Your company just hired 50 new employees across three departments, but six months later, turnover hits 30% and productivity lags behind projections. Meanwhile, your top performers feel overlooked, compliance training sits incomplete, and leadership keeps asking why workforce costs keep climbing without matching results.
This scenario plays out daily across organizations that treat people management as an administrative afterthought rather than a strategic advantage.
Human resource management represents the systematic approach to optimizing your workforce, from attracting and developing talent to creating cultures where both employees and businesses thrive. When done strategically, HRM transforms scattered people processes into coordinated systems that drive measurable business impact, reduce operational friction, and build competitive advantage through your most valuable asset.
Let’s dive into what strategic HR management actually does, unpack the seven core functions that drive real organizational value, and look at what’s changing the workforce management game heading into 2026. You’ll discover how to measure HRM effectiveness, develop essential skills for HR leadership, and see how integrated platforms can transform traditional people processes into strategic business operations.
Key takeaways
- Human resource management is a growth lever, not an admin function: modern HRM directly impacts retention, productivity, and competitive advantage by aligning people strategy with business goals.
- The seven core HRM functions work as a system: workforce planning, hiring, development, performance, compensation, engagement, and compliance must operate together to drive sustained organizational performance.
- Data-driven HR decisions outperform intuition: tracking metrics like time-to-productivity, turnover cost, and engagement correlation proves HR’s impact on revenue and operational efficiency.
- Future-ready HR teams are built for change: AI-enabled automation, continuous learning, workforce resilience, and DEIB integration are essential to attract and retain talent in 2026 and beyond.
- monday work management turns HR strategy into execution: centralized workflows, automation, and real-time dashboards help HR teams scale operations, reduce manual work, and focus on high-impact initiatives.
What is human resource management?
Human resource management (HRM) is the strategic approach organizations use to manage their workforce — from recruitment and onboarding through performance management, development, and retention. This means coordinating how you attract talent, develop skills, measure performance, and create workplace cultures where employees and businesses thrive together.
When a tech company slashes turnover by ten% through smart retention programs, that’s money in the bank. Same when a retail chain gets new store managers fully productive in 45 days instead of 90. That’s HRM delivering dollars and cents, not just shuffling papers.
Strategic HRM moves beyond transactional people management to become a driver of organizational success. When HR teams shift from manual, paper-based processes to integrated systems that provide real-time visibility into workforce data, they spend less time on administrative work and more time on strategic initiatives that create competitive advantage.
Defining HRM in today’s digital workplace
In 2026, the reality is that HR has evolved from filing cabinets and reactive problem-solving to data-powered workforce strategy that drives business outcomes. Today’s HRM leverages data analytics, intelligent automation, and centralized digital platforms to make informed decisions about every aspect of workforce management.
Traditional HR departments managed employee files, processed paperwork, and responded to issues as they arose. Strategic HRM proactively analyzes workforce patterns, predicts future needs, and implements strategies that align talent management with business objectives.
A centralized digital workspace allows HR teams to maintain real-time visibility into employee data across departments. They track performance metrics that matter to leadership and coordinate complex workflows spanning recruitment, onboarding, development, and retention.
Understanding the strategic evolution of human resources
Companies no longer see HR as just paperwork processors — they’re now strategic partners who directly impact the bottom line through smart people decisions. Personnel management treated employees as administrative concerns.
Strategic HRM recognizes that workforce decisions directly impact competitive advantage, innovation capacity, and financial performance.
This evolution positions HR professionals as business partners who contribute to strategic planning. When a company plans to enter a new market, strategic HRM identifies the talent requirements, develops acquisition strategies, and creates development programs that build necessary capabilities.
Cross-functional workflows elevate HRM’s strategic role even further. HR processes no longer exist in isolation — they connect with project management, financial planning, and operational execution.
