Imagine transforming a high-stakes client conference from a logistical puzzle into a strategic masterpiece. In just six months, you could be orchestrating an event for 500+ attendees that not only generates qualified leads for sales but also delivers major brand impact and measurable ROI. This is the power of strategic event management.
Event management transforms complex coordination challenges into structured, measurable business outcomes. It’s the strategic discipline that connects initial planning through post-event analysis, ensuring every activity aligns with organizational objectives. Unlike basic party planning, it requires systematic coordination across multiple workstreams, vendor relationships, and success metrics that prove business value.
This guide covers everything from defining measurable objectives to selecting the right venues. You’ll discover the seven essential planning stages, proven strategies for managing complex stakeholder relationships, and how to build scalable event operations that consistently deliver results.
Key takeaways
- Treat events as strategic growth engines, not one-off projects: modern event management connects planning, execution, and measurement to clear business goals like pipeline growth, customer retention, and brand authority.
- Follow a structured, seven-stage framework to reduce risk: defining objectives early, coordinating vendors centrally, and closing the loop with post-event analysis ensures consistent, repeatable success.
- Centralize event operations to eliminate chaos at scale: managing timelines, budgets, vendors, and stakeholders in one system prevents missed details, conflicting updates, and last-minute firefighting.
- Standardize processes while staying flexible: reusable templates, workflows, and checklists improve efficiency across events while still allowing customization for different formats, audiences, and objectives.
- Use monday work management to scale with confidence: unified dashboards, automation, and AI-powered risk insights give teams real-time visibility across multiple events, helping them deliver measurable ROI without added complexity.
What is event management?
At its core, event management brings order to chaos — it’s the discipline of turning complex logistics into business wins by coordinating everything from initial planning to final analysis. It encompasses the complete lifecycle from initial concept development through post-event measurement, involving budget oversight, vendor coordination, stakeholder communication, risk mitigation, and performance analysis.
Forget party planning — event management demands strategic thinking that connects every activity to business goals, juggles competing stakeholder needs, and keeps multiple moving parts in sync.
The discipline covers everything from setting measurable objectives and developing detailed project plans to coordinating vendors, managing budgets, and analyzing results.
Event managers oversee venue selection, technology integration, marketing campaigns, attendee experience design, and financial control. They maintain communication with executives, team members, and external partners throughout the event lifecycle.
Event management vs event planning
While often used interchangeably, event planning and event management serve distinct functions within the event lifecycle. Understanding these differences helps organizations assign the right responsibilities and set appropriate expectations for each role.
Aspect Event planning Event management
Scope Tactical execution of specific event elements Strategic oversight of entire event lifecycle and portfolio
Timeline Focuses on pre-event and day-of activities Spans from initial concept through post-event analysis
Strategic focus Implements predetermined plans and logistics Defines objectives, measures ROI, aligns with business strategy
Stakeholder involvement Coordinates with vendors and operational teams Manages executive relationships and cross-departmental collaboration
Decision authority Executes within established parameters Makes strategic decisions about format, budget, and objectives
It’s important to note that event planning functions as a critical subset of event management.
Planners handle the detailed logistics, including venue setup, catering coordination, and registration management. On the other hand, event managers maintain strategic oversight, connect event activities to business outcomes, and build long-term relationships that support organizational goals beyond individual events.
How event management drives business success
Strategic event management delivers measurable impact across revenue, relationships, and brand visibility. Trade shows generate qualified leads, conferences strengthen customer loyalty, and product launches create concentrated market momentum.
When events are aligned to business goals, they move deals forward, deepen relationships, and improve ROI — turning events from one-off costs into repeatable growth assets.
Core components of event management
Successful event management rests on four foundational pillars that work together to transform strategic vision into executed reality. Each component plays a distinct role while interconnecting with the others to create cohesive event operations:
Pillar 1: strategic planning and organization
Strategic planning isn’t just paperwork — it’s your roadmap that keeps every decision aligned with what actually matters. This component involves defining objectives that align with business goals, identifying target audiences and their needs, establishing success metrics that measure real impact, and developing comprehensive timelines that account for dependencies across workstreams.
Strategic decisions include choosing between virtual, hybrid, or in-person formats based on audience preferences and business objectives. Teams must determine the right event scale and scope to achieve goals within budget constraints. Mapping the attendee journey from initial awareness through post-event follow-up ensures each interaction supports overall objectives.
Component 2: budget and financial control
Financial management encompasses budget creation, real-time cost tracking, and ROI measurement throughout the event lifecycle. Comprehensive budgets account for all major categories while maintaining flexibility to adjust as circumstances change.
A typical corporate conference allocates resources across several key areas:
- Venue and catering: 30% of total budget.
- Marketing and promotion: 25% of total budget.
