Your marketing budget is working hard — email campaigns, paid social, content, events, maybe even a trade show or two. But when revenue reports come in, the picture is fuzzy. Which channels are actually converting? Where are prospects dropping off? And why does everything feel disconnected?
That’s the cost of running channels in silos. Campaigns launch, clicks come in, but without coordination and visibility, momentum breaks between touchpoints and opportunities stall.
Marketing channels are the pathways that carry your message to your audience — through inboxes, search results, social feeds, podcasts, events, and beyond. The right mix does more than generate awareness. It builds connected journeys, reinforces messaging at every stage, and turns scattered activity into measurable growth.
It’s time to stop guessing and start building a channel strategy that performs. Below, discover the marketing channels driving results in 2026 — from SEO foundations to AI-powered personalization — plus practical ways to choose the right mix, align teams, and turn every channel into a revenue contributor.
Key takeaways
- Start with your audience, not the channels: Choose marketing channels based on where your customers spend time and how they prefer to receive information, not what’s trendy or easy to execute.
- Focus on two-three channels you can execute well: Small businesses achieve more impactful results by mastering fewer channels rather than spreading efforts thin across many platforms.
- Integrate channels for maximum impact: Coordinate messaging and timing across channels so they work together — use social media for awareness, email for nurturing, and PPC for conversion.
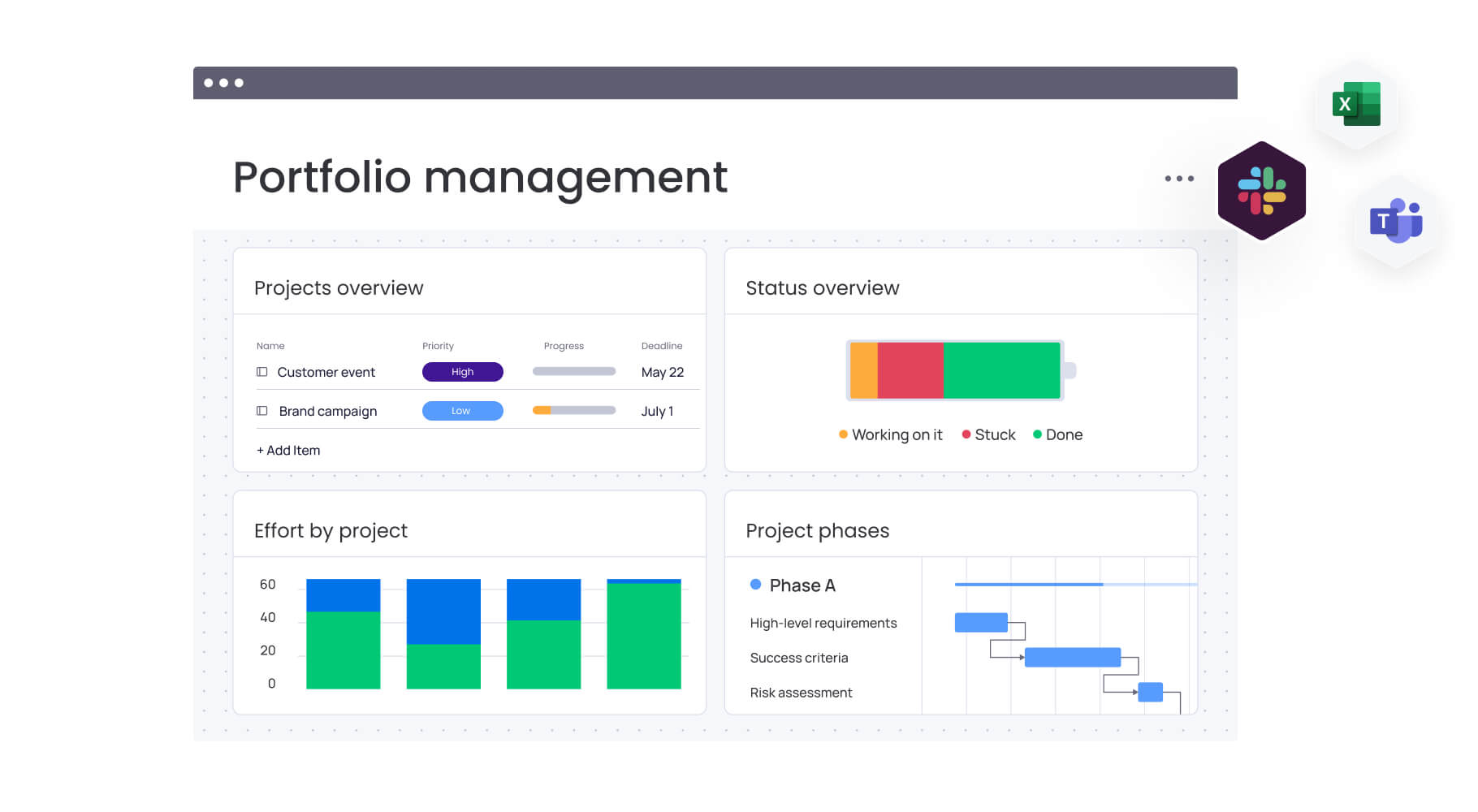
- Coordinate multi-channel campaigns with monday work management: Map campaign timelines, assign channel responsibilities, and track performance across all marketing activities from unified dashboards and automated workflows.
- Measure what matters most: Track cost per acquisition, conversion rates, and ROI consistently across channels to identify which drive the most valuable customers for your business.
What are marketing channels?
Marketing channels are the pathways businesses use to reach, engage, and convert their target audiences. Think of them as bridges connecting your products or services with the people who need them — whether through email, social media, search engines, or traditional media like print and television.
Even the most brilliant products gather dust without the right marketing channels. Your channels aren’t just nice-to-haves — they’re the difference between obscurity and a packed sales pipeline. The right mix of channels transforms how organizations connect with customers, coordinate campaigns, and measure success.
