Inside sales has quietly become the default for how modern teams grow revenue. Buyers are comfortable meeting over video, asking detailed questions in shared docs, and making high-value decisions without ever sitting across a table. That shift has changed more than logistics: it has reshaped roles, skills, costs, and the way pipelines are built and managed.
So what does that actually mean for your team?
This article breaks it down from every angle. It clarifies how inside sales differs from outside sales and telemarketing in structure and intent, not just location. It also explores how reps spend their time, how they move deals from first touch to signed contract, and how they manage high volumes without losing personalization.
By the end, the full operating model becomes clear. Not just a definition, but a practical understanding of how inside sales works, why it scales, and how to evaluate whether it is the right engine for predictable, sustainable growth.
Key takeaways
- Inside sales can reduce selling costs by 40–60% without sacrificing results: Remote execution removes travel expenses while allowing reps to engage more prospects daily across wider geographies.
- Role specialization can shorten sales cycles by 25–40%: Assigning SDRs to qualification and AEs to closing improves focus, expertise, and handoff clarity throughout the pipeline.
- High-performing inside sales reps manage 40–60 active opportunities at once: Virtual selling enables higher deal volume through faster meetings, quicker follow-ups, and fewer scheduling constraints.
- Teams that rely on sales data outperform intuition-led selling: Tracking metrics like call-to-meeting rates, email responses, and pipeline velocity makes performance gaps visible and repeatable.
- Solutions like monday CRM helps teams maintain pipeline visibility at scale: Visual workflows, automation, and AI-driven insights support consistent execution across dozens of active deals.
What is inside sales?
At its core, inside sales focuses on closing deals remotely. Representatives work from offices, homes, or shared spaces and rely on digital channels to connect with prospects anywhere, building the same trusted relationships traditionally formed face to face.
Rather than traveling to meetings, teams manage the full sales process through CRM platforms, video conferencing, and automation. What began as phone-based selling has matured into a structured revenue model that uses AI and data analytics to improve consistency, visibility, and decision-making across every interaction.
Here’s what makes today’s inside sales teams actually work:
- Remote selling environment: Representatives connect with prospects globally from centralized locations, eliminating travel while maintaining personal connections.
- Technology-driven operations: Digital tools power every aspect from initial outreach to deal closure, making tech proficiency essential.
- Scalable processes: Standardized workflows handle high prospect volumes efficiently while keeping interactions personalized.
- Data-driven decisions: Analytics guide strategy, showing what works and helping teams adjust approaches based on measurable results.
Understanding how inside sales actually works
Inside sales performs best when responsibilities are clearly divided across the sales process. Sales development reps focus on qualifying leads and booking meetings, while account executives manage demonstrations and close deals. This structure aligns with broader market trends, including growing adoption of generative AI across sales and marketing teams, which has made automation and specialization increasingly important.
Clear role ownership also allows each function to develop deeper expertise while keeping opportunities moving steadily through the pipeline. Deals typically progress through defined stages — lead generation, qualification, nurturing, demonstration, negotiation, and closure — each supported by clear criteria and measurable activities.
Separating inside sales from telemarketing
Inside sales is often confused with telemarketing, but the two models serve very different purposes. Understanding these keys differences (detailed in the table below) can help organizations design the right processes, incentives, and expectations.
| Aspect | Inside sales | Telemarketing |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship focus | long-term relationship building through expertise | short-term transactions with minimal follow-up |
| Sales cycle | multi-touch process spanning weeks or months | single-call attempts at immediate conversion |
| Product complexity | complex solutions requiring education | simple products with straightforward value |
| Representative skills | deep product and industry knowledge | script-based communication |
| Technology use | CRM, video conferencing, automation platforms | basic phone systems |
| Compensation | salary plus commission on closed deals | hourly wages or per-call payment |
As the table indicates, sales emphasizes long-term relationship building, multi-touch engagement, and education around complex solutions. Telemarketing, by contrast, is built around high call volume and immediate conversion, typically with minimal follow-up or personalization.
Inside sales reps also invest time in understanding customer challenges, guiding prospects through decisions, and building trust through expertise. On the other hand, telemarketing prioritizes efficiency and reach, relying on scripts and repetition to generate short-term outcomes.
Inside sales performs best when responsibilities are clearly divided across the sales process. Sales development reps focus on qualifying leads and booking meetings, while account executives manage demonstrations and close deals.