- Technology and production: 20% of total budget.
- Staff and operations: 15% of total budget.
- Contingency reserves: ten% of total budget.
Real-time financial tracking prevents cost overruns by identifying budget variances early enough to take corrective action. Effective financial control means knowing exactly where money goes, comparing actual spending against projections, and demonstrating return on investment to stakeholders who approve event budgets.
Component 3: vendor and stakeholder coordination
Managing multiple relationships simultaneously requires structured communication channels and centralized coordination systems. Event managers coordinate with diverse vendor types, including venues, caterers, AV providers, marketing agencies, and transportation providers. They also maintain alignment with internal stakeholders such as executives, marketing teams, operations staff, and sales leadership.
Each relationship involves distinct communication needs, approval processes, and coordination requirements. Successful coordination depends on:
- Defined communication protocols: regular check-ins and status updates.
- Centralized vendor information: contact details, contracts, and deliverables in one place.
- Defined approval workflows: establish who signs off on what and when.
- Accountability tracking: ensuring commitments are met on schedule.
Component 4: technology and digital infrastructure
Events require integrated technology stacks that support registration management, attendee communication, live streaming, data collection, and performance analysis. The technology infrastructure affects both operational efficiency and attendee experience quality.
Essential technology components include:
- Registration systems: capture attendee data and process payments.
- Event apps: facilitate networking and engagement.
- Communication platforms: maintain stakeholder alignment.
- Analytics capabilities: measure event performance and attendee behavior.
When your tech stack is fully integrated, you get the insights you need in real time, enabling data-driven decisions about event performance and attendee engagement.
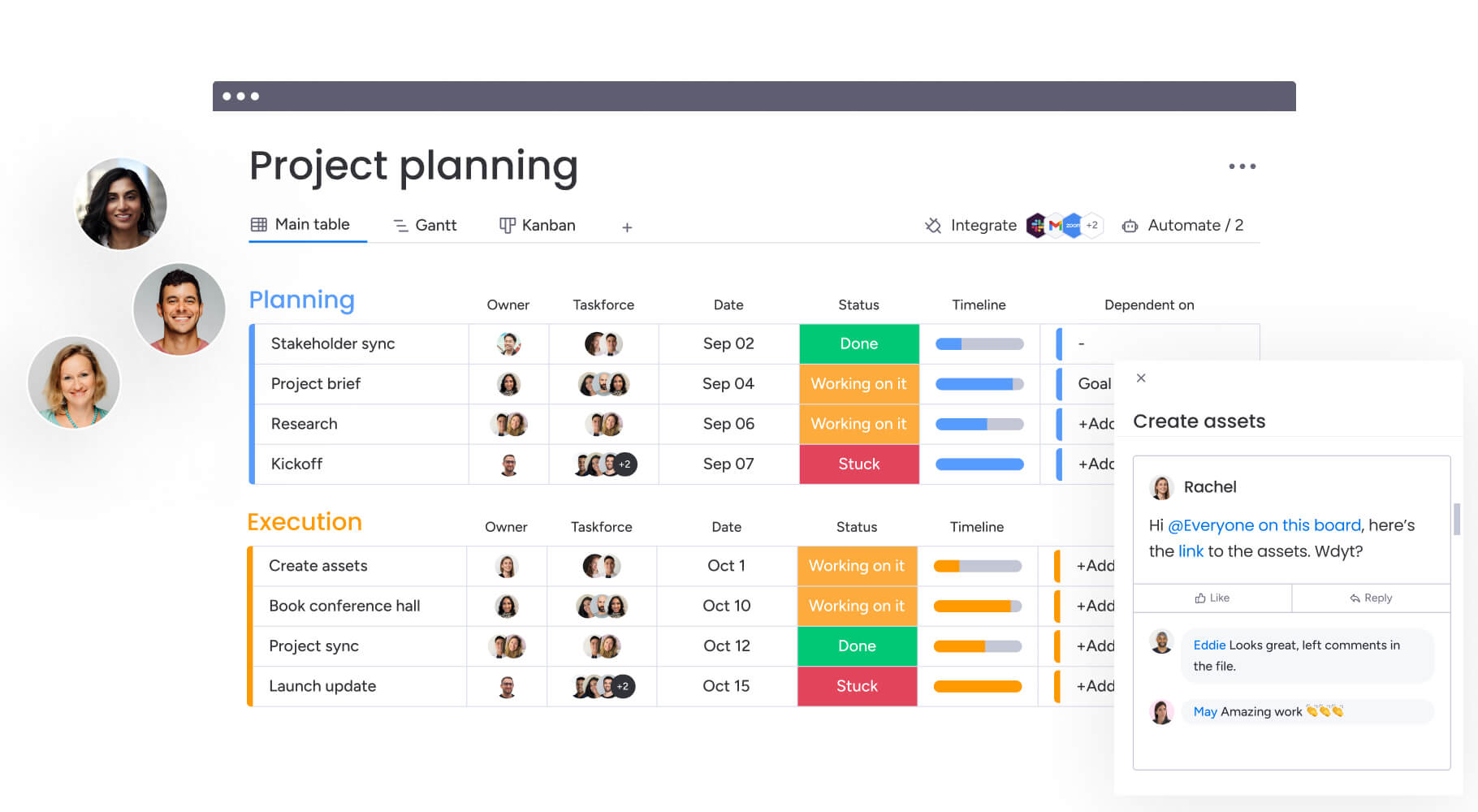
Try monday work managementThe 7 essential stages of event planning
The event planning framework provides a sequential roadmap that guides event managers from initial concept through final analysis. Each stage builds upon previous work while often overlapping with other stages as events progress from planning to execution.