Marketing channel definition
A marketing channel is simply any way you talk to customers — from emails that land in their inbox to the Instagram posts they scroll past during lunch breaks. Each one gives you a unique opportunity to connect, convince, and convert.
Channels fall into two main categories:
- Digital channels: Email marketing, social media, search engines, and content marketing.
- Traditional channels: Print advertising, direct mail, television, radio, and in-person events.
Each channel has its own rules, reaches different people, and comes with its own resource demands — master these differences and you’ll maximize your marketing impact.
Also keep in mind that the right channel depends on three key factors:
- Where your audience spends time: Different demographics prefer different platforms.
- How they prefer to receive information: Some respond to visual content, others to written communication.
- What stage of the buying journey they’re in: Awareness, consideration, or decision phase.
Some channels excel at building awareness (social media, content marketing), while others drive conversion (email, PPC advertising). Most successful businesses coordinate multiple channels, creating consistent experiences across touchpoints.
Why marketing channels matter for business growth
Your channel choices can make or break your growth trajectory. Pick the right mix and you’ll reach more qualified prospects, turn more browsers into buyers, and squeeze more value from every marketing dollar.
- Expanded audience reach: Different channels access different audience segments. Social media reaches younger demographics, while email connects with existing customers. Using multiple channels ensures visibility where your audience is active.
- Cost-effective resource allocation: Not all channels require the same investment. Organic channels like SEO and content marketing deliver long-term value without ongoing ad spend. Paid channels like PPC provide immediate results with predictable costs.
- Data-driven optimization: Digital channels provide detailed analytics on audience behavior, campaign performance, and conversion paths. This data reveals which channels drive the most valuable customers, allowing teams to refine strategy over time.
How marketing channels connect businesses to customers
Marketing channels guide prospects through different stages from initial awareness to final purchase and beyond:
Customer journey stages:
- Awareness stage: Channels like social media, content marketing, and SEO introduce your brand to new audiences.
- Consideration phase: Email marketing, webinars, and retargeting ads nurture interest and provide detailed information.
