Your project just missed another deadline, the stakeholder meeting turned into damage control, and your team is working harder than ever, but results keep falling short. You’re witnessing the gap between good intentions and consistent execution, where traditional project management approaches collapse under the weight of distributed teams, tight timelines, and constant change.
This article breaks down 12 proven project management best practices that work in real organizational environments. You’ll learn how to implement outcome-focused planning, build transparency into workflows, leverage AI for predictive insights, create measurement systems that drive continuous improvement, and roll out new practices without disrupting current projects.
Try monday work managementKey takeaways
- Define measurable success criteria like “achieve 10,000 active users in 90 days” rather than simply “launch product” to guide every project decision toward real outcomes.
- Make project status visible to all stakeholders in real time so teams spend less time reporting and more time executing.
- Identify bottlenecks and critical paths early using visual tools to prevent delays and allocate resources where they matter most.
- Use AI-powered risk monitoring to detect patterns like declining team velocity or resource overallocation weeks before deadlines, giving you time to intervene instead of scrambling.
- Set up automated notifications and reports to eliminate the hours per week project managers spend on manual coordination, freeing up time for strategic thinking.
What are project management best practices?
The best project management practices aren’t theoretical — they’re battle-tested approaches that consistently deliver results. Think of them as flexible playbooks that evolve with your data and business reality, not rigid rulebooks collecting dust on a shelf.
Today’s top-performing teams focus on results, not just following procedures. They look at the data — how the project’s progressing, who’s overloaded, what stakeholders actually need — and adjust their approach accordingly.
What elevates project management to a strategic advantage? Three core characteristics consistently appear in high-performing organizations:
- Radical transparency: Every stakeholder can access real-time project status without scheduling meetings or sending emails.
- Data-driven decision making: Project managers base choices on actual metrics — team velocity, resource utilization, risk probability — rather than gut feelings.
- Continuous alignment: Daily tasks connect directly to strategic objectives, so team members understand not just what they’re doing but why it matters.
The shift from static rules to adaptive frameworks represents the most significant change in project management. Traditional methodologies treated projects as predictable sequences. Modern practices acknowledge uncertainty and build in mechanisms for rapid course correction.
Why yesterday's project management playbook needs an upgrade
Old-school project management is breaking under today’s pressures. What used to be small hiccups have become project-killing problems, especially with teams spread across locations and businesses needing results faster than ever.
Manual coordination is eating up productive hours
Project managers spend a large chunk of their week on coordination activities — status meetings, email chains, manual report compilation, and schedule reconciliation. This represents 40% of a typical work week dedicated to activities that generate no direct project value.
Teams waste collective hours tracking down updates that should be automatically visible. A single status meeting with 8 participants consumes 8 person-hours, yet the information shared is often outdated within days. Organizations essentially pay skilled professionals to manually aggregate information that modern systems can surface automatically.
Visibility gaps are growing across distributed teams
Remote and hybrid work has exposed coordination weaknesses that were manageable when teams shared physical space. A project manager in New York can’t walk over to a developer in Austin to check progress. Stakeholders in London can’t glance at a board to see what’s blocked.
These visibility gaps create dangerous lag between when problems emerge and when leaders become aware of them. By the time a risk surfaces in a weekly status meeting, it may have already derailed the timeline. Distributed teams need real-time visibility into who’s working on what, where dependencies exist, and which tasks are at risk — without constant check-ins that interrupt deep work.
Scaling challenges increase as organizations grow
Processes that work brilliantly for a 5-person team collapse under the weight of enterprise complexity. A simple spreadsheet tracks work items effectively until you have 50 concurrent projects. Manual resource allocation works until you need to balance capacity across 200 people.
As organizations scale, coordination overhead grows exponentially while old tools and processes remain linear. Project managers spend more time managing the system than managing the work.
Try monday work management12 project management best practices for complex organizations
What makes these practices work? They bridge the gap between your plans and what actually happens. Each one fixes a specific pain point where traditional methods typically fall apart. These 12 proven approaches transform how teams coordinate work, make decisions, and deliver results.
1. Start with outcome-focused project charters
Start every project by defining what success actually means —not just what you’ll deliver. Get specific: “We need 10,000 active users,” not just “launch the product.” When your team knows exactly what winning looks like, they’ll make smarter decisions along the way.