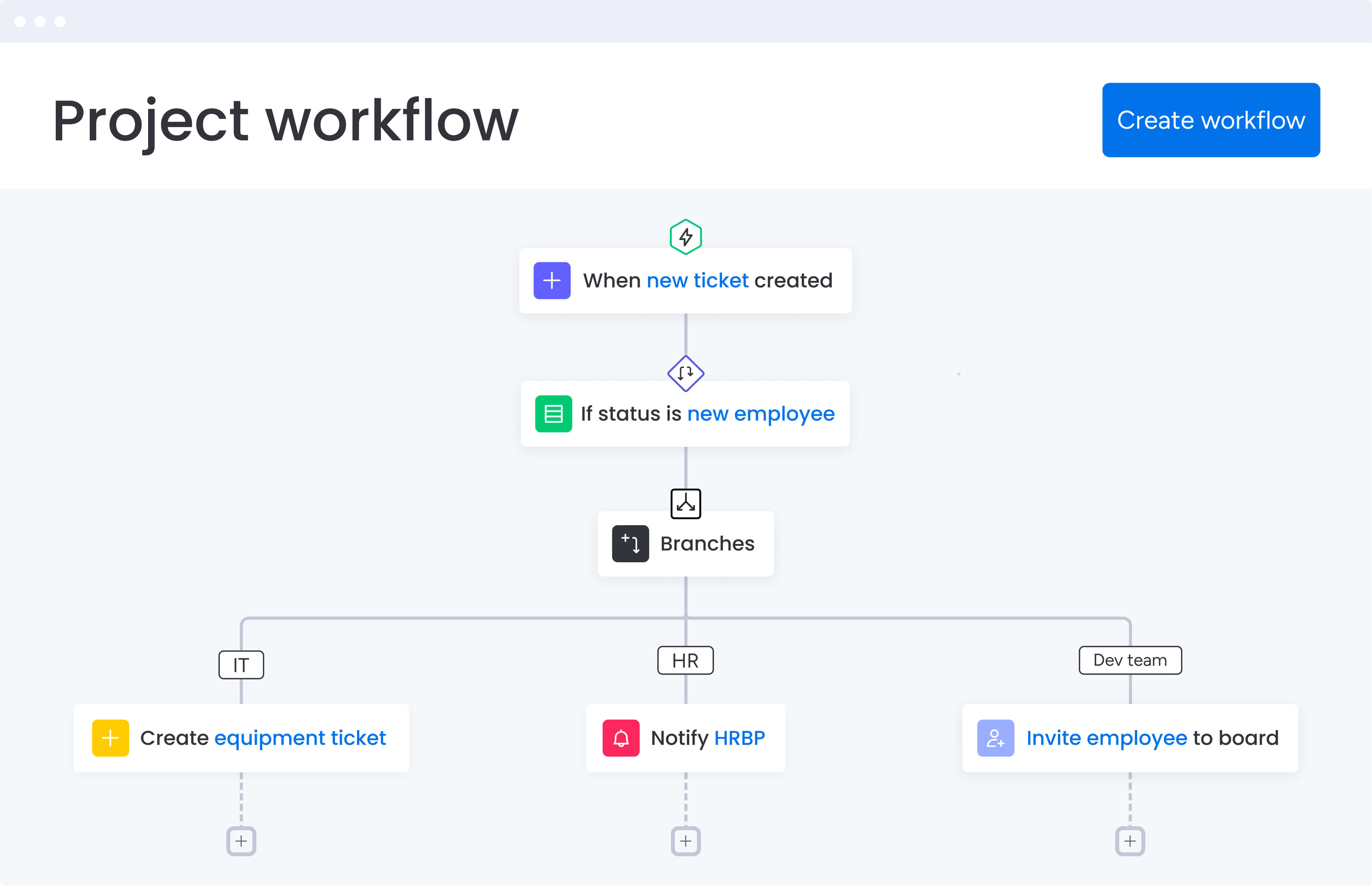
The 7 core functions of human resource management
Effective HRM encompasses seven interconnected functions that work together to optimize workforce performance and organizational success. These functions operate most effectively when integrated through unified systems that provide visibility and coordination across all HR activities.
Function 1: strategic workforce planning and analytics
Strategic workforce planning analyzes current workforce capabilities and predicts future talent needs based on business objectives, market conditions, and organizational strategy, functioning as a key component of enterprise resource management. This function examines skill inventories, succession risks, demographic trends, and capability gaps that could constrain business growth.
The process involves several key activities:
- Forecasting hiring needs: analyzing department and role requirements across time horizons.
- Identifying critical skills: determining capabilities that become more important as business evolves.
- Developing succession plans: ensuring leadership continuity through structured planning.
Data analytics transforms workforce planning from educated guessing to evidence-based strategy. Organizations track workforce metrics across departments, including turnover rates by role and manager, time-to-productivity for different positions, and skill gap analyses that reveal training needs.