- Conversion: PPC advertising, sales calls, and promotional emails drive immediate action.
- Post-purchase: Customer email programs, loyalty initiatives, and community platforms keep customers engaged long after the initial sale.
Organizations need integrated channel management to coordinate messaging across these touchpoints and track customer movement between channels.
Marketing channels vs marketing platforms: key differences
It’s easy to blur the line between marketing channels and marketing platforms — and that confusion can lead to wasted budget, duplicated tools, or teams optimizing the wrong thing.
A marketing channel is the approach you use to reach your audience. Email marketing, content marketing, social media marketing, SEO — these define how you communicate and where your message shows up.
A marketing platform is the technology that powers that channel. Mailchimp or HubSpot for email. WordPress for content. Facebook or LinkedIn to execute your social strategy.
The difference may seem subtle, but it shapes smarter decisions:
-
Channels are strategic: they’re chosen based on where your audience spends time and how they prefer to engage.
-
Platforms are tactical: they’re selected based on features, integrations, scalability, and cost.
-
Channels evolve slowly: email, search, and social remain core communication paths for years.
-
Platforms change rapidly: tools rise, fall, merge, and update as technology advances.
The comparison table below breaks this distinction down clearly so teams can align strategy before investing in tools.
| Aspect | Marketing channels | Marketing platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Method or approach to reach and engage customers | Specific service used to execute channel strategy |
| Examples | Email marketing, content marketing, social media marketing, SEO | Mailchimp, HubSpot, Facebook, Google Ads, WordPress |
| Purpose | Define how you communicate with your audience | Provide technology and infrastructure for communication |
| Control level | Strategic decision about audience reach and engagement | Tactical decision about execution capabilities |
| Longevity | Evolve slowly and remain relevant for years | Change frequently as technology advances |
For example, a business might decide email marketing is critical because its audience responds well to direct communication. That’s the channel decision. Only after that do they compare platforms like Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or HubSpot to determine which one best supports deliverability, automation, and reporting needs.
Digital vs traditional marketing channels
The smartest marketers don’t pick sides in the digital versus traditional debate — they blend both worlds based on who they’re trying to reach and what they need to accomplish. While digital channels dominate in growth and adoption, traditional channels still deliver value in specific contexts.
Digital marketing channels overview
Digital channels live where your customers spend hours daily — on their phones, laptops, and tablets. They’ve become marketing’s main event because you can track everything, target with laser precision, and often spend less to get more.
Key advantages of digital channels:
- Real-time performance data: You can see how many people clicked an ad, opened an email, or visited a webpage within minutes of launching a campaign.
- Precise targeting: Reach specific demographics, interests, behaviors, and even individual users.
- Low barriers to entry: Starting a blog, building an email list, or creating social media profiles requires minimal upfront investment.
- Two-way communication: Customers can comment on social posts, reply to emails, or chat with support teams in real-time.
This real-time tracking enables quick adjustments and continuous optimization. A B2B software company can target IT directors at companies with 500+ employees in specific industries. This interactive engagement builds stronger relationships and provides valuable feedback.
Traditional marketing channels overview
Traditional marketing channels are offline methods that predate the internet. While digital channels capture most marketing budgets, traditional channels remain effective for specific audiences and objectives.
Strengths of traditional channels include:
- Geographic targeting and broad reach: Television, radio, and outdoor advertising reach large audiences without requiring internet access or digital literacy.
- Inherent trust: A feature in a major newspaper or magazine signals legitimacy in ways digital advertising may not.
- Multi-sensory engagement: Physical materials create lasting impressions through touch, sight, and sometimes smell.
Local radio, community newspapers, and direct mail efficiently reach specific neighborhoods or regions. A well-designed brochure engages multiple senses in ways digital channels cannot replicate.
Integrating digital and traditional strategies
The most effective marketing strategies combine digital and traditional channels to create comprehensive coverage and reinforce messaging. This integrated approach ensures customers encounter consistent messaging regardless of where they engage with your brand.