Following this structured approach ensures nothing gets overlooked while maintaining flexibility for event-specific requirements.
Step 1: define objectives and set measurable goals
Your objectives aren’t just checkboxes — they’re the foundation that shapes every planning decision and ultimately determine if your event succeeded. Effective objectives align with broader business goals while remaining specific enough to guide tactical decisions.
Setting the right objectives requires balancing qualitative and quantitative targets:
- Qualitative goals: strengthening brand awareness, building industry relationships, positioning as thought leader.
- Quantitative goals: generating specific number of qualified leads, achieving target satisfaction scores, securing pipeline opportunities.
SMART goal frameworks ensure objectives are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This structured approach transforms vague aspirations into actionable targets that guide every planning decision.
Stage 2: design the event experience and format
Experience design is where strategy gets real — turning your objectives into formats that work and creating paths that guide attendees from start to finish. Format selection depends on audience preferences, business objectives, and budget parameters. Options include conferences, workshops, networking events, or hybrid experiences.
Agenda development requires careful balance between educational content that delivers value, networking opportunities that build relationships, and business activities that advance organizational goals. Attendee journey mapping identifies every touchpoint from initial invitation through post-event follow-up, ensuring each interaction supports overall objectives.
Key design considerations include:
- Audience segmentation: different groups with varying needs and interests.
- Accessibility requirements: ensuring inclusive participation for all attendees.
- Technology integration: enhancing rather than complicating the experience.
- Content variety: mixing formats to maintain engagement throughout.
Stage 3: select venues and secure vendors
Systematic venue selection evaluates options against capacity requirements, location accessibility, technology capabilities, and budget constraints. The evaluation process includes developing detailed RFPs that specify requirements, conducting site visits that assess actual conditions, and comparing proposals using weighted criteria that reflect priorities.
Vendor evaluation extends beyond venues to include caterers, AV providers, transportation companies, and specialized service providers. Contract negotiation covers critical terms including:
- Cancellation policies: protection against unforeseen circumstances.
- Force majeure clauses: coverage for events beyond control.
- Setup and breakdown times: operational scheduling requirements.
- Catering minimums: food and beverage commitments.
- Technology specifications: equipment and support requirements.
Backup plans account for potential vendor failures or last-minute changes. Centralized vendor information management improves coordination by maintaining contact details, contract terms, payment schedules, and communication history in accessible systems.
Stage 4: launch marketing and promotion campaigns
Integrated marketing campaigns drive registration and build anticipation through multiple channels working in concert. Channel selection depends on audience behavior — email works for direct outreach, social media for community building, partnerships for expanded reach, and paid advertising for targeted awareness.
Effective campaign elements include:
- Compelling event descriptions: value propositions that resonate with target audiences.
- Speaker profiles: highlighting expertise and drawing power.
- Agenda highlights: key sessions and networking opportunities.
- Social proof: testimonials from past attendees.
Timeline management ensures marketing activities build momentum through early awareness campaigns, registration push periods, and final reminder sequences. Consistent messaging across all touchpoints reinforces value propositions and maintains brand alignment.
Stage 5: manage registration and attendee communication
Registration process design balances information collection needs with user experience simplicity. Optimized registration forms capture essential data without creating friction that reduces completion rates. Payment processing integration enables smooth transactions while maintaining security standards.
Ongoing attendee communication maintains engagement throughout the pre-event period:
- Pre-event information: logistics, agenda updates, preparation tips.
- Reminder sequences: reducing no-shows through timely notifications.
- Expectation setting: aligning attendee preparation with event format.
- Special request handling: dietary restrictions, accessibility needs, accommodation preferences.
Stage 6: execute the event with precision
Day-of-event operations require meticulous coordination across multiple workstreams and real-time problem-solving when unexpected challenges arise. Setup coordination ensures all elements are in place before attendees arrive, from technology testing to signage placement.