2. Map dependencies visually before kickoff
Visual dependency mapping reveals bottlenecks and risks that linear task lists hide. Teams use visual tools to chart which tasks depend on others, which resources are shared across multiple workstreams, and where external dependencies create vulnerability.
A software development project might reveal that 3 different features all depend on a single API integration, making that integration the critical path.
- Sequence work strategically: Prioritize critical path activities
- Allocate resources to bottlenecks: Prevent delays before they occur
- Build contingency plans: Prepare alternatives for high-risk dependencies
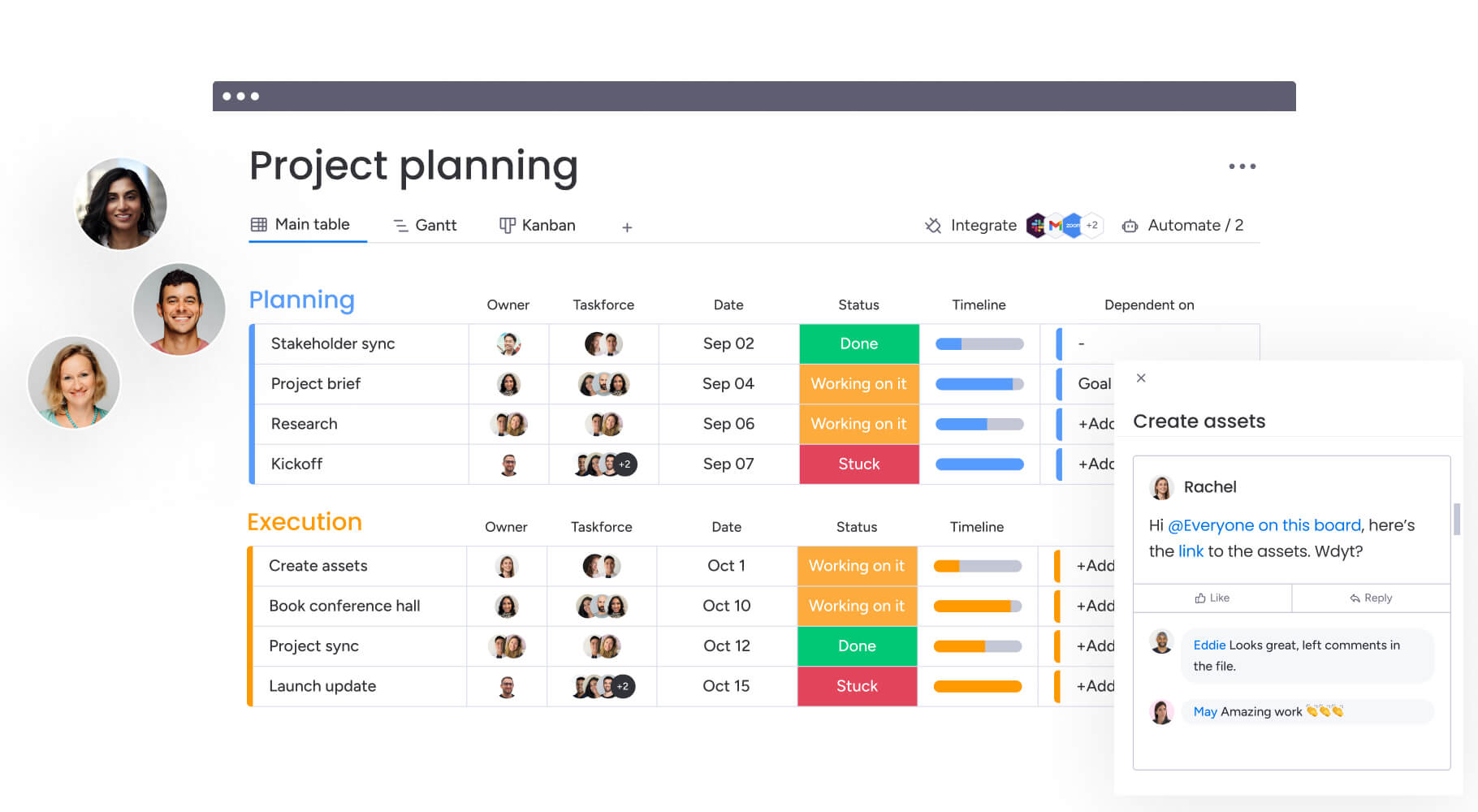