Integration examples:
- Cross-channel amplification: Run television commercials to build broad awareness, then use retargeting ads to reach viewers who search for the brand online.
- Bridge offline and online: QR codes on print advertisements direct readers to landing pages.
- Social amplification: Social media campaigns amplify traditional advertising by encouraging customers to share experiences.
Cross-channel attribution further helps businesses understand how different channels work together to drive conversions. A customer might first hear about a product through a podcast ad, research it through organic search, receive a promotional email, and finally make a purchase after seeing a billboard reminder.

15 essential marketing channels to drive growth
These channels outlined below represent the most effective options for businesses today, covering both digital and traditional approaches. Each offers difference advantages and works best in specific contexts.
1. Email marketing
Email marketing delivers direct communication with customers and prospects through targeted messages. It consistently provides strong return on investment due to low costs and high conversion rates among engaged subscribers.
Key benefits:
- Advanced segmentation: Email platforms enable sophisticated customization based on customer behavior, purchase history, and engagement level.
- Automated campaigns: Triggered email campaigns respond to customer actions without manual intervention, including welcome series, abandoned cart emails, and re-engagement campaigns.
2. Search engine optimization (SEO)
SEO optimizes website content to rank higher in search engine results pages, focusing on earning organic visibility for relevant search queries.
Why SEO works:
- Sustainable traffic: Once your content ranks well, it continues attracting visitors without ongoing ad spend.
- Authority building: Higher search rankings signal authority and trustworthiness to users.
- Cost efficiency: While SEO requires upfront investment in content creation and technical optimization, it doesn’t charge per click or impression.
3. Social media marketing
Social media marketing uses platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to connect with audiences, share content, and build brand awareness.
Social media advantages:
- Relationship building: Foster ongoing relationships with customers through regular posting and conversation.
- Viral potential: Compelling content can reach far beyond your immediate followers when people share and engage.
- Real-time interaction: These platforms enable immediate interaction with audience feedback, building community and trust.
4. Content marketing
Content marketing creates valuable, relevant content to attract and engage target audiences. Rather than directly promoting products, it provides information that helps customers solve problems.
Content marketing benefits:
- Expertise positioning: Publishing insightful content establishes your expertise and positions you as a trusted source.
- SEO enhancement: Quality content improves search rankings by satisfying user intent.
- Lead generation: Valuable content attracts potential customers and builds your email list with qualified prospects.
5. Pay-per-click advertising (PPC)
PPC is paid advertising where businesses pay each time someone clicks their ad. Google Ads and social media advertising platforms are the most common PPC channels.
PPC advantages:
- Immediate results: PPC campaigns can start driving traffic and leads within hours of launch.
- Precise targeting: These platforms offer sophisticated targeting options by demographics, interests, behaviors, and locations.
- Budget control: PPC allows exact spending limits and real-time adjustments without long-term commitments.
6. Video marketing
Video marketing uses video content to communicate messages, demonstrate products, or tell brand stories across platforms like YouTube, social media, and websites.
Video marketing strengths:
- Higher engagement: Video content typically receives more interaction than text or static images.
- Multi-platform distribution: A single video can be shared across multiple platforms and channels.
- Emotional connection: Visual storytelling creates stronger emotional bonds with audiences.
7. Influencer marketing
Influencer marketing partners with individuals who have established audiences to promote products or services.
Influencer marketing benefits:
- Trusted recommendations: Recommendations from trusted figures carry more weight than traditional advertising.
- Audience access: Influencers provide immediate access to engaged, relevant audiences.
- Content creation: They produce authentic content that can be repurposed across your own channels.
8. Affiliate and referral marketing
Affiliate and referral marketing are performance-based channels where partners earn commissions for driving sales or leads.
Performance-based advantages:
- Results-only payment: You only pay for actual results, making this low-risk compared to exposure-based channels.
- Network leverage: Partners leverage their own networks to promote your products.
- Higher conversion rates: Recommendations from trusted sources increase conversion rates.