Staff briefings align team members on roles, responsibilities, and communication protocols. Decision-making hierarchies enable quick responses to issues without bottlenecks. Contingency plan activation addresses problems ranging from technology failures to weather disruptions.
Real-time monitoring tracks attendee satisfaction and engagement levels, enabling immediate adjustments to improve experience quality. Successful execution means attendees experience seamless events while behind-the-scenes teams manage complexity that remains invisible to participants.
Stage 7: analyze results and gather insights
Comprehensive post-event analysis combines quantitative metrics with qualitative feedback to provide complete pictures of event performance and improvement opportunities. Analysis components include:
- Quantitative metrics: attendance numbers, engagement levels, lead generation results, financial performance.
- Qualitative feedback: attendee surveys, stakeholder input, team debriefs.
- ROI calculation: connecting costs to measurable business outcomes.
- Improvement identification: what worked well and what needs adjustment.
Documentation captures lessons learned, updates standard processes based on new insights, and creates institutional knowledge that improves future event planning. This continuous improvement cycle ensures each event builds on previous successes while addressing identified gaps.
Types of events in modern business
Each event type needs its own playbook, but the fundamentals of solid event management still apply across the board. Understanding type-specific characteristics helps event managers allocate resources appropriately and set realistic expectations.
Corporate events and professional conferences
Corporate events are company-sponsored gatherings designed to achieve specific business objectives through structured programming and strategic attendee selection. These events typically involve multiple stakeholder groups — executives set strategic direction, sales teams leverage networking opportunities, marketing teams manage brand presentation, and operations teams handle logistics.
Common corporate event types include:
- Annual shareholder meetings: fulfilling governance requirements.
- Product launches: generating market awareness and excitement.
- Customer conferences: strengthening relationships and gathering feedback.
- Industry summits: positioning organizations as thought leaders.
Budget considerations reflect the strategic importance and expected ROI, with larger conferences often representing significant investments. Success metrics focus on business outcomes like pipeline generated, partnerships formed, and brand perception shifts rather than just attendee satisfaction scores.
Virtual and hybrid event formats
Digital transformation has expanded event possibilities beyond traditional in-person gatherings, creating new opportunities to reach broader audiences while reducing costs and environmental impact.
Virtual events occur entirely online through platforms that support live streaming, interactive sessions, and digital networking. Hybrid events combine in-person and virtual elements, allowing remote participation while maintaining face-to-face interaction benefits.
Technology is the backbone of any successful digital event. Key requirements include platforms that have these essential components:
- Reliable streaming platforms: must support thousands of concurrent viewers without interruption.
- Engagement features: tools like polls, Q&A, and chat are critical for maintaining audience attention.
- Digital networking capabilities: virtual breakout rooms or one-on-one meeting schedulers facilitate valuable connections.
- Content accessibility: all content should be available on-demand through accessible event planning software.
Engagement strategies differ from in-person events. Shorter session lengths combat screen fatigue, interactive elements maintain attention, and on-demand content extends event value. These formats reduce travel costs and carbon footprints while potentially reaching significantly more attendees than venue capacity allows.
Trade shows and industry exhibitions
Trade shows are B2B marketing events where companies showcase products to industry audiences actively looking for solutions. Effective management focuses on attention-grabbing booth design, efficient lead capture, and competitor awareness that sharpens positioning.
Success depends on strong pre-event promotion, engaging on-site conversations, and disciplined post-event follow-up. Performance is measured by lead quality, cost per lead, and pipeline impact — not just booth traffic or brand visibility.

Critical event management skills for success
Event management excellence in 2026 requires diverse capabilities that combine project management discipline, creative problem-solving, and interpersonal effectiveness.
Developing these skills below enables event managers to handle complexity while maintaining focus on strategic objectives.
Remember, the most successful event managers master both technical competencies and soft skills that enable effective collaboration across diverse stakeholder groups.
Skill 1: project management and organizational excellence
Project management principles provide the structural foundation for successful event execution. Scope definition establishes boundaries around what the event will and won’t include, preventing scope creep that derails timelines and budgets. Timeline management involves identifying critical paths, building in buffer time for unexpected delays, and maintaining visibility into dependencies.
Resource allocation ensures the right people work on appropriate activities based on skills and availability. Risk mitigation identifies potential problems early and develops contingency plans before issues become critical. Effective project management means maintaining control over complex coordination while remaining flexible enough to adjust when circumstances change.
Skill 2: communication and stakeholder engagement
Managing diverse stakeholder groups requires tailoring communication approaches to different audiences and priorities.
