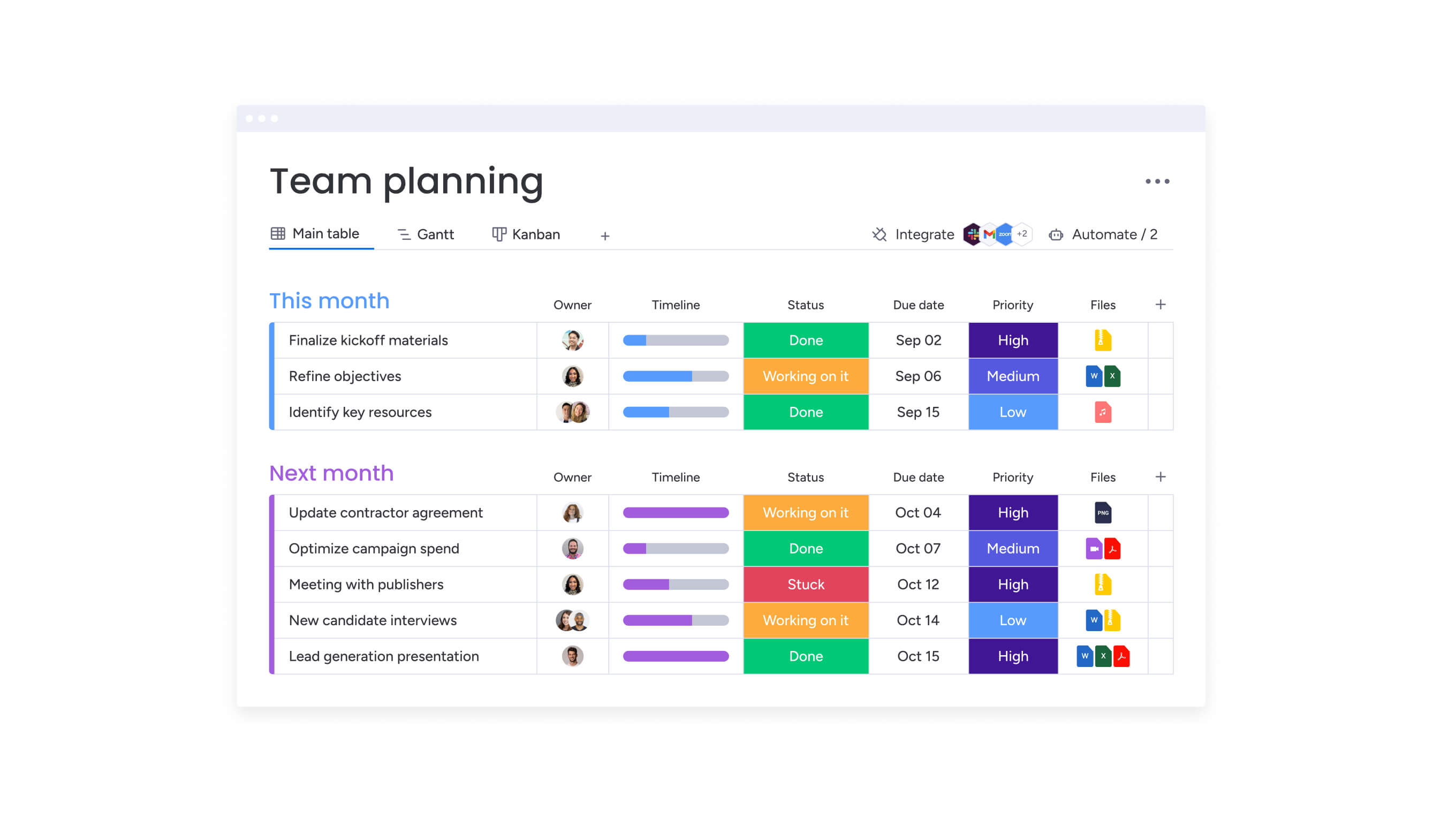
- Gantt charts display timelines, durations, and dependencies, helping teams plan sequence and capacity.
- List views provide fast scanning, sorting, and filtering by priority, owner, or deadline.
The same underlying tasks can appear in multiple views at once. Individual contributors might work from lists, managers might track flow in Kanban, and leadership might review timelines in Gantt. The key is choosing a structure that supports clarity without forcing everyone into the same perspective.
Use labels, priorities, and contextual tags sparingly to add additional dimensions — not complexity. When done right, structure makes work easier to see, not harder to manage.
Try monday work managementStep 3: Scale from personal to team coordination
Shared task lists give everyone visibility into who’s working on what, when deliverables are due, and where bottlenecks are forming. This transparency enables proactive coordination rather than reactive firefighting.
Build effective team task management by establishing clear ownership for every task, creating visibility without micromanagement, and balancing workload based on actual availability rather than equal division. Use reusable templates to capture recurring processes, and define communication protocols that keep everyone informed without constant interruptions.