9. SMS and mobile messaging
SMS and mobile messaging channels communicate directly through text messages and mobile messaging apps.
Mobile messaging benefits:
- Immediate attention: Text messages are typically read within minutes of receipt.
- High open rates: SMS open rates significantly exceed email, often reaching 95% or higher.
- Personal connection: Direct messages to mobile devices feel more intimate than other channels.
10. Podcast marketing
Podcast marketing uses audio content to reach audiences through podcast platforms and shows.
Podcast marketing advantages:
- Engaged audiences: Podcast listeners are typically highly engaged and loyal, spending 30-60 minutes with content.
- Authority building: Long-form conversation formats allow you to demonstrate knowledge and personality.
- Multitasking consumption: Audiences can consume podcast content while commuting, exercising, or doing household activities.
11. Event and experiential marketing
Event and experiential marketing creates memorable, interactive experiences through trade shows, conferences, product launches, and workshops.
Event marketing strengths:
- Personal connections: Face-to-face interactions build stronger relationships than digital channels.
- Real-time feedback: Events provide real-time responses and questions from attendees.
- Comprehensive brand experience: They showcase your full brand value across multiple touchpoints in a concentrated timeframe.
12. Direct mail marketing
Direct mail marketing sends physical mail directly to prospects’ homes or businesses.
Direct mail benefits:
- Tangible impact: Physical materials create lasting impressions that recipients can touch, hold, and display.
- Reduced competition: Fewer businesses use direct mail, making messages stand out in physical mailboxes.
- Geographic precision: Direct mail enables precise geographic and demographic targeting.
13. Commerce media networks
Commerce media networks are advertising platforms within e-commerce sites where brands can promote products to shoppers.
Commerce media advantages:
- High purchase intent: Audiences on commerce platforms are already in buying mode.
- Contextual relevance: Ads appear alongside related products in highly relevant contexts.
- Sales attribution: Commerce media networks provide detailed analytics on sales attribution.
14. Voice and conversational marketing
Voice and conversational marketing uses voice assistants, chatbots, and conversational interfaces to engage customers.
Conversational marketing benefits:
- 24/seven availability: Automated conversational systems provide constant customer service.
- Personalized responses: AI-powered systems tailor responses to individual needs.
- Scalable interactions: Conversational marketing handles multiple conversations simultaneously.
15. Strategic partnership marketing
Strategic partnership marketing collaborates with complementary businesses to reach shared audiences and create mutual value.
Partnership advantages:
- Audience expansion: Partnerships provide access to your partner’s customer base.
- Credibility boost: Association with trusted brands enhances your reputation.
- Cost sharing: Partners split marketing expenses while amplifying reach.
How to select the right mix of marketing channels
Choosing channels without a strategy is like throwing darts blindfolded. Instead, be methodical: analyze where your audience hangs out, what resources you can realistically commit, and which business goals you’re prioritizing.
This section provides a framework for making informed channel decisions that align with your business goals.
Step 1: Define your target audience and buyer journey
Channel selection starts with understanding who you’re trying to reach and how they make decisions. Different audiences prefer different channels, and the same person uses different channels at different stages of their buying journey.
Audience analysis factors:
- Demographics: Age, location, income levels, and job roles influence channel preferences.
- Information consumption: B2B buyers often research through industry publications and LinkedIn, while B2C consumers might discover products through social media.
- Journey mapping: Different channels serve different stages of the customer journey.
Creating detailed buyer personas and mapping their preferred communication channels provides a foundation for channel selection. When you understand your audience deeply, channel decisions become more straightforward.
Step 2: Assess resources and channel requirements
Each channel requires different levels of investment in time, money, and expertise. Realistic assessment of available resources prevents overextension and ensures quality execution.
Resource considerations:
- Financial investment: Some channels require significant upfront investment (PPC advertising, event marketing), while others can start with minimal spend (content marketing, social media).
- Skill requirements: Different channels demand different skills — matching channel requirements with available skills ensures effective execution.