Inside sales vs outside sales: understanding the key differences
Inside and outside sales serve different purposes across the sales funnel. Choosing the wrong approach can increase costs, slow deal velocity, and create friction for buyers. Selecting the right model, however, supports stronger relationships, better margins, and more predictable growth.
Core differences in approach
Inside sales focuses on building relationships through consistent, digital-first interactions. Representatives rely on phone calls, video meetings, email, and messaging to stay connected with prospects. Success depends on reading verbal cues, maintaining engagement during virtual presentations, and creating rapport without being physically present.
This approach aligns with modern buying behavior, with research finding that 22.3% of people at work in the U.S. teleworked or worked from home for pay.
Outside sales, by contrast, emphasizes face-to-face engagement and physical presence. Representatives meet prospects on-site, deliver hands-on demonstrations, and build trust through in-person experiences.
The practical differences between these approaches include:
- Communication channels: Inside sales uses phone, video, email, and messaging for all interactions, while outside sales prioritizes in-person meetings supplemented by digital communication.
- Relationship building: Inside sales maintains connection through frequent touchpoints and consistent availability, while outside sales creates memorable face-to-face experiences.
- Product demonstrations: Inside sales conducts demos through screen-sharing with interactive elements, while outside sales provides physical product access.
- Territory management: Inside sales serves prospects anywhere without geographic limits, while outside sales operates within defined travel regions.
Cost and efficiency comparison
One of the biggest differences between inside and outside sales shows up in how time and budget are allocated. Travel, territory coverage, ramp-up time, and daily meeting capacity all shape the true cost of closing a deal.
The table below breaks down these variables side by side, highlighting how each model affects travel expenses, time per prospect, geographic reach, technology investment, and scalability.
| Cost factor | Inside sales | Outside sales |
|---|---|---|
| Travel expenses | Minimal, limited to occasional events | Significant ongoing costs for flights, hotels, meals |
| Time per prospect | 30-60 minutes per interaction, multiple daily meetings | Half-day to full-day commitments including travel |
| Geographic reach | Unlimited global reach from single location | Limited by travel logistics and time |
| Ramp-up time | 3-6 months to full productivity | 6-12 months including territory learning |
| Technology investment | CRM, video tools, automation platforms | CRM plus travel management systems |
| Scalability | High — add reps without territory conflicts | Limited — new reps need territory assignment |
In practice, inside sales representatives often manage 40 – 60 active opportunities at once, while outside sales reps typically handle 15 – 25 due to travel commitments. That higher volume can translate into a lower cost per deal for inside teams, although outside sales may offset higher costs with larger average contract values in certain markets.
Choosing the right model
Deciding between inside and outside sales depends on the product, the buyer, and the size of the deal. There is no universal answer, but aligning the sales model with buying expectations makes the decision clearer.
Inside sales works best for:
- SaaS products that translate well to virtual demonstrations.
- Subscription services that benefit from frequent engagement.
- Deals under $50,000, where travel costs impact margins.
- Tech-savvy buyers comfortable with remote meetings.
- Markets that require fast scaling across regions.
- Buying committees that benefit from coordinated virtual sessions.
Outside sales makes sense for:
- Enterprise deals exceeding $100,000.
- Complex equipment that requires physical inspection.
- Relationship-driven industries that expect in-person engagement.
- Traditional buyers who prefer face-to-face meetings.
- Products that require on-site installation or evaluation.
Many organizations succeed with a hybrid approach. Inside sales teams handle qualification and early relationship building, while outside sales steps in for high-value, late-stage conversations. This balance helps control costs while delivering a personal experience when it matters most.
To support either model, teams also need clear visibility into pipelines, activities, and customer interactions. Platforms like monday CRM connect sales data, communication, and workflows in one place, helping teams adapt their sales approach while staying aligned on goals and execution.

What do inside sales representatives do?
Inside sales representatives manage the full sales cycle, from initial outreach to signed contracts, without leaving their desk. Their role goes far beyond making calls. They research target accounts, qualify leads, deliver virtual demos, negotiate terms, and collaborate with internal teams to ensure long-term customer success.
Generate and qualify leads
Inside sales representatives actively identify potential customers across multiple channels, including social platforms, review sites, and industry events. They analyze LinkedIn profiles and company websites to identify organizations that align with the ideal customer profile before initiating contact.