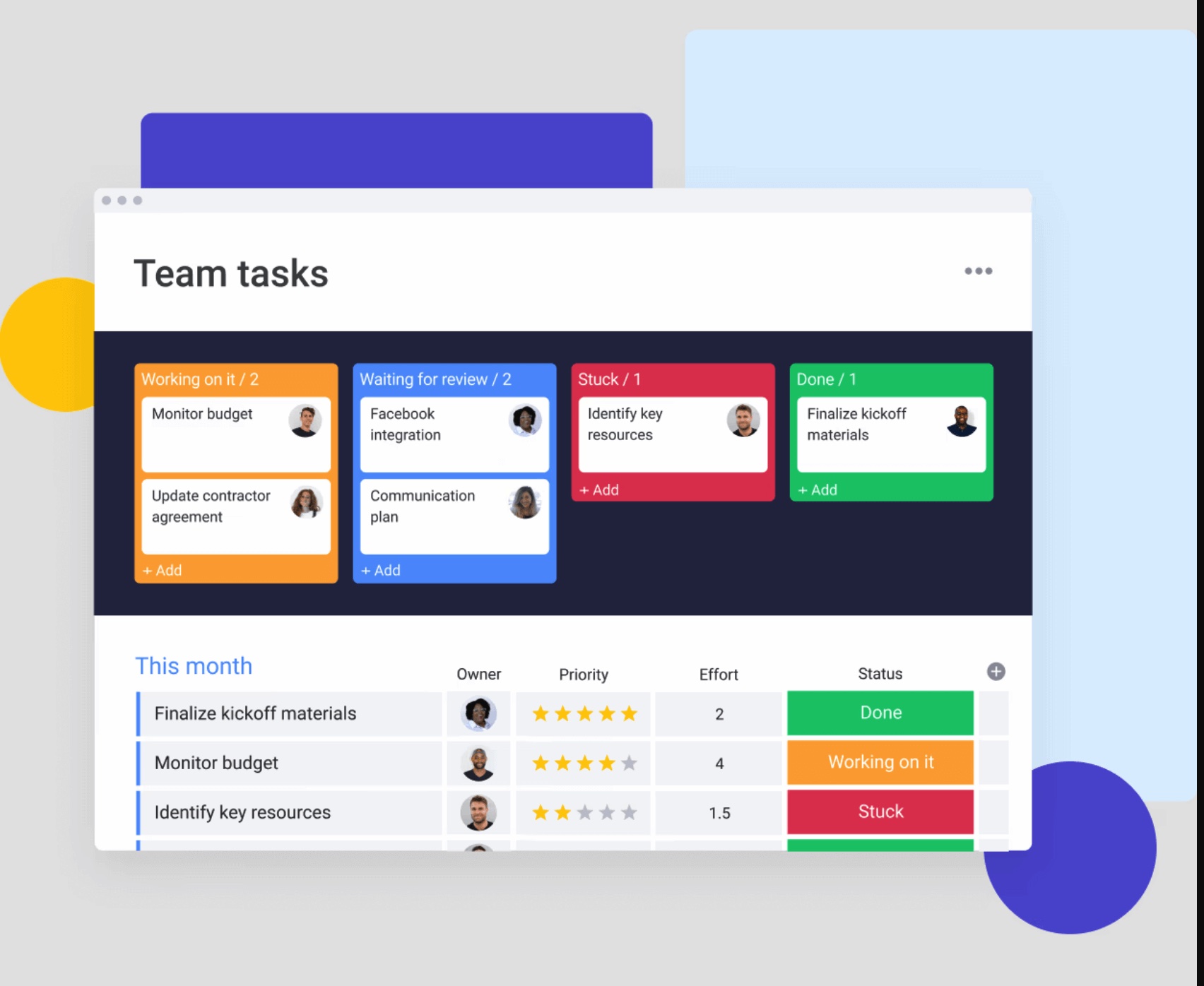
3. Build transparency into every workflow
True transparency lets stakeholders check progress without bombarding your team with questions. They can see who’s handling what, where things stand, and what’s holding up progress — all in real time. When decisions and roadblocks are immediately visible, everyone stays aligned without the meeting overload.
4. Automate status updates and reporting
Automated status updates eliminate the manual reporting overhead that consumes project manager time. When a task moves to “Complete,” stakeholders receive notifications automatically. When a deadline approaches, reminders trigger without manual intervention.