- Time commitment: Channels vary dramatically in time requirements.
Social media demands daily attention, while content marketing requires consistent production over months. Understanding these requirements helps you choose channels you can sustain long-term.
Step 3: Evaluate channel ROI and performance potential
Not all channels deliver equal returns. Evaluating potential performance helps prioritize investment toward channels most likely to drive business results.
Performance evaluation methods:
- Historical analysis: If you’ve used certain channels before, analyze past results to inform future decisions.
- Industry benchmarks: When you lack historical data, industry benchmarks provide guidance on expected performance.
- Testing approach: Rather than committing large budgets to unproven channels, start with small tests to validate effectiveness.
Step 4: Align channels with business objectives
Different business objectives require different channel approaches. Channel selection should directly support what you’re trying to accomplish.
Objective-based channel selection:
- Brand awareness: Prioritize channels that maximize reach and impressions, such as content marketing, social media, and podcast sponsorships.
- Lead generation: Focus on channels that capture contact information, including content offers, email marketing, and PPC campaigns.
- Sales conversion: Target high-intent buyers through PPC advertising, promotional emails, and retargeting campaigns.
- Customer retention: Maintain relationships through email marketing, loyalty programs, and customer communities.
Emerging marketing channels for 2026
Marketing never stands still. What feels experimental today often becomes standard practice tomorrow — and the brands that move early tend to capture the biggest gains.
The channels below are gaining momentum quickly. They’re no longer fringe ideas, but they’re not yet overcrowded either. That creates a window of opportunity: space to test, learn, and build capability before competitors flood in. For teams willing to experiment strategically, these emerging channels can unlock new reach, deeper engagement, and a meaningful edge in 2026 and beyond.
AI-powered personalization at scale
Artificial intelligence enables hyper-personalized marketing across channels in ways previously impossible without massive manual effort.
AI personalization capabilities:
- Real-time adaptation: AI systems automatically adjust messages based on user behavior and preferences in real-time.
- Predictive insights: They use historical data to anticipate customer needs and optimal timing.
- Continuous improvement: AI continuously improves campaign performance without manual intervention, learning from each interaction to deliver increasingly relevant experiences.
Privacy-first marketing solutions
Growing privacy regulations and consumer awareness are reshaping how businesses collect and use customer data.
Privacy-first approaches:
- Direct relationships: Businesses are building direct relationships to collect customer information rather than relying on third-party data.
- Permission-based communication: All communications are permission-based, with transparent opt-in processes.
- Transparency focus: Privacy-first businesses communicate how they collect, use, and protect customer data, building trust through transparency.
Immersive and interactive experiences
Emerging technologies create engaging customer experiences that go beyond traditional content and advertising.
Immersive technology applications:
- Augmented reality: Overlays digital information on real-world environments, letting customers visualize products in their spaces.
- Virtual reality: Creates fully immersive brand experiences through headsets.
- Interactive content: Polls, quizzes, calculators, and gamified experiences engage audiences more deeply than static content.
How to build an integrated multi-channel marketing strategy
The difference between good and great marketing? Integration. When channels work together with coordinated messaging and timing, the combined impact exceeds the sum of individual channel results. This section outlines how to create cohesive multi-channel strategies that amplify your marketing effectiveness.
Step 1: Create unified workflows across channels
Coordinating multiple channels requires systematic workflows that ensure consistency and timing alignment across all touchpoints.
Workflow coordination elements:
- Brand consistency: Your brand voice and key messages must align across all channels.
- Message frameworks: Create message frameworks that define core themes, then adapt those themes for each channel’s format.
- Strategic sequencing: Channel activities should be sequenced for maximum impact — a product launch might start with social media teasers, followed by email announcements, supported by PPC advertising.
Core messages and assets can be adapted for different channel requirements, maximizing the value of content creation efforts.