This research supports the creation of targeted prospect lists based on firmographic data, buying intent, and behavioral signals. Strong preparation improves outreach relevance and increases response rates.
The qualification process determines which prospects merit continued investment. Representatives often rely on the BANT framework to weigh up readiness and fit:
- Budget: The financial resources available for purchase.
- Authority: The level of decision-making power within the organization.
- Need: The business challenges the solution addresses.
- Timeline: The expected timeframe for making a purchase decision.
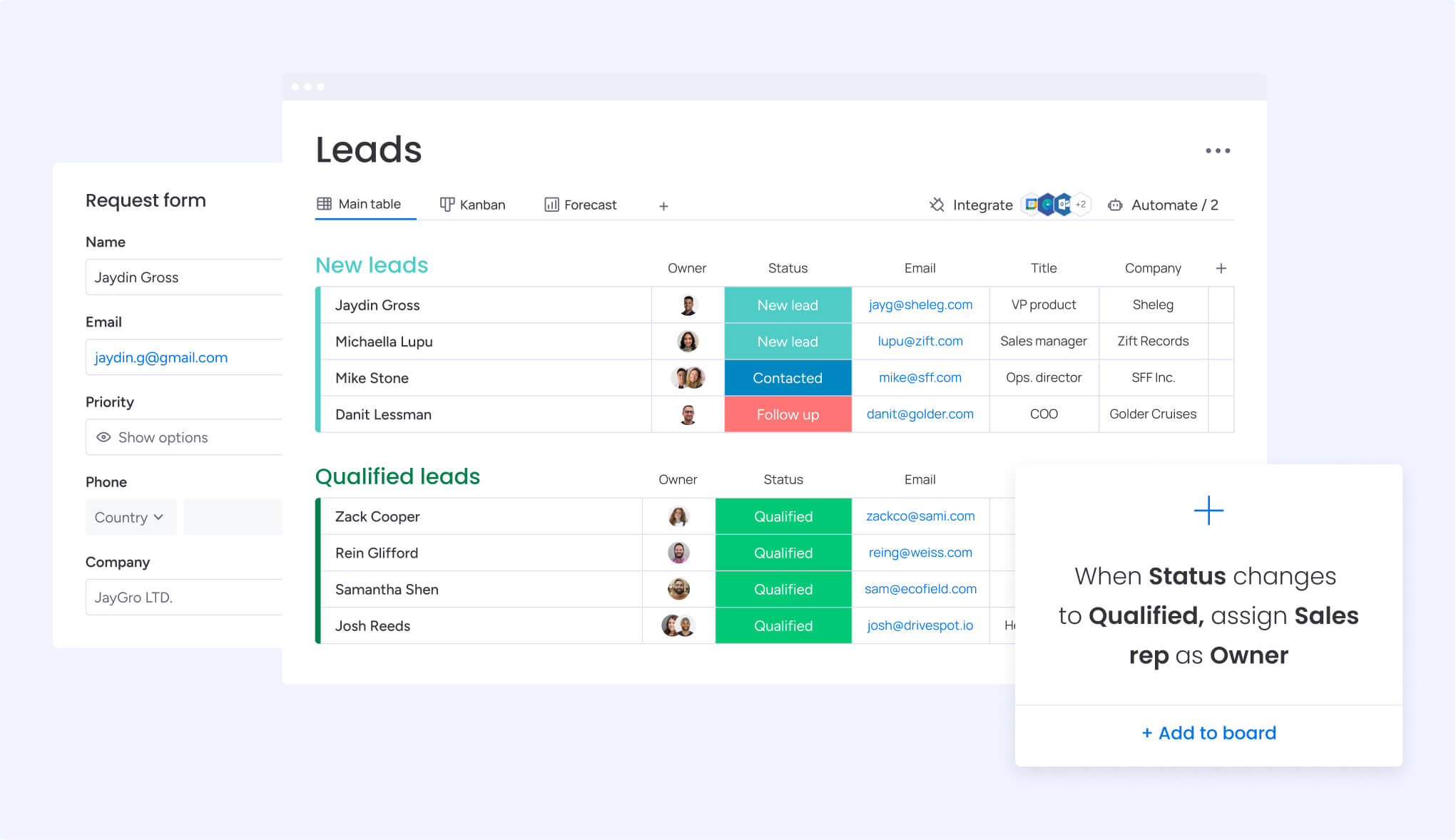
Initial outreach typically happens through personalized emails, phone calls, or social messages to confirm interest and gather additional insight. In 2026, intelligent CRM platforms like monday CRM helps teams track lead sources, qualification status, and next steps in centralized dashboards.