Teams using work management software like monday work management can set up automation rules that replicate their most time-consuming reporting activities, ensuring updates contain enough context to be actionable.
5. Implement AI-powered risk monitoring

AI analyzes patterns across projects to identify risks before they become problems. Machine learning algorithms detect signals that human project managers might miss:
- Team velocity declining: Week-over-week productivity drops
- Dependency chains growing: Complexity increasing beyond manageable levels
- Resource overallocation: Single team members stretched across multiple projects
6. Allocate resources based on skills and capacity
Strategic resource allocation matches people to projects based on both their capabilities and their current workload. Instead of assigning whoever is available, teams consider who has the right skills, who has capacity, and who would benefit from the development opportunity.
7. Create feedback loops at every milestone
Continuous feedback loops build learning into project execution rather than saving it for post-mortems. At each milestone, teams pause to assess what’s working, what’s not, and what adjustments would improve outcomes.
8. Standardize processes without sacrificing flexibility
Process standardization creates efficiency without imposing rigidity. Teams develop templates and frameworks that embed best practices while allowing customization for specific project development needs.
9. Connect daily tasks to strategic goals

monday work management company objectives board
Every task connects directly to a strategic objective, so team members understand how their work contributes to organizational success. This alignment transforms task completion from a checklist exercise into meaningful progress toward important goals.
10. Track leading indicators not just deadlines
Leading indicators predict project success or failure before deadlines arrive through effective time management. Instead of just tracking whether tasks finish on time, teams monitor signals like:
- Team velocity: Work completion rates over time
- Stakeholder engagement: Participation in reviews and decisions
- Quality metrics: Defect rates, rework frequency
- Dependency resolution: Speed of addressing blockers
11. Document decisions in real time
Decision documentation captures not just what was decided but why, who was involved, and what alternatives were considered. A product team might document why they chose a specific technical architecture, including the trade-offs considered and the factors that drove the decision. monday workdocs enables this documentation directly within project workflows.
12. Conduct data-driven retrospectives
Retrospectives use project metrics to identify improvement opportunities rather than relying solely on subjective impressions. Teams analyze actual data on cycle times, resource utilization, risk realization, and outcome achievement to understand what worked and what didn’t.
How to roll out new practices without disrupting current projects
Transforming project management practices while maintaining current project momentum requires a strategic rollout approach that builds confidence through demonstrated success. The key is implementing changes gradually while proving value at each stage.
Choose pilot teams strategically
Pilot teams should be influential enough that their success creates organizational credibility, but not so critical that failure would cause significant business impact. Look for teams that are open to change, have strong leadership support, and work on projects with clear success metrics.
The ideal pilot team characteristics include size (5-15 members for manageable scope), timeline (2-4 month project development cycles for measurable results), leadership (at least one respected champion), and influence (credible voices that others trust).
Select 2-3 pilot teams to run simultaneously, providing enough data points to identify patterns while keeping the scope manageable.
Create templates that embed best practices
Templates transform abstract practices into concrete workflows that teams can follow immediately. A project charter template might include sections for outcome-focused success criteria, dependency mapping, and stakeholder communication plans — embedding multiple best practices into a single starting point.
Build templates for your most common project types:
- Product launches: Include market research, go-to-market planning, success metrics
- Process improvements: Feature current state analysis, stakeholder mapping, change management
- System implementations: Cover technical requirements, user training, rollback plans
Each template should include instructions, example content, and links to supporting resources.
Build momentum with quick wins
Quick wins demonstrate value before skepticism takes root. Identify practices that show immediate impact with minimal implementation effort. Automated status updates often qualify — teams see time savings within the first week.
Target practices that reduce visible pain points:
- Status meeting complaints: Implement automated updates first
- Visibility requests: Deploy transparency practices immediately
- Resource conflicts: Introduce capacity planning tools
Document and communicate these wins explicitly, showing the time saved, risks avoided, or quality improved.
Scale based on measured success
Scaling happens in phases, with each phase informed by data from previous implementations. After pilot teams demonstrate success, expand to a broader group of early adopters — teams that volunteered or expressed interest.
A typical scaling timeline spans 6-12 months:
- Pilot phase: 2-3 months for initial teams
- Early adopter phase: 3-4 months for expanded group
- Organization-wide rollout: 3-5 months for full implementation
This measured approach allows you to address issues when they affect dozens of people rather than hundreds.