Function 2: talent acquisition and recruitment
Talent acquisition encompasses the comprehensive process of attracting, sourcing, interviewing, and hiring qualified candidates who align with both role requirements and organizational culture. This function extends beyond posting job openings to include employer branding, candidate relationship management, and strategic sourcing that builds talent pipelines before positions become urgent.
AI and automation increasingly improve efficiency and reduce bias in recruitment:
- Automated screening: AI analyzes hundreds of applications in minutes, identifying candidates whose experience matches role requirements.
- Smart matching: systems compare applicant profiles against successful employees in similar roles.
- Workflow automation: interview scheduling, status updates, and candidate communications happen automatically.
Integrated systems track candidates from initial application through final offer, maintaining visibility into recruitment pipeline health and bottlenecks.
Teams using monday work management can categorize candidate applications by experience level, extract key qualifications from resumes, and automate interview scheduling workflows without manual intervention through HR requests automation.
Function 3: learning and development programs
Learning and development (L&D) represents the systematic approach to enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and capabilities to meet current job requirements while preparing for future roles. Effective L&D programs align individual growth with organizational needs, creating development paths that benefit both employees and the business.
The shift toward continuous learning reflects changing workforce expectations and accelerating skill obsolescence. L&D now emphasizes:
- Ongoing development: microlearning and personalized development plans replace annual training events.
- Just-in-time skill building: learning happens when employees need specific capabilities.
- Career pathway alignment: development connects to advancement opportunities.
Digital platforms enable tracking of training completion, skill assessments, and development progress across the organization through comprehensive HR service management systems. HR teams identify which employees have completed required compliance training, which teams show skill gaps in emerging technologies, and which individuals demonstrate readiness for advancement.
Function 4: performance management systems
Performance management encompasses the ongoing process of setting expectations, monitoring progress, providing feedback, and evaluating employee contributions to organizational goals. Contemporary approaches emphasize continuous feedback loops, transparent goal tracking, and development-focused conversations.
The transformation away from traditional annual reviews reflects research showing that infrequent, backward-looking evaluations do little to improve performance or engagement. Modern performance management includes:
- Regular feedback: employees receive ongoing input on their performance.
- Goal transparency: workers understand how their contributions connect to organizational objectives.
- Development focus: conversations emphasize growth and improvement opportunities.
Effective systems track both individual and team performance metrics, enabling data-driven decisions about promotions, compensation adjustments, and development needs. Organizations can connect individual performance goals to departmental objectives and organizational priorities, creating line of sight from daily work to strategic outcomes.
Function 5: compensation and benefits strategy
Compensation and benefits strategy encompasses the systematic approach to designing competitive, equitable, and motivating reward packages that attract and retain talent while managing costs effectively. This function balances multiple considerations simultaneously.
Key components include:
- Market analysis: understanding prevailing compensation for similar roles.
- Internal equity: ensuring fair pay for comparable work across departments.
- Performance differentiation: rewarding high contributors appropriately.
- Budget management: controlling costs while remaining competitive.
Integrated systems help track compensation data across the organization, identify pay equity gaps that require attention, and analyze the effectiveness of benefits programs through utilization rates and employee feedback, often supported by HR help desk software for employee inquiries.
Function 6: employee engagement and relations
Employee engagement represents the emotional commitment and connection employees have to their work, team, and organization. Employee relations encompasses the ongoing effort to maintain positive workplace relationships, resolve conflicts constructively, and foster communication between management and staff.
Engagement initiatives create measurable business impact through multiple channels:
- Recognition programs: celebrate contributions and reinforce desired behaviors.
- Communication channels: keep employees informed and heard.
- Team-building activities: strengthen relationships across departments.
- Conflict resolution: address workplace issues before they escalate.
The business impact appears in multiple metrics — engaged employees show higher productivity, improved customer service, lower absenteeism, and stronger retention. Research demonstrates that improving holistic employee health can generate $1,100–$3,500 in economic value per employee annually.
Function 7: compliance and risk management
Compliance and risk management ensures adherence to employment laws, regulations, and organizational policies while mitigating workforce-related risks. This function protects both the organization and its employees through proactive risk identification and mitigation strategies.
HR teams navigate compliance requirements across four critical areas:
- Equal employment opportunity: regulations governing fair hiring and treatment.
- Workplace safety: requirements for maintaining safe working conditions.
- Data privacy: laws protecting employee information and personal data.