With this visibility, representatives can see which campaigns generated leads, which content prospects engaged with, and which qualification criteria have already been confirmed.
Conduct virtual product demonstrations
Running effective virtual product demonstrations requires a different skill set than in-person presentations. Representatives tailor each demo to the prospect’s specific needs, prepare relevant examples, and anticipate technical or operational questions.
Successful virtual demos follow several proven practices:
- Technical preparation: Testing audio, video, and screen sharing in advance.
- Engagement tactics: Using polls, questions, and interactive moments.
- Value focus: Highlighting business outcomes rather than feature lists.
- Follow-up materials: Sharing recordings and resources after the session.
Representatives learn to interpret verbal cues, manage on-camera presence, and create clear visual experiences through screen sharing. They handle technical challenges calmly while maintaining engagement throughout the conversation.
Visual pipelines and customizable dashboards make demonstrations more compelling by showing prospects how a real sales process would look in practice.
Build relationships digitally
Inside sales reps also build strong business relationships without in-person interaction by consistently delivering value and showing genuine interest in prospect success. A multichannel approach helps maintain presence across the buying journey.
Effective digital relationship building includes:
- Personalized interactions: Referencing past conversations and company milestones.
- Value-added content: Sharing relevant insights, trends, and resources.
- Consistent presence: Checking in regularly without applying pressure.
- Genuine expertise: Positioning as a trusted advisor rather than a seller.
During longer sales cycles, representatives maintain momentum by providing educational materials, industry analysis, and proactive recommendations. CRM data supports personalization by tracking key details about each prospect’s business, priorities, and preferences.
Manage pipeline and close deals
Inside sales representatives manage multiple opportunities at once while guiding each deal toward a successful close. This requires regular pipeline reviews, clear next-step planning, and early identification of potential risks.
The virtual closing process typically involves:
- Handling objections through video or phone conversations.
- Negotiating terms via email and calls.
- Coordinating contracts using digital signature tools.
- Recognizing buying signals, such as implementation questions or reference requests.
Pipeline visibility plays a critical role at this stage. Modern platforms like monday CRM help representatives track deal progress, automate reminders, and collaborate across teams. AI-powered insights assist by identifying sentiment, prioritizing high-value opportunities, and reducing manual updates.

Essential inside sales skills for 2026
Inside sales puts every interaction on display. There is no handshake to lean on, no on-site visit to build rapport. Progress depends on how clearly a rep communicates, how well they listen, how confidently they move through tools, and how effectively they manage their time.
The sections that follow break down the capabilities that truly move the needle. From running engaging virtual conversations to using CRM data with intention, from prioritizing the right deals to adapting quickly when buyers shift direction,
Master virtual communication
Clear and engaging virtual communication allows representatives to build rapport without physical presence. Messaging must adapt to each channel while remaining consistent in value and positioning.
Effective virtual communication techniques include:
- Vocal variation: Adjusting tone and pace to maintain attention.
- Strategic video use: Knowing when video strengthens connection.
- Compelling writing: Crafting subject lines that earn responses.
- Visual awareness: Identifying hesitation or excitement through voice cues.
Representatives develop a professional on-camera presence using thoughtful backgrounds, lighting, and body language. They also learn when phone or email is more effective than video.
Listen actively in digital conversations
Active listening in virtual settings requires heightened attention to tone, pauses, and unspoken concerns. Representatives confirm understanding through clarifying questions rather than assumptions.
Strong digital listening practices include:
- Detailed note-taking: Capturing critical information in real time.
- Follow-up questions: Uncovering deeper needs and priorities.
- Key point summaries: Ensuring alignment across stakeholders.
- Distraction management: Minimizing multitasking during calls.
- Strategic silence: Allowing space for thoughtful responses.
Navigate sales technology confidently
Technology proficiency has a direct impact on productivity and results. Inside sales representatives work across CRM systems, video platforms, email automation, and sales intelligence solutions.