Try monday work managementMeasuring what matters in project management
Measurement in modern project management focuses on metrics that predict outcomes and drive immediate action, not metrics that simply document what already happened. The most effective measurement systems provide early warning signals and actionable insights that improve project success rates.
Essential metrics for project health
Project health metrics predict success or failure before deadlines arrive. Team velocity measures how much work teams complete in each time period, revealing capacity trends that forecast whether current commitments are realistic.
Key leading indicators include:
- Stakeholder engagement: Tracks how actively key stakeholders participate in reviews and decisions
- Risk probability: Assesses the likelihood and impact of identified risks
- Dependency resolution rate: Monitors how quickly teams address blockers
These leading indicators provide early warning signals that allow intervention before problems cascade.
Building dashboards that drive action

Actionable dashboards surface the information that requires immediate attention while keeping supporting context accessible. The most effective dashboards follow a 3-tier structure that prioritizes information by urgency and relevance.
Dashboard structure for maximum impact:
- Critical alerts at the top: Risks that require immediate action
- Key metrics in the middle: Leading indicators of project health
- Detailed breakdowns at the bottom: Supporting data for deeper analysis
Dashboard design should be tailored for specific audiences:
- Executive dashboards: Emphasize strategic alignment and outcome progress
- Project manager dashboards: Focus on resource allocation and risk mitigation
- Team member dashboards: Highlight individual tasks and dependencies
Using insights to continuously improve
Continuous improvement happens when teams systematically analyze metrics to identify patterns and opportunities. Monthly metric reviews examine trends across projects: which types of projects consistently run over budget, which teams deliver ahead of schedule, which risk categories materialize most often.
The improvement cycle operates at 2 levels:
- Individual project adjustments: Based on real-time metrics
- Organizational process improvements: Based on cross-project patterns
The difference between traditional and modern project management metrics becomes clear when you compare what teams measure — and why.
| Traditional metrics | Modern metrics | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Tasks completed | Value delivered to stakeholders | Completion doesn’t equal success — stakeholder value does |
| Budget variance | ROI and outcome achievement | Staying on budget matters less than achieving intended outcomes |
| Schedule adherence | Leading indicators of timeline risk | Knowing you’ll miss a deadline weeks in advance allows intervention |
| Resource utilization | Team capacity and skill alignment | High utilization without the right skills creates burnout and poor quality |
| Status report frequency | Real-time visibility and transparency | Reporting cadence matters less than continuous access to current information |
5 lessons for a successful project management transformation
Most transformation efforts crash and burn—not because the ideas are bad, but because teams stumble into the same implementation pitfalls time and again. Understanding these pitfalls helps teams avoid the mistakes that derail even well-intentioned improvement efforts.
Lesson 1: Don’t change everything at once
Try changing everything at once, and you’ll watch your teams shut down from overload. Hit them with new tools, processes, metrics, and communication styles simultaneously, and guess what happens? They’ll revert to their old ways the minute pressure hits.
Most teams simply can’t handle learning several new methods while keeping projects moving forward. If you’ve already overwhelmed your team, pull back to just 2-3 essential practices, prove they work, then build from there.
Lesson 2: Don’t skip getting stakeholder buy-in
Top-down mandates without grassroots support create compliance without commitment. Teams follow new practices mechanically when monitored but abandon them when attention shifts.
Real transformation requires stakeholders at all levels understanding why changes matter and how they benefit from them. Building genuine buy-in requires:
- Involving stakeholders: In identifying problems and evaluating solutions
- Sharing decision-making: In shaping implementation approaches
- Demonstrating value: Through concrete examples and quick wins
Lesson 3: Don’t choose complexity over simplicity
The temptation to build sophisticated, comprehensive solutions often produces systems too complex for daily use. Teams abandon elaborate frameworks in favor of simple approaches that actually fit their workflow.
Simplicity wins because it reduces friction. The best practices are those teams can follow consistently without heroic effort. Start with the minimum viable practice that solves the problem, then add complexity only when needed.
Lesson 4: Never underestimate the power of habits
Existing workflows create invisible resistance to change through muscle memory and established routines. Teams revert to familiar approaches automatically, especially under stress.
Overcoming habit requires:
- Making new practices easier: Than old ones
- Providing consistent reminders: During the transition period
- Celebrating visible adoption: To reinforce new behaviors
The transition period typically spans 6-8 weeks — the time required for new behaviors to become automatic.