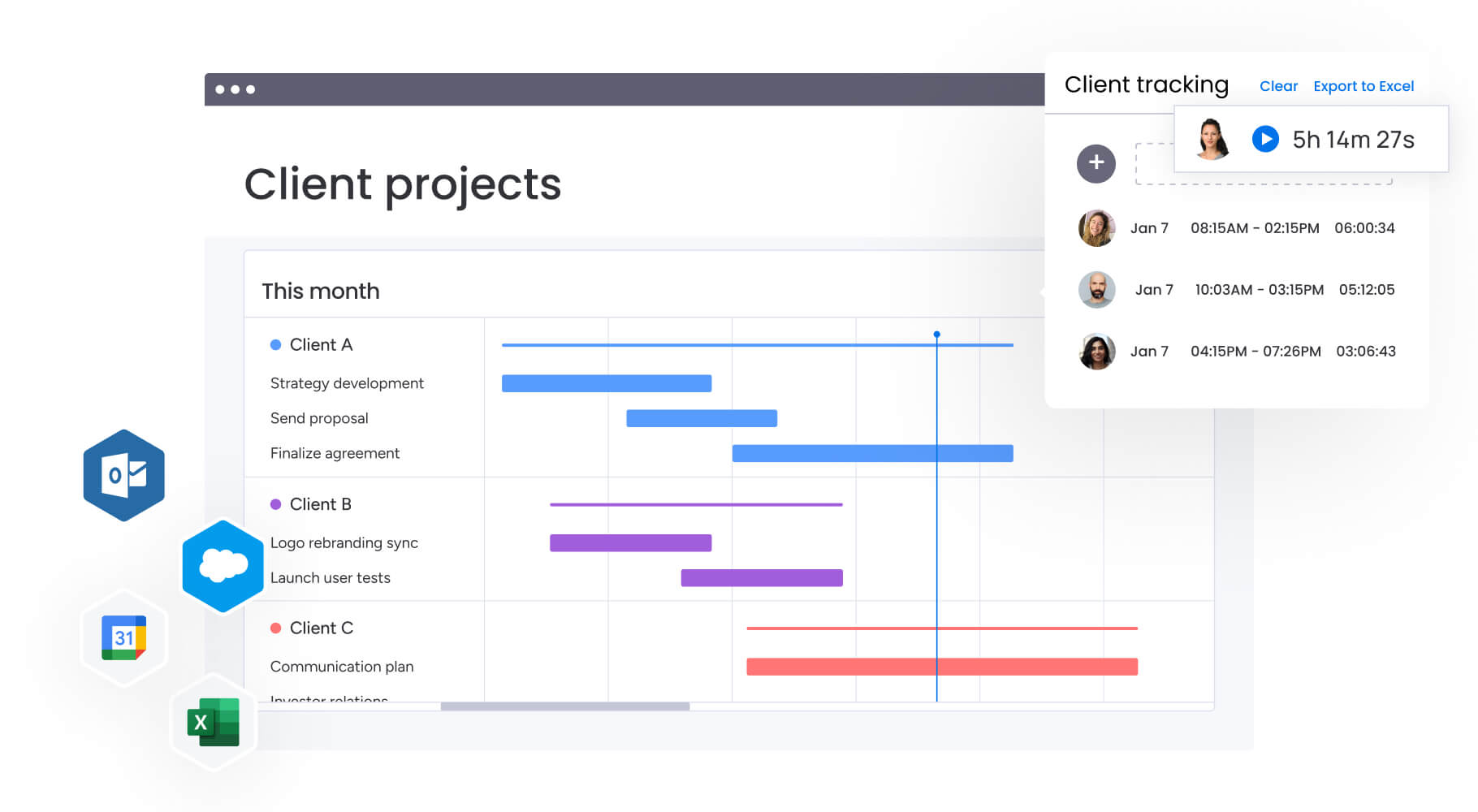
Teams using modern platforms like monday work management can map out campaign timelines, assign responsibilities for different channels, and monitor progress across all activities from a single workspace using Gantt charts and dashboards.