Essential technical skills include:
- CRM efficiency: Log activities without disrupting workflow.
- Video troubleshooting: Resolve issues quickly to avoid awkward delays.
- Screen-sharing mastery: Highlight key features effectively.
- Automation leverage: Scale outreach without losing personalization.
Intuitive platforms like monday CRM reduce technology complexity with easy-to-use interfaces: reps can then focus on selling rather than fighting with software, using drag-and-drop pipelines and no-code automations to adapt processes instantly.
Manage time and priorities effectively
Inside sales representatives balance prospecting, follow-ups, live conversations, and administrative work throughout the day. Effective time management directly affects pipeline health and overall performance.
Effective prioritization means:
- High-value focus: Concentrate on opportunities most likely to close.
- Activity batching: Group similar tasks to maintain focus.
- Data-driven decisions: Use CRM insights to identify promising prospects.
- Pipeline balance: Maintain healthy prospecting while advancing current deals.
Analyze data for strategic decisions
Top-performing representatives rely on metrics and insights to refine their approach. They track conversion rates, response patterns, and pipeline velocity to understand what drives success.
Data analysis skills help representatives:
- Identify patterns: Recognize what makes deals successful.
- Adjust outreach: Modify approaches based on response data.
- Translate insights: Convert data into actionable strategies.
- Optimize timing: Determine best times for different activities.
Adapt quickly to change
Inside sales environments evolve rapidly due to new technologies, shifting markets, and changing buyer expectations. Representatives who adapt quickly maintain momentum and relevance.
Adaptation requires:
- Industry awareness: Staying current with market trends.
- Tool mastery: Learning new platforms as they emerge.
- Message flexibility: Refining positioning based on feedback.
- Principle focus: Applying core sales skills across changing tactics.

“With monday CRM, we’re finally able to adapt the platform to our needs — not the other way around. It gives us the flexibility to work smarter, cut costs, save time, and scale with confidence.”
Samuel Lobao | Contract Administrator & Special Projects, Strategix
“Now we have a lot less data, but it’s quality data. That change allows us to use AI confidently, without second-guessing the outputs.”
Elizabeth Gerbel | CEO
“Without monday CRM, we’d be chasing updates and fixing errors. Now we’re focused on growing the program — not just keeping up with it."
Quentin Williams | Head of Dropship, Freedom Furniture
“There’s probably about a 70% increase in efficiency in regards to the admin tasks that were removed and automated, which is a huge win for us.“