Lesson 5: Avoid focusing on activity instead of outcomes
Focusing on adoption metrics rather than outcome metrics creates false confidence. High adoption rates mean nothing if projects don’t improve.
Measure what matters:
- Time savings: Hours recovered from manual processes
- Risk reduction: Problems prevented or caught early
- Outcome achievement: Goals met or exceeded
- Stakeholder satisfaction: Improved experience and confidence
These outcome metrics reveal whether transformation is working.
How AI revolutionizes project management best practices

AI doesn’t replace your judgment—it supercharges it. It processes mountains of project data to spot patterns you’d never catch on your own, no matter how experienced you are. The most effective AI applications in project management augment rather than replace human decision-making, providing advanced pattern recognition and predictive capabilities.
Predictive insights that prevent delays
AI analyzes historical project data to identify patterns that predict timeline risks before they materialize. Machine learning algorithms examine thousands of completed projects to understand which combinations of factors — team size, dependency complexity, stakeholder engagement levels — correlate with delays.
When a current project exhibits similar patterns, the AI flags the risk weeks before traditional indicators would reveal it. This early warning allows project managers to intervene proactively:
- Adding resources: Before bottlenecks form
- Simplifying scope: To reduce complexity
- Accelerating dependency resolution: To prevent cascading delays
Intelligent resource recommendations
AI-powered resource allocation considers skills, capacity, development goals, and project requirements simultaneously to recommend optimal team assignments. Instead of project managers manually evaluating dozens of potential team members, AI surfaces the best matches based on comprehensive criteria.
These recommendations improve both project outcomes and team development. For example, monday work management’s AI capabilities include features that automatically match tasks with the right people based on complexity, context, and capacity.
Automated risk detection at scale
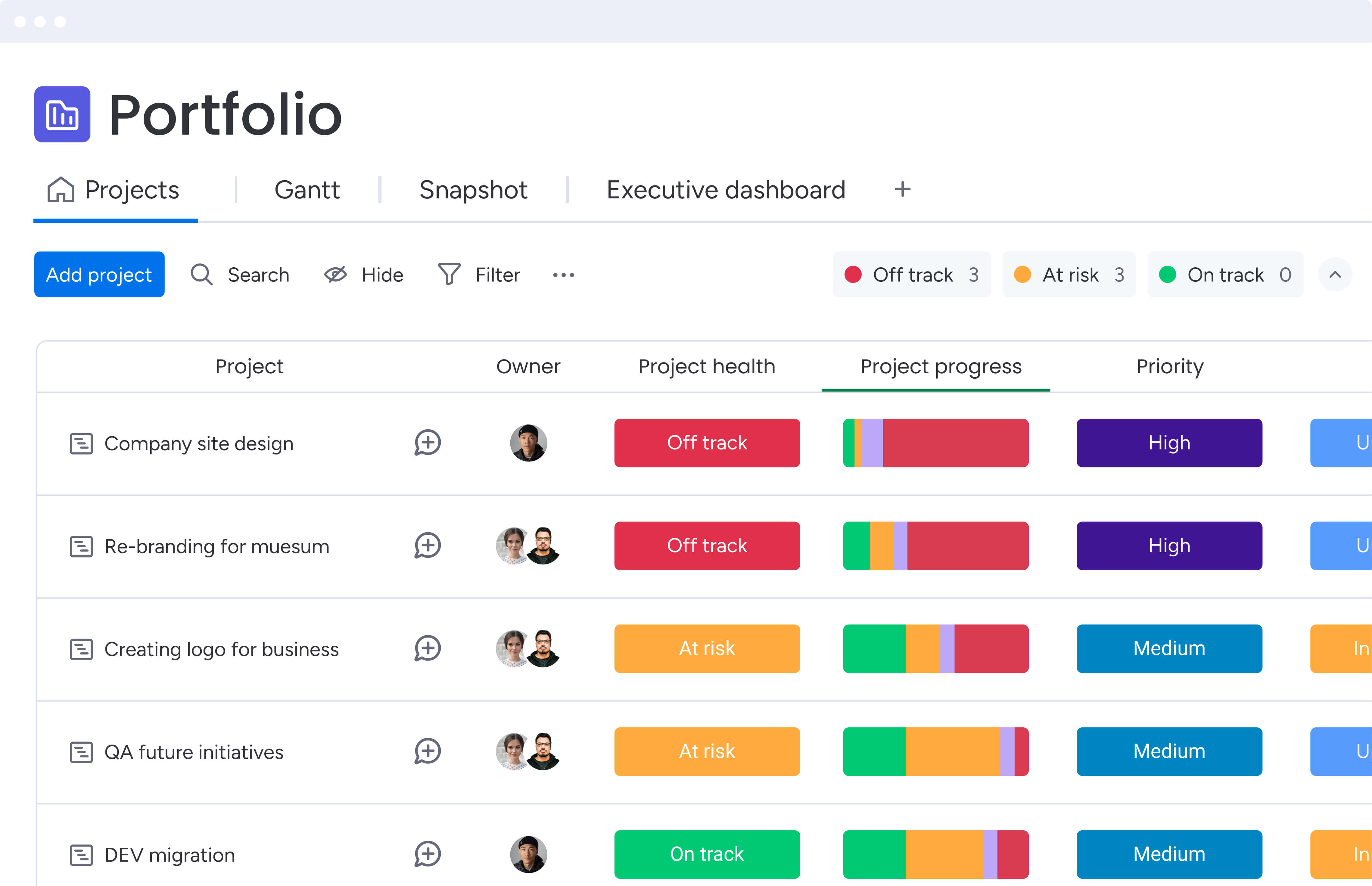
Pattern recognition across multiple concurrent projects reveals risks that individual project managers can’t see. AI detects when a single resource is becoming overallocated across several projects, when similar projects are competing for the same dependencies, or when organizational capacity is approaching limits.
This portfolio-level visibility prevents problems that emerge from the interaction between projects rather than within individual projects. The platform’s Portfolio Risk Insights continuously monitors project health and surfaces critical issues automatically.
Self-optimizing project workflows
AI learns from project execution data to suggest workflow improvements. When certain task sequences consistently create bottlenecks, or when specific approval processes regularly cause delays, AI identifies these patterns and recommends adjustments.
These insights drive continuous process improvement based on actual performance data rather than assumptions. Teams using monday work management benefit from AI Blocks that can categorize data, summarize updates, and extract actionable insights automatically.