Effective delegation specifies the desired outcome, deadline, and success criteria while leaving execution details to the person doing the work. This balance between clarity and autonomy drives both accountability and engagement.
Step 4: Connect and automate your workflows
Connect your task lists to the systems where work originates and needs to flow. Calendar sync ensures time-blocked tasks appear as protected focus time. Communication platform integrations create seamless updates between task management and team conversations.
Set up automated task creation from emails, form submissions, and recurring schedules to eliminate manual entry. AI capabilities enhance this by intelligently categorizing tasks by type, urgency, and workflow, then extracting key information like deadlines and dependencies without manual tagging.
The best systems handle routine coordination automatically while keeping humans in charge of strategic decisions and judgment calls. Reserve automation for the repetitive stuff: prioritization, resource allocation, and handling exceptions still need human judgment.
Looking for an easy-to-implement template? Check out this team task list template.

Scale task management across teams with monday work management
As work grows more complex, task lists need to evolve from personal tools into shared execution systems. With monday work management, you support this transition by giving teams a flexible way to organize tasks, visualize progress, and coordinate work across functions.
Core task management capabilities
Teams can choose the views that match how they work, from lists for day-to-day execution, to Kanban boards for tracking flow, to timeline and workload views for planning capacity and dependencies. Everyone works from the same underlying tasks, without forcing a single perspective.
Automations reduce coordination overhead by handling routine updates. When a task moves forward, stakeholders can be notified automatically, follow-up work can be created, and dashboards stay up to date without manual reporting.
Dashboards provide visibility across projects and teams, helping leaders understand progress, spot bottlenecks, and see how daily work connects to broader initiatives.
How AI supports task management
AI features in monday work management are designed to assist, not automate decision-making. They can help categorize incoming work, suggest priorities based on deadlines and dependencies, and surface potential risks — while leaving judgment and final decisions with people.
Tools like AI Blocks and monday sidekick can help teams build workflows, find information, and reduce manual setup, so more time goes into execution rather than organization.

Enterprise-level coordination benefits
When teams share task visibility, dependencies become easier to manage and handoffs smoother. Work connects more clearly across departments, reducing last-minute conflicts and duplicated effort.
By linking tasks to projects and higher-level goals, organizations gain clearer insight into whether execution aligns with strategy rather than what feels urgent in the moment.
Build task management systems that scale with your organization
Task lists transform from simple productivity tools into strategic execution systems when implemented with the right structure, automation, and organizational alignment. The progression from individual task tracking to enterprise-wide workflow coordination requires platforms that can adapt to growing complexity while maintaining simplicity for daily users.
Teams that nail their task management approach simply outperform their competitors. They execute faster, use their people more effectively, and actually connect their big-picture strategy to daily work. Teams spend less time coordinating and more time delivering value when task systems provide the right information to the right people at the right time.
Getting serious about task management doesn’t just make your team more productive — it transforms how your entire organization executes. Projects complete on schedule because dependencies are visible and managed proactively. Teams collaborate more effectively because workload and priorities are transparent. Leaders make more informed decisions because they have real-time visibility into execution progress and resource allocation.
Try monday work managementFAQs
What is a task list with examples?
A task list is an organized collection of work items that need completion, each with ownership, deadlines, and success criteria. Personal task list examples include "draft quarterly budget proposal," "schedule team 1:1 meetings," and "review vendor contracts." Work project examples include "finalize product requirements document," "conduct user testing sessions," and "prepare launch presentation."
How do task lists differ from project plans?
Task lists represent the actionable components within broader project plans, focusing on specific work items that need completion rather than overall project structure and strategy. Project plans define objectives, scope, timelines, resources, and success criteria at a high level, while task lists break those plans into concrete actions with ownership and deadlines.
What is the ideal number of daily tasks?
The 3-3-3 rule provides the following framework: 3 important tasks that advance strategic objectives, 3 urgent tasks that address immediate needs, and 3 maintenance tasks that keep systems running smoothly. This distribution totals 9 tasks daily, balancing different work types without overwhelming capacity.
Can task lists help with ADHD and focus challenges?
Task lists function as external memory systems that reduce cognitive load and provide structure that supports focus. For individuals with ADHD, task lists eliminate the mental burden of remembering everything and reduce decision fatigue about what to work on next. The structure and visual organization help maintain attention on current priorities while reducing anxiety about forgotten commitments.
Which task list platforms work best for teams?
Effective team task management tools provide shared visibility, flexible views, automation capabilities, and integration with communication platforms. Key evaluation criteria include whether the tool supports multiple organizational methods, enables workload balancing, provides real-time collaboration, integrates with existing tech stack, and scales from small teams to enterprise deployments.
How do you transition from paper to digital task lists?
Migration begins with a complete brain dump that captures all current commitments from paper lists, sticky notes, and mental tracking into a digital system. Next, organize captured tasks using categories, priorities, and deadlines that match how you think about work. Then establish a daily review habit where you check the digital system first thing each morning and update it throughout the day as new tasks emerge.