Kyle Dorman | Department Manager - Operations, Ray White
"monday CRM helps us make sure the right people have immediate visibility into the information they need so we're not wasting time."
Luca Pope | Global Client Solutions Manager at Black Mountain
“In a couple of weeks, all of the team members were using monday CRM fully. The automations and the many integrations, make monday CRM the best CRM in the market right now.”
Nuno Godinho | CIO at VelvBenefits of inside sales for revenue growth
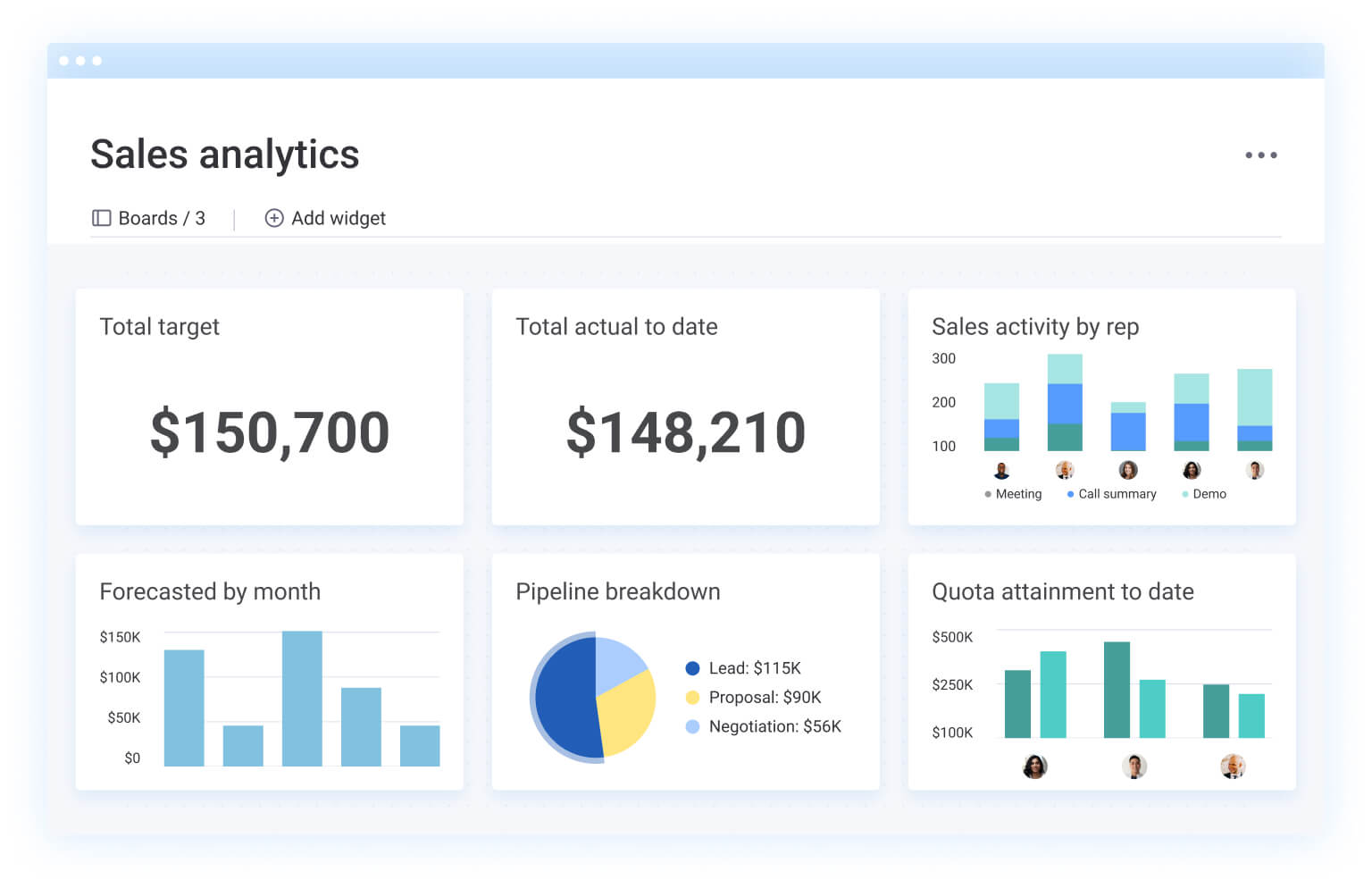
Before making the shift, it is important to understand both the immediate gains and the long-term advantages this model delivers.
Reduce costs without sacrificing results
Inside sales significantly lowers operating costs while maintaining strong performance. By eliminating travel expenses, reducing office requirements, and increasing daily prospect engagement, representatives spend more time selling and less time in transit.
Compared with field sales teams, inside sales representatives engage with a lot more prospects each day.
Many organizations see a 40–60% reduction in cost per lead while sustaining, or improving, conversion rates. The cost savings are significant, with the average U.S. domestic itinerary air fare reaching $397 in Q1 2025, illustrating the ongoing travel costs that inside sales largely avoids.
The cost improvements include:
- Lower overhead: Reduced per-representative expenses.
- No geographic limitations: Eliminate need for regional offices.
- Faster onboarding: Representatives reach productivity within 3-6 months versus 6-12 months for outside sales.
Accelerate sales cycles
Inside sales shortens time to close by enabling more frequent prospect interactions and faster response times. Representatives schedule multiple meetings each day without travel constraints, helping deals maintain momentum and move forward without unnecessary delays.
Questions are answered immediately, resources are shared instantly, and follow-ups happen quickly. This responsiveness keeps prospects engaged and reduces the risk of stalled opportunities.
Digital tools enable:
- Faster proposal delivery: Send documents for immediate review.
- Streamlined approvals: Reduce administrative delays.
- Quick follow-ups: Schedule meetings within days, not weeks.
- Maintained momentum: Prevent prospects from losing interest.
Organizations typically experience a 25–40% reduction in sales cycle length after transitioning to inside sales.
Scale without geographic limits
Inside sales also allows teams to expand into new markets without opening regional offices or hiring locally based representatives. Centralized teams can support prospects across time zones and regions, increasing reach without proportional cost increases.