Foster a project management culture that delivers consistent results
Creating sustainable project management excellence requires more than implementing individual practices — it demands building an organizational culture that values transparency, data-driven decisions, and continuous improvement. The most successful organizations embed these principles into their daily operations, prioritizing outcome achievement over process compliance while encouraging experimentation and learning from failures.
Transform these 12 best practices from abstract concepts into daily operational reality with monday work management. The platform’s Gantt charts, Kanban boards, and dependency tracking enable visual mapping and transparency, while cross-project dashboards surface resource allocation, budget utilization, and risk exposure without manual reporting overhead.
Try monday work managementFAQs
What are the 5 C's of project management?
The 5 Cs of project management are communication (ensuring information flow among stakeholders), collaboration (fostering teamwork across functions), coordination (aligning activities and resources), control (monitoring progress and managing changes), and closure (formally completing projects and capturing lessons learned).
What is the 80/20 rule for project managers?
The 80/20 rule in project management states that 80% of project outcomes typically result from 20% of the work. This suggests project managers should identify and prioritize the critical few activities that drive the most value rather than treating all tasks as equally important.
What are the 5 fundamentals of project management?
The 5 fundamentals of project management are objectives (defining what success looks like), realistic planning (creating achievable timelines and resource allocations), effective communication (keeping stakeholders informed and aligned), proactive risk management (identifying and mitigating potential issues), and continuous monitoring (tracking progress and adjusting as needed).
How do project management best practices differ from program management?
Project management best practices focus on delivering specific initiatives with defined scope and timelines. Program management practices coordinate multiple related projects to achieve strategic objectives, emphasizing portfolio-level resource allocation, dependency management across projects, and alignment with organizational strategy.
When should organizations review their project management practices?
Organizations should review project management practices annually as part of strategic planning, after completing major initiatives to capture lessons learned, when project success rates decline below acceptable levels, and when significant organizational changes alter how work gets done.
What are the 4 Ps of strategic project management?
The 4 Ps of strategic project management (SPM) are purpose (aligning projects with organizational strategy), people (ensuring the right skills and capacity), process (establishing efficient workflows and governance), and performance (measuring outcomes and driving continuous improvement).