Written communication includes emails that drive action, comprehensive proposals that secure approvals, and detailed reports that demonstrate value. Verbal communication encompasses persuasive presentations that gain buy-in, effective negotiations that achieve favorable terms, and calm crisis management that maintains confidence during problems.
Different stakeholders need different information at different frequencies:
- Executives: high-level progress updates and strategic alignment.
- Operational teams: detailed coordination information and timelines.
- Vendors: specific requirements and delivery expectations.
- Attendees: event details and engagement opportunities.
Skill 3: technology proficiency and digital fluency
Event management requires comfort with diverse technology platforms and the ability to evaluate new capabilities quickly. Essential platforms include registration systems that capture attendee data, project management solutions that coordinate activities, communication platforms that maintain alignment, and analytics capabilities that measure performance.
Emerging technologies continue transforming event capabilities:
- AI-powered insights: predict attendance patterns and optimize resource allocation.
- Automation workflows: reduce manual tasks and ensure consistency.
- Virtual reality experiences: create immersive engagement opportunities.
Technology proficiency enables more efficient operations, improved attendee experiences, and data-driven decision-making that improves event outcomes over time.
How to use technology and AI for event success
Technology has transformed event management from manual, paper-based processes into integrated digital ecosystems that improve efficiency, enhance experiences, and enable data-driven decision-making. Modern platforms solve real coordination challenges while providing capabilities that weren’t possible with traditional approaches. Organizations that leverage these technologies gain significant competitive advantages in event execution and attendee satisfaction.
Solution 1: comprehensive event management platforms
Integrated platforms centralize event management activities in unified systems that eliminate fragmentation and improve coordination. Having all event data in one place improves decision-making by connecting information across workstreams, reduces manual work by eliminating duplicate data entry, and increases accuracy by maintaining single sources of truth.
Key platform capabilities include:
- Registration management: capturing attendee data and processing payments.
- Attendee communication: maintaining engagement throughout event lifecycle.
- Vendor coordination: tracking contracts, deliverables, and payments.
- Reporting dashboards: providing real-time visibility into event progress.
Teams coordinate more effectively when everyone works from the same information rather than maintaining separate spreadsheets and email threads.
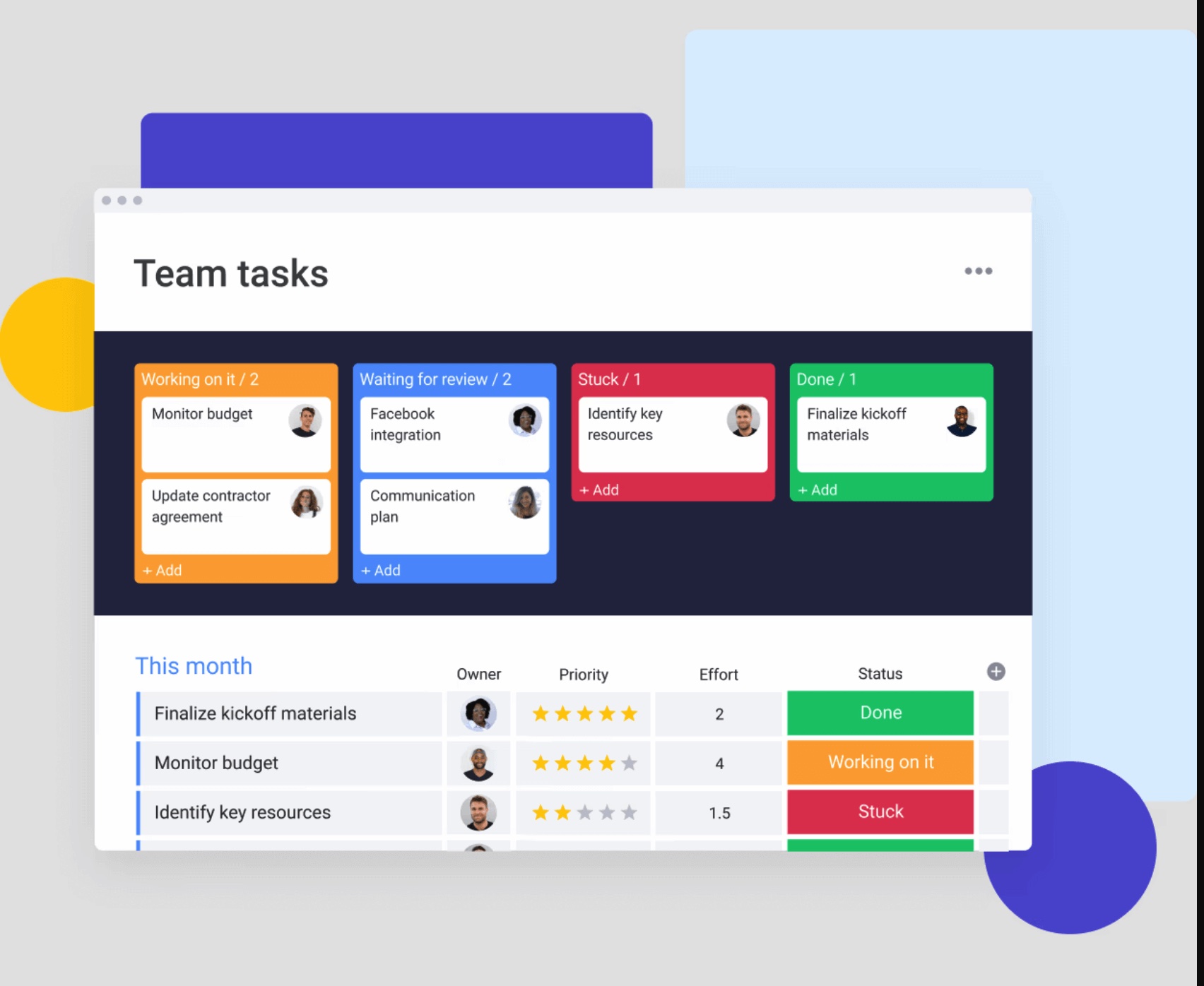
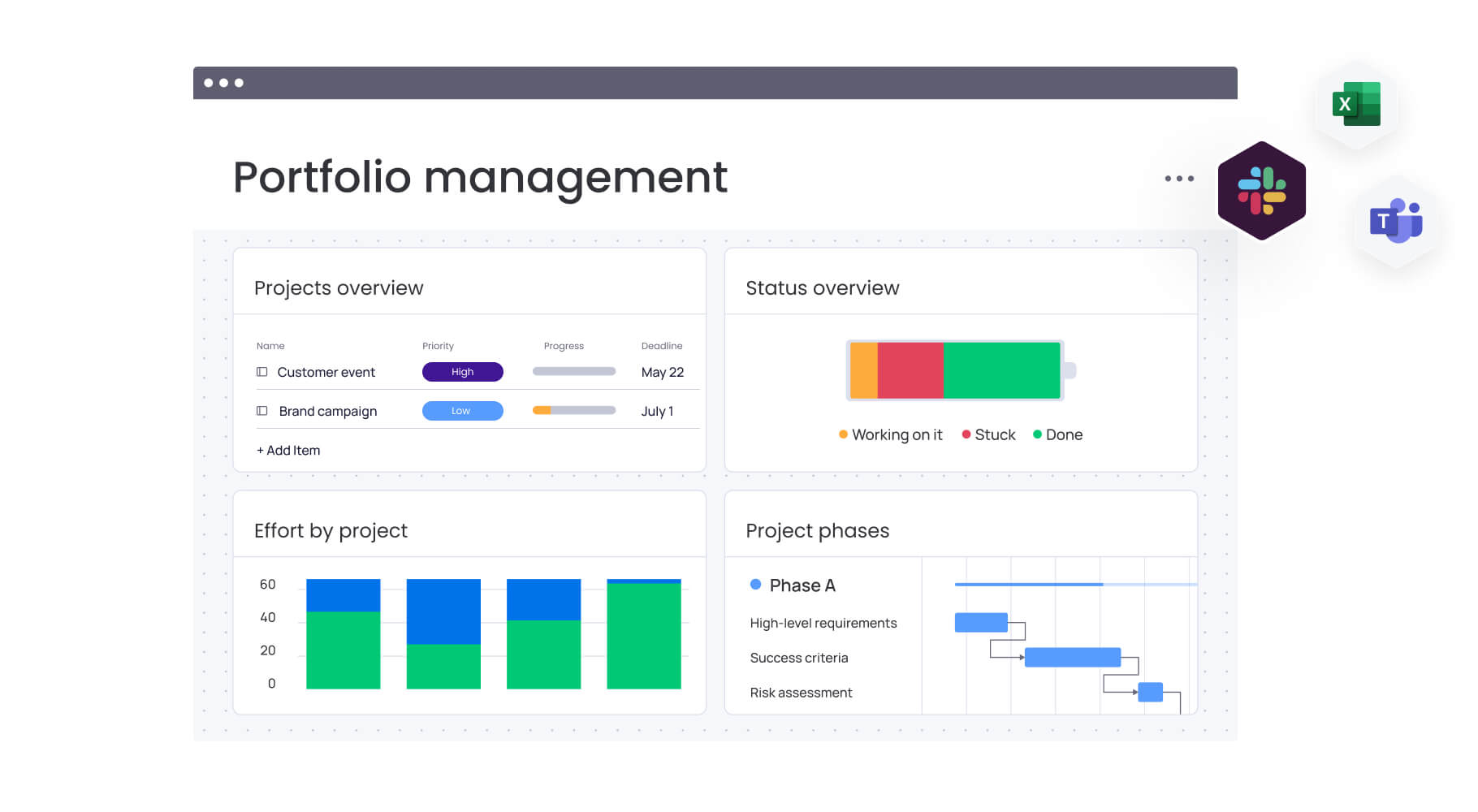
Intelligent platforms like monday work management support this approach by bringing together project planning, resource allocation, and performance tracking in one customizable workspace.