Scaling advantages include:
- Territory flexibility: Reps can be added without geographic conflicts.
- International reach: Global markets can be served from a single location.
- Process consistency: Standards remain uniform across regions.
- Market testing: New opportunities can be evaluated quickly and efficiently.
Make smarter decisions with data
Every interaction in inside sales can be tracked and analyzed, creating a rich foundation for optimization. Calls, emails, and meetings provide insights into messaging effectiveness, common objections, and buying signals.
With consistent data, teams can move from assumptions to evidence-based decisions. Patterns become visible, enabling continuous improvement across the sales process.
Data-driven improvements help teams:
- Identify successful patterns: Replicate what works.
- Optimize timing: Determine best outreach schedules.
- Personalize approaches: Tailor strategies based on behavior.
- Enable coaching: Provide targeted feedback and training.
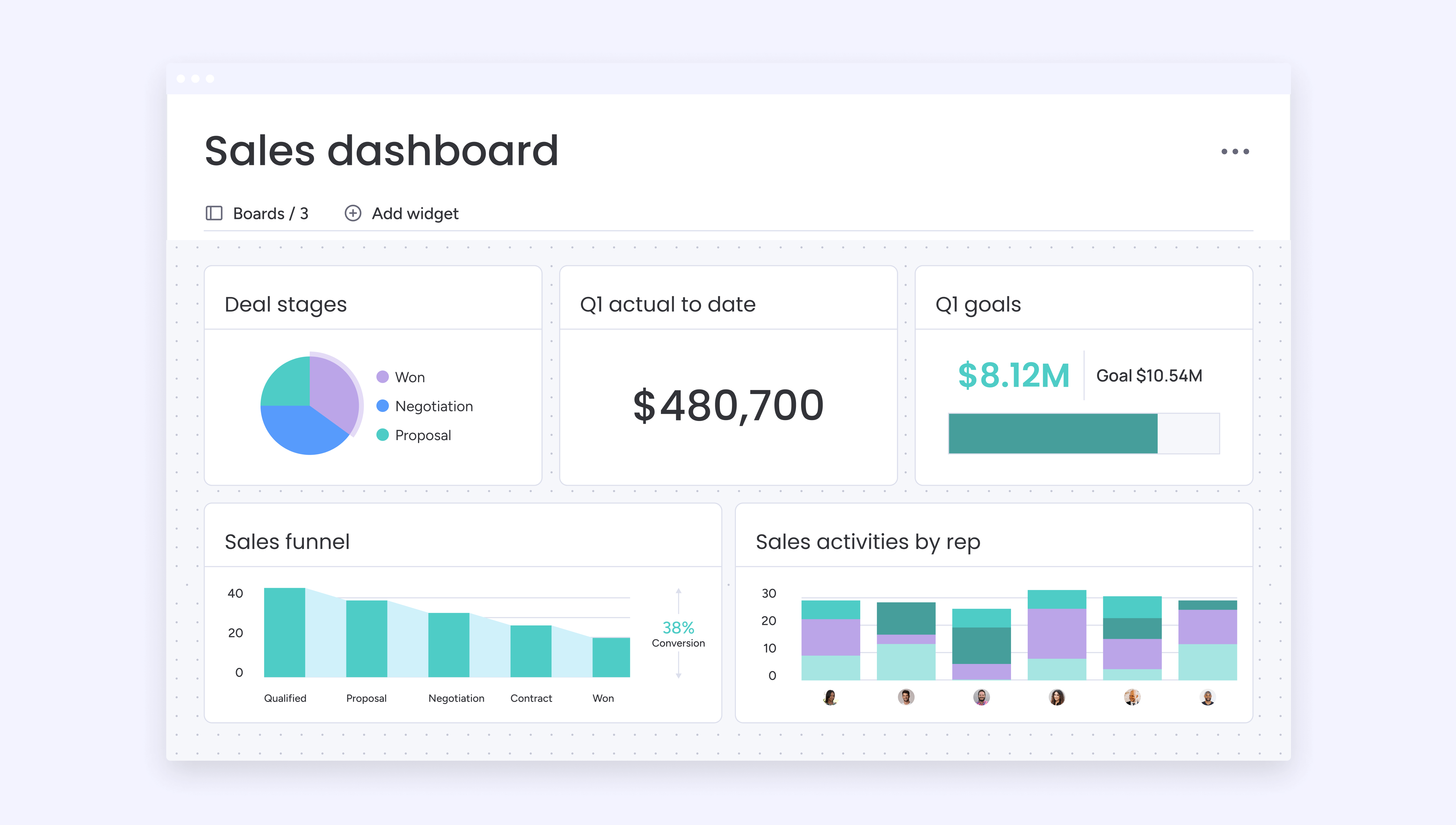
Analytics available through platforms like monday CRM provide real-time visibility into pipeline health, conversion rates, and individual performance. Custom dashboards highlight what is working, while AI-driven insights surface opportunities for improvement.