- Wage and hour: regulations governing compensation and working time.
Organizations must maintain accurate records, conduct required training, and implement policies that demonstrate good-faith compliance efforts.
Try monday work managementHow human resource management transforms organizations
Effective HRM creates measurable business impact that extends far beyond administrative efficiency. Strategic HRM drives organizational transformation through people-centered approaches that optimize workforce performance, build competitive advantage, and create workplace cultures where employees and businesses thrive together.
Creating competitive advantage through people
Your competitors can copy your products and match your prices, but they can’t clone your people. Smart HRM builds teams that give you an edge no one can easily duplicate. While competitors can copy products, match prices, or adopt similar technologies, they cannot easily replicate an organization’s unique combination of talent, culture, and workforce capabilities.
The competitive impact appears in multiple forms:
- Faster time-to-market: effective team coordination and role definition eliminates confusion and delays.
- Improved customer service: engaged employees who care about outcomes deliver exceptional experiences.
- Accelerated innovation: diverse, well-developed teams bring varied perspectives to problem-solving.
- Rapid market response: strong HRM enables quick assessment of workforce implications and resource redeployment.
When organizations use monday work management to centralize HR processes through HR service management, they gain the agility to respond quickly to market changes. The platform enables teams to assess workforce implications, adjust hiring priorities, redeploy resources, and build new capabilities without starting from scratch.
Measuring HRM impact on business performance
HRM demonstrates business value through key performance indicators and metrics that connect people processes to organizational outcomes. The shift from measuring inputs to measuring outcomes reflects HRM’s evolution into strategic business partnership.
Important metrics that demonstrate HRM value include:
- Employee turnover costs: calculating the full cost of turnover reveals the financial impact of retention strategies.
- Time-to-productivity: measuring how quickly new employees reach full productivity quantifies onboarding effectiveness.
- Engagement correlation: analyzing the relationship between engagement scores and business metrics shows direct impact.
- Revenue per employee: tracking revenue generated per employee reveals workforce productivity trends.
- Training ROI: measuring performance improvements among trained employees quantifies development investments.
Organizations implementing comprehensive HRM metrics demonstrate to leadership exactly how workforce investments contribute to business performance, securing resources for strategic initiatives.
HRM vs traditional HR: the strategic difference
The leap from paper-pushing HR to strategic workforce management changes everything about how companies build and leverage their teams. Understanding this difference helps organizations assess their current HR maturity and identify opportunities to create greater business value.
Aspect Traditional HR Strategic HRM
Focus Administrative tasks and compliance checkbox completion Strategic business partnership and workforce optimization
Decision making Reactive, policy-based responses to problems Proactive, data-driven strategic planning
Metrics Activity-based tracking (hires completed, training hours) Outcome-based measurement (engagement, retention, performance)
Technology use Basic record-keeping systems Integrated analytics and automation platforms
Organizational role Support function handling employee issues Strategic partner contributing to competitive strategy
Employee relationship Transactional interactions Continuous engagement and development focus
As the table above implies, old-school HR waits for problems to happen, then scrambles to fix them. Strategic HRM gets ahead of issues, spots hidden opportunities, and builds systems that turn your workforce into a competitive weapon.
Essential skills every HR manager needs
Today’s best HR leaders blend deep people skills with sharp business sense and hands-on tech savvy. The most successful professionals develop a diverse skill set that enables them to navigate complex organizational challenges while driving strategic impact.
Keep in mind that these competencies work together to create HR leaders who can execute strategy, drive results, and build organizational capability.
Skill 1: digital and technical competencies
Technology skills have become essential for HR managers who must leverage HR information systems, data analytics platforms, and automation capabilities. HR professionals with strong technical competencies can fully leverage platforms to automate routine work and generate insights that drive strategic decisions.
Key digital competencies include:
- Data analysis: interpreting workforce metrics and creating actionable insights from employee data.
- Platform management: configuring workflows, customizing dashboards, and troubleshooting system issues.
- Process automation: identifying repetitive processes and implementing automated solutions.
- Digital communication: facilitating remote collaboration and virtual employee engagement.
Teams using monday work management can build these competencies while working, as the platform’s intuitive interface makes it easy to create automated workflows, analyze workforce data, and maintain engagement across distributed teams.
Skill 2: strategic business partnership
HR managers must understand business operations, financial impact, and organizational strategy to serve as effective business partners. This requires moving beyond HR functional expertise to develop broader business acumen.