Solution 2: AI for portfolio risk and resource optimization
AI spots patterns humans miss — like when three events are competing for the same resources or when your budget is trending toward trouble across multiple projects. Practical AI applications in event management include predicting attendance patterns based on historical data and market conditions, identifying budget overruns before they become critical by analyzing spending trends, and flagging potential scheduling conflicts across event portfolios.
AI-powered insights help event managers make proactive decisions rather than reactive adjustments. For organizations managing multiple simultaneous events, AI becomes essential for maintaining comprehensive visibility.
The Portfolio Risk Insights feature on monday work management analyzes patterns across event portfolios to surface risks like resource overallocation, timeline compression, or budget variance — a capability that is particularly valuable when manual oversight cannot track every detail.
Solution 3: automation for workflow efficiency
Automation reduces manual activities and ensures consistency across events by handling repetitive processes without human intervention. Automated workflows can manage email sequences that nurture registrants from initial sign-up through post-event follow-up, approval workflows that route budget requests and contract reviews to appropriate stakeholders, and assignment triggers based on event milestones.
Reminder systems reduce no-shows while freeing event managers to focus on strategic activities and creative problem-solving. Automation also reduces human error in routine processes, ensuring consistent execution across multiple events. When integrated into platforms like monday work management, these automations become part of the natural workflow rather than separate systems to manage.
8 proven strategies for event management success
These strategies aren’t theoretical — they’re the difference-makers that top event teams rely on when deadlines loom and stakeholders get anxious. Each strategy contributes to overall event excellence while supporting the others. Implementing these strategies systematically creates a foundation for scalable event management operations that deliver measurable business results.
Strategy 1: establish objectives with measurable KPIs
Translating business goals into specific, measurable event objectives provides the foundation for all planning decisions and success measurement. Lead generation events might target specific numbers of qualified leads meeting defined qualification criteria. Brand awareness events could aim for social media impressions and media mentions. Customer satisfaction events might set satisfaction score targets and repeat attendance rates.
Realistic targets based on historical performance and market conditions prevent setting expectations that cannot be met. Aligning objectives with stakeholder expectations ensures everyone evaluates success using the same criteria.
Strategy 2: create cross-functional team workflows
Effective collaboration between departments and external partners requires defined roles, communication protocols, and decision-making processes. Role definition establishes who owns which decisions and deliverables, preventing gaps and overlaps. Communication protocols specify how information flows, what updates different stakeholders receive, and when escalation is appropriate.
Managing competing priorities requires negotiation skills and executive alignment on what matters most. Collaborative platforms facilitate cross-functional coordination by centralizing information, tracking commitments, and maintaining communication history.
Strategy 3: implement Agile planning methodologies
Agile principles adapted for event management include iterative planning that refines details as information becomes available, regular check-ins that maintain alignment and identify issues early, and flexibility to adjust based on feedback and changing circumstances.
Detailed planning provides structure while maintaining ability to pivot when circumstances change. Shifting from in-person to hybrid format when attendance projections change becomes manageable rather than chaotic. Agile approaches help manage uncertainty by building in adjustment points rather than assuming all decisions can be made upfront.
Strategy 4: utilize real-time dashboards for visibility
Dashboards provide instant visibility into event progress, budget status, and key metrics that enable faster decision-making and proactive problem-solving. Different dashboard types serve different audiences:
- Executive dashboards: high-level progress against major milestones and budget targets.
- Operational dashboards: detailed task completion and vendor deliverables.
- Financial dashboards: spending against budget categories with variance alerts.
Real-time visibility means issues surface immediately rather than during weekly status meetings, enabling intervention before small problems become major crises.
Strategy 5: develop standardized templates and processes
Build standardized processes that save time and maintain quality, while leaving room for adaptation based on the unique needs of each event. Organizations benefit from standardizing planning checklists that ensure nothing is overlooked, vendor evaluation criteria that enable objective comparisons, communication templates that maintain brand consistency, and budget formats that facilitate financial tracking.
Templates reduce planning time by providing starting points rather than blank pages. Standard processes ensure quality consistency while allowing customization for unique event needs.