Build flexible, attractive careers
Inside sales roles appeal to experienced professionals seeking flexibility and balance. Removing geographic constraints allows organizations to recruit from broader talent pools and access specialized skills regardless of location.
The talent advantages include:
- Remote work options: Attract top performers regardless of location.
- Improved work-life balance: Reduce turnover through flexibility.
- Career progression: Provide paths to management and executive roles.
- Skill development: Build valuable technology and communication abilities.
Enable real-time coaching
Inside sales environments make continuous coaching easier and more effective. Managers can listen to calls, review written communications, and provide immediate guidance that drives improvement.
Collaboration extends beyond manager coaching:
- Team learning: Proven strategies are shared quickly.
- Collaborative problem-solving: Challenges are addressed collectively.
- Best practice sharing: Top performers set clear benchmarks.
- Targeted development: Coaching focuses on specific skill gaps.
Drive predictable growth with monday CRM
nside sales is not just about cutting travel costs. It changes the rhythm of your revenue team. Conversations happen faster, decisions rely on real data, and results depend on how well your process holds together under pressure.
When the foundation is strong, the advantages compound. Teams start to see:
- Faster response times: Prospects get answers quickly, which keeps deals moving and builds trust early.
Broader reach: Reps can work across regions and time zones without the limits of territory travel.
Continuous optimization: Performance data highlights what is working so teams can adjust in real time.
This approach is especially powerful for complex, consultative sales. Trust still matters. Expertise still matters. The difference is that everything is supported by clear visibility instead of scattered spreadsheets and guesswork.
monday CRM brings that visibility into one connected workspace. With it, teams can:
- See the full pipeline: Every deal, stage, and next step is clear at a glance.
Automate routine work: Follow-ups, reminders, and status changes happen without manual effort.
Use AI insights: High-priority deals and potential risks surface before they become problems.
Reps spend more time selling and less time updating systems. Leaders gain confidence in forecasts because the data is live and shared. That is when inside sales stops feeling reactive and starts driving steady, predictable growth.
Frequently asked questions
Is inside sales harder than outside sales?
Inside sales requires different skills rather than being inherently harder than outside sales. Success depends on matching individual strengths to role requirements — including strong virtual communication and technology skills for inside sales, compared with travel management and in-person relationship building for outside sales roles.
How much do inside sales representatives earn?
Entry-level sales development representatives (SDRs) typically earn $40,000–$60,000 annually, including base salary and commission. Experienced account executives often earn $80,000–$150,000 or more, depending on industry, company size, and individual performance, with top performers in high-value industries exceeding these ranges.
Can inside sales handle complex enterprise deals?
Inside sales effectively manages complex enterprise deals through virtual relationship building, structured discovery processes, and coordinated team selling. Many technology companies close seven-figure deals entirely through inside sales models, demonstrating that the approach works for high-value, complex sales when executed correctly.
What's the career path for inside sales professionals?
The typical career progression moves from SDR to account executive, followed by sales management roles such as sales director or VP of sales. Many professionals also transition into outside sales, marketing, customer success, or executive roles where revenue expertise continues to add value.
How do you measure inside sales performance?
Effective measurement combines activity metrics such as calls made and meetings scheduled, conversion rates from lead to opportunity and opportunity to close, and outcome metrics including revenue generated, deal size, and sales cycle length. Leading indicators help forecast performance, while lagging indicators reflect actual results.
Will AI replace inside sales representatives?
AI enhances rather than replaces inside sales representatives by managing administrative work and delivering actionable insights. Representatives remain focused on relationship building, complex problem-solving, and strategic thinking, while AI supports data entry, timeline summaries, and routine communications to improve overall productivity.