Strategic partnership capabilities encompass several areas:
- Financial acumen: understanding budgets, ROI calculations, and cost-benefit analysis.
- Strategic thinking: connecting workforce planning to business goals and market conditions.
- Cross-functional collaboration: understanding how different departments operate and contribute to organizational success.
These skills enable HR managers to speak the language of business and demonstrate HR’s financial impact through data-driven insights and strategic recommendations.
Skill 3: data-driven decision making
HR managers must collect, analyze, and act on workforce data to make informed decisions. The shift from intuition-based to evidence-based HR practices reflects broader organizational expectations for data-driven decision making.
Essential capabilities for data-driven HR include:
- Metrics identification: selecting relevant KPIs that align with business objectives.
- Trend analysis: identifying patterns in employee data to predict future needs.
- Predictive analytics: using data to forecast turnover, performance, and workforce requirements.
- Reporting and visualization: presenting data insights in formats that drive action.

5 game-changing HRM trends for 2026
HRM continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing workforce expectations, and new business challenges. Organizations must adapt to these trends to remain competitive in attracting talent, engaging employees, and building workforce capabilities.
Trend 1: AI and automation revolution in HR
Artificial intelligence and automation are transforming every aspect of HRM, from recruitment to performance management. AI capabilities that seemed futuristic just years ago now represent practical solutions that HR teams use daily, with current adoption showing 35% of core HR processes in the United States already using generative AI in operational settings.
Key AI applications in HRM include:
- Automated candidate screening: evaluating applications in minutes rather than hours.
- Predictive analytics: identifying turnover risk patterns before employees leave.
- Intelligent workflow automation: adapting processes based on context and data.
- Sentiment analysis: revealing patterns in employee feedback and communication.
Organizations leveraging monday work management can access AI capabilities that categorize employee data automatically, extract insights from documents like performance reviews, and automate routine processes that previously consumed significant time.
Trend 2: building workforce resilience and agility
Companies that can’t adapt quickly when markets shift are getting left behind. That’s why building resilient teams has become non-negotiable for survival. The ability to adapt quickly to disruptions and changing business conditions has become essential for long-term success.
Resilience-building approaches include:
- Flexible workforce models: supporting remote and hybrid arrangements that adapt to changing conditions.
- Skill diversification: developing capabilities across multiple areas to reduce dependency risks.
- Rapid deployment systems: reassigning resources quickly when priorities shift.
- Continuous learning programs: building adaptive capacity through ongoing skill development.
Trend 3: DEIB as business imperative
Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging (DEIB) has evolved from a compliance requirement to a strategic business priority. Research consistently shows that diverse teams make improved decisions, create more innovative solutions, and achieve stronger financial performance.
DEIB initiatives focus on:
- Inclusive recruitment: removing bias from hiring processes to attract diverse talent.
- Equitable development: ensuring all employees have growth opportunities regardless of background.
- Belonging initiatives: creating workplace cultures where everyone feels valued and included.
- Accountability systems: tracking DEIB metrics and holding leaders responsible for progress.
Trend 4: sustainability and ESG in HR strategy
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are becoming integral to HR strategy. Investors, customers, and employees increasingly evaluate organizations based on ESG performance, making this a competitive differentiator.
ESG-related HR initiatives include:
- Sustainable workplace practices: reducing environmental impact through remote work and green office policies.
- Social responsibility programs: supporting community engagement and social impact initiatives.
- Governance structures: ensuring transparent workforce management and ethical decision-making.
- Employee wellbeing priorities: focusing on mental health and work-life balance as core values.
Trend 5: continuous learning ecosystems
Organizations are moving beyond traditional training programs to create comprehensive learning ecosystems that support ongoing skill development. This shift reflects accelerating skill obsolescence and changing employee expectations about development opportunities.
Learning ecosystem components include:
- Microlearning platforms: delivering bite-sized content that fits into busy schedules.
- Peer-to-peer learning: facilitating knowledge sharing between employees.
- AI-powered personalization: customizing learning paths based on individual needs and goals.
- Integration with work processes: embedding learning directly into daily activities and workflows.
Transform your HRM with monday work management
Organizations using monday work management transform traditional HR processes into strategic, data-driven operations.
The platform addresses core HRM challenges — fragmented systems, manual processes, limited visibility, and disconnected workflows — while maintaining enterprise-grade security that protects sensitive employee data, functioning as comprehensive HR help desk software.