Strategy 6: design memorable attendee experiences
Creating engaging, valuable experiences requires understanding attendee expectations and designing touchpoints that deliver value while advancing business objectives. Experience mapping identifies every interaction from invitation through post-event follow-up, ensuring each touchpoint supports overall goals.
Touchpoint optimization improves critical moments like registration, arrival, networking, and content consumption. Personalization strategies tailor experiences to different attendee segments with varying needs and interests. Balance educational content that delivers knowledge, networking opportunities that build relationships, and entertainment that creates positive associations.
Strategy 7: build comprehensive risk mitigation plans
Spotting potential disasters before they happen and having backup plans ready means your team can handle surprises without breaking a sweat. Common event risks and their mitigation strategies include:
- Weather disruptions: backup venue options or virtual contingencies.
- Technology failures: redundant systems and manual workarounds.
- Vendor issues: pre-qualified backup vendors and clear SLAs.
- Low attendance: flexible capacity planning and marketing escalation.
Contingency plans specify who makes what decisions under different scenarios. Communication protocols ensure teams coordinate effectively during crises. Risk assessment frameworks help prioritize which risks deserve the most attention and resources.
Strategy 8: continuously measure and optimize performance
Set up ways to track both hard numbers and subjective feedback — this gives you the complete picture you need to make each event better than the last. Data collection methods include registration systems, surveys, social media monitoring, and sales tracking. Analysis techniques identify patterns and insights from raw data.
Translating insights into actionable improvements means updating processes, adjusting strategies, and building on what works. Post-event reviews document lessons learned while memories are fresh. Teams that actually review what worked and what didn’t after each event don’t just feel more confident — they deliver better results with less stress as their playbook evolves.

How to centralize event management for scalable success
Running multiple events at once quickly exposes the limits of spreadsheets, email threads, and disconnected tools. Without a centralized system, teams lose visibility, miss dependencies, and struggle to maintain consistency as event volume grows.
Scalable event management brings planning, execution, and performance tracking into one shared workspace. When teams work from the same system, they can coordinate more effectively, spot issues earlier, and deliver high-quality events without increasing overhead.
With monday work management, teams manage all events — from small internal sessions to large conferences — in a single, flexible workspace. This removes fragmentation and creates a clear source of truth across timelines, budgets, and stakeholders.
Centralized event management makes it easier to:
- Maintain portfolio-level visibility: track all events by status, priority, owner, or date without jumping between tools.
- Coordinate resources across events: see workloads clearly and avoid overbooking people or vendors.
- Standardize processes without losing flexibility: use reusable templates for planning while tailoring details for different event types.
- Track budgets and timelines in real time: catch issues early instead of reacting after problems escalate.
Automation further reduces manual work and keeps events moving smoothly:
- Route vendor contracts and approvals automatically.
- Trigger reminders for deadlines and payments.
- Send registration confirmations and event updates without manual follow-up.
Because everything lives in one workspace, communication stays connected to the work itself. Conversations, files, and decisions remain tied to each event, giving teams and stakeholders the context they need without unnecessary access.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com’s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.
Frequently asked questions
What are the 7 stages of event planning?
The seven stages of event planning include defining objectives and setting measurable goals, designing the event experience and format, selecting venues and securing vendors, launching marketing and promotion campaigns, managing registration and attendee communication, executing the event with precision, and analyzing results and gathering insights. Each stage builds on the previous one while maintaining flexibility for adjustments as circumstances change.
Do you need a degree to be an event manager?
You don't need a degree to become an event manager, though degrees in hospitality, marketing, or business can be helpful. Many successful event managers enter the field through related roles like marketing coordination, project management, or operations, building skills through practical experience and specialized certifications. What matters most is developing strong organizational, communication, and problem-solving abilities through hands-on experience.
What is the highest salary for an event planner?
Event planner salaries vary significantly based on location, experience, and event complexity. Senior event managers in major metropolitan areas typically earn $80,000-$120,000 annually, while directors of events at large organizations can earn $120,000-$180,000 or more depending on industry sector and event scale. Specialized expertise in areas like corporate conferences or trade shows often commands premium compensation.
What certifications are best for event managers?
Recognized industry certifications include Certified Meeting Professional (CMP) from the Events Industry Council, Certified Special Events Professional (CSEP) from the International Live Events Association, and Digital Event Strategist (DES) certification for virtual and hybrid event specialization. These certifications demonstrate expertise and commitment to professional development, often leading to enhanced career opportunities.
How do you measure event management success?
Event management success measurement requires both quantitative metrics like attendance numbers, budget adherence, and lead generation, and qualitative feedback including attendee satisfaction surveys, stakeholder input, and team debriefs. Success metrics must align with original event objectives, whether those focus on revenue generation, brand awareness, customer engagement, or employee development.