Step 2: Coordinate cross-functional marketing teams
Multi-channel marketing involves multiple team members with different specializations. Effective coordination ensures these specialists work together rather than in isolation.
Team coordination strategies:
- Clear responsibilities: Clarify responsibilities for different channels and activities to prevent gaps and overlaps.
- Regular communication: Establish regular check-ins and update processes through shared workspaces.
- Aligned objectives: Align team goals with overall marketing strategy so everyone works toward the same business objectives.
Organizations using monday work management break down silos between marketing, sales, content, and design teams working on channel strategies. Shared workspaces, real-time collaboration features, and unified communication ensure all team members have visibility into cross-channel activities.
Step 3: Automate repetitive channel activities
Let robots handle the repetitive stuff — like scheduling posts or triggering welcome emails — so your team can tackle the work that actually requires human creativity and strategic thinking.
Automation opportunities:
- Cross-channel triggers: Set up processes that trigger actions across multiple channels, such as adding content downloaders to email nurture sequences.
- Content scheduling: Plan and distribute content across platforms in advance to ensure consistent presence.
- Performance alerts: Automated alerts notify teams of significant changes in channel performance.
Teams leverage monday work management automations to handle repetitive activities from content approval processes to campaign launch sequences, ensuring every detail is accounted for while freeing teams to focus on strategic work.
Step 4: Track performance across all channels
Comprehensive measurement approaches reveal how channels work together to drive business results.
Performance tracking essentials:
- Attribution analysis: Understanding how different channels contribute to conversions is essential for smart budget allocation.
- Customer journey mapping: Track customer journeys across multiple touchpoints to see how channels work together.
- ROI measurement: Measure return on investment for individual channels and overall strategy.
Organizations gain visibility through monday work management dashboards that monitor channel performance, track ROI across different marketing activities, and generate reports on marketing effectiveness with real-time data.
Turn your marketing channel strategy into results now
Marketing channels are only as effective as your ability to execute them consistently and measure their impact. Channel selection is just the starting line. The winners in marketing don’t stop there — they create playbooks that translate strategy into daily actions everyone on the team understands and executes.
When you have the right operational foundation, marketing channels become powerful engines for sustainable growth. Teams execute campaigns faster, maintain consistency across touchpoints, and adapt quickly based on real-time performance data. This operational excellence transforms good channel strategies into exceptional business results.
The key is connecting your channel planning to execution through workflows that keep everyone aligned and accountable. With proper coordination systems in place, your marketing channels work together to create experiences that drive meaningful customer engagement and business growth.
Try monday work managementFrequently asked questions
What is the main focus of marketing channels?
The main focus of marketing channels is creating pathways for businesses to reach, engage, and convert their target audiences into customers. These channels serve as bridges between your offerings and the people who need them, enabling consistent communication and relationship-building throughout the customer journey.
How many marketing channels should a small business use?
Small businesses should start with two-three channels they can execute well rather than spreading efforts too thin across many channels. Focus on channels where your audience is most active and where you have the resources to maintain consistent, quality engagement.
Which marketing channel typically has the highest ROI?
Email marketing consistently shows high ROI across industries due to its low costs and strong conversion rates among engaged subscribers. However, the most effective channel varies by business type, audience, and execution quality.
How do you measure marketing channel effectiveness?
Marketing channel effectiveness is measured through key metrics like cost per acquisition, conversion rates, return on investment, and customer lifetime value. Track these metrics consistently across channels to understand which drive the most valuable outcomes for your business.
What is an example of a digital marketing communication channel?
Social media marketing is a digital marketing communication channel that allows businesses to share content, engage with customers, and build brand awareness. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn enable direct interaction with audiences through posts, comments, and messages.
What is the difference between owned, paid, and earned marketing channels?
The difference between owned, paid, and earned marketing channels lies in who controls the property and how you gain visibility. Owned channels are properties you control, like your website and email list. Paid channels are advertising you purchase, like Google Ads and sponsored social posts. Earned channels are publicity you gain through others, like word-of-mouth, media coverage, and organic social shares.