By leveraging the platform, teams move beyond disconnected spreadsheets and email chains that create administrative burden and obscure strategic insights.
Automate essential HR workflows
monday work management’s automation capabilities transform routine HR work into efficient, error-free processes. HR teams create custom automations for recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and compliance tracking without technical expertise.
Practical automation applications include:
- Recruitment automation: automate the hiring process so candidates move through stages automatically, triggering interview reminders and background checks via [HR requests automation].(https://monday.com/blog/service/hr-requests-automation/).
- Onboarding workflows: new hire approval triggers equipment requests, training assignments, and orientation scheduling.
- Performance management: regular check-ins schedule automatically with feedback compilation from multiple stakeholders.
- Compliance tracking: certification expirations and training renewals trigger automatic reminders before deadlines.
AI Blocks enhance these automations by adding intelligent capabilities. The platform categorizes candidate applications by qualifications, extracts key information from resumes, analyzes employee feedback sentiment, and generates summaries of performance review comments.
Connect HR across your organization
monday work management breaks down silos between HR and other departments by creating integrated workflows that connect workforce management with business operations.
Integration capabilities enable:
- Cross-departmental project management: HR initiatives connect with business projects for unified execution.
- Resource allocation coordination: employee skills and availability become visible to project managers.
- Goal alignment tracking: individual performance links to organizational priorities.
- Communication centralization: all HR-related discussions exist in one accessible location.
Drive decisions with real-time HR analytics
The platform’s dashboard and reporting capabilities provide HR teams with data insights needed to make strategic decisions and demonstrate business value.
Analytics capabilities include:
- Workforce metrics tracking: key HR KPIs appear in real-time dashboards.
- Predictive analytics: patterns identify future workforce needs and risks.
- Performance visualization: employee achievement and development progress display clearly.
- Compliance reporting: automated reports generate for regulatory requirements.

Building the future of work through strategic HRM
Smart people management isn’t just nice to have anymore — it’s the bedrock of success in a business world that’s more unpredictable than ever. Organizations that embrace HRM as a strategic function — rather than an administrative necessity — position themselves to attract top talent, build resilient cultures, and adapt quickly to market changes.
The transformation requires more than good intentions or policy updates. It demands integrated systems that connect people processes to business outcomes, data-driven insights that inform strategic decisions, and automation that frees HR professionals to focus on high-value activities that drive competitive advantage.
Organizations using monday work management gain the operational foundation needed to execute strategic HRM at scale. Get started today.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com‘s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.
Frequently asked questions
What are the 7 main functions of human resource management?
The seven main functions of human resource management are strategic workforce planning and analytics, talent acquisition and recruitment, learning and development programs, performance management systems, compensation and benefits strategy, employee engagement and relations, and compliance and risk management. These functions work together to optimize workforce performance and organizational success.
How is HRM different from traditional HR departments?
HRM differs from traditional HR by focusing on strategic business partnership rather than administrative tasks, using data-driven decision making instead of reactive responses, and measuring business impact rather than activity completion. Strategic HRM proactively analyzes workforce patterns and implements strategies that align talent management with business objectives.
What skills do you need for successful human resource management?
Successful human resource management requires digital competencies for managing HR technology and data analytics, strategic business partnership skills to align workforce planning with organizational goals, and data-driven decision-making abilities. HR managers must also develop financial acumen and cross-functional collaboration capabilities.
How can organizations measure HRM effectiveness?
Organizations measure HRM effectiveness through key performance indicators such as employee turnover rates, time-to-hire, employee engagement scores, training ROI, and revenue per employee. These metrics connect people processes to organizational outcomes and demonstrate how workforce investments contribute to business performance.
What role does technology play in HRM?
Technology enables HRM to automate routine processes, analyze workforce data for strategic insights, and create integrated workflows that connect HR with other business functions. Modern HRM leverages data analytics, intelligent automation, and centralized digital platforms to make informed decisions about workforce management.
What are the biggest trends shaping HRM in 2026?
The biggest HRM trends for 2026 include AI and automation in HR processes, building workforce resilience and agility, implementing DEIB as a business imperative, integrating sustainability and ESG considerations, and creating continuous learning ecosystems. These trends reflect technological advancement, changing workforce expectations, and new business challenges.
 Get started
Get started


