Revenue teams often celebrate hitting quarterly targets while 15% of the previous quarter’s customers quietly disappear. The math is brutal: every departing customer takes their future revenue with them, and replacing that loss costs five times more than retention would have.
Customer churn hits where it hurts most: growth runway, revenue certainty, and ultimately, company valuation. Whether customers cancel subscriptions or simply stop buying, churn creates revenue leakage that compounds over time. Understanding what drives these departures gives leaders the foundation to build strategies that actually work.
This guide digs into what churn really means for your bottom line, identifies the most accurate ways to measure it, and outlines specific strategies to tackle different types of customer departures.
Key takeaways
- Track churn early to save customers before they leave: monitor usage patterns, support tickets, and engagement drops to spot at-risk customers 30-90 days before they actually churn.
- Focus on both customer count and revenue impact: a 5% monthly churn rate compounds to 46% annual loss, requiring massive acquisition just to stay flat before any growth happens.
- Perfect your onboarding to prevent early departures: customers who complete structured onboarding show 40-60% higher retention than those who struggle through self-implementation.
- Use health monitoring to automate retention: set up real-time dashboards that track customer engagement and trigger proactive outreach when health scores drop into danger zones.
- Win back churned customers with targeted campaigns: 10-30% of churned customers will return when you address their original departure reasons with improved features or personalized offers through platforms like monday CRM.
What is customer churn?
Customer churn occurs when customers end their business relationship with your company through subscription cancellations, contract non-renewals, or purchase cessation. Every business experiences churn across software, physical products, and professional services.
Understanding the different types of churn allows you to build growth plans that deliver. By categorizing why customers leave, you can make smarter calls about resource allocation and apply the specific strategies needed to protect your revenue.
Customer churn definition
Customer churn tracks how fast you’re losing customers over time. Most teams track it as a percentage: monthly for subscription businesses, quarterly or annually for longer sales cycles.
Customer churn specifically measures the number of customers or accounts lost during a given period, rather than the revenue impact of those losses. For example, if a company begins a quarter with 1,000 customers and loses 50 by quarter-end, this represents a 5% quarterly churn rate.
Key measurement considerations:
- Time period selection: monthly churn compounds differently than annual rates.
- Comparison accuracy: comparing churn across different time frames requires careful calculation.
- Business model alignment: shorter sales cycles usually track monthly churn, while annual contracts focus on yearly rates.
Voluntary vs involuntary churn
Customer departures fall into two distinct categories based on why they leave. Understanding this distinction helps you develop targeted prevention strategies for each type.
Voluntary churn happens when customers actively choose to leave. Common reasons include:
- Service quality dissatisfaction: customers become unhappy with your product performance or support experience.
- Competitive displacement: customers find a competitor offering they prefer.
- Need elimination: customers no longer require what you’re offering.
- Value perception mismatch: customers decide you’re not worth the price.
This type of churn often signals deeper issues; maybe your product doesn’t quite fit the market, your competitors are outmaneuvering you, or your customer experience needs work.
Involuntary churn occurs when customers leave due to circumstances beyond their direct control:
- Failed payment processing: transactions decline due to insufficient funds or bank restrictions.
- Expired credit cards: payment methods reach expiration dates without customer updates.
- Outdated billing information: address changes or new payment details never make it into the system.
- Technical glitches: system errors prevent successful payment processing or service continuation.
These are customers who wanted to stay but got lost due to operational or technical friction. Revenue teams can leverage automated payment tracking to identify involuntary churn patterns early, enabling proactive outreach before customers slip away due to preventable technical issues.
Customer churn vs revenue churn
These two metrics measure different aspects of customer loss and give you complementary insights for your revenue team. Customer churn counts how many people or accounts are leaving, while revenue churn measures the financial impact of those departures.
| Metric | Customer churn | Revenue churn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of customers who stop using the product | Percentage of recurring revenue lost from existing customers |
| Calculation | (Customers lost ÷ Starting customers) × 100 | (Revenue lost ÷ Starting MRR) × 100 |
| Business impact | Measures relationship volume and customer base health | Measures financial impact and revenue sustainability |
| Strategic focus | Customer success, retention programs, product adoption | Pricing strategy, expansion revenue, account management |
| Example scenario | Losing ten customers represents 10% customer churn | Losing one enterprise customer might represent 15% revenue churn |
Low customer churn paired with high revenue churn indicates you are losing high-value enterprise accounts. Conversely, high customer churn with low revenue churn suggests a loss of many small accounts while keeping your “whales.”
How to calculate customer churn rate?
Accurate churn measurement is the foundation of any retention strategy. Without precise calculations, you cannot identify trends or measure if your improvement efforts are working. Follow these three steps to audit your performance.
Step 1: apply the basic customer churn formula
The standard formula for calculating customer churn rate is straightforward:
(Customers Lost During Period ÷ Customers at Start of Period) × 100
Let’s break down each component to ensure accurate calculation:
- Customers lost during period: total customers who ended their relationship during your measurement time frame, including both voluntary cancellations and involuntary losses.
- Customers at the start of the period: total active customers at the beginning of your measurement period, before any losses or additions.
- Calculation result: a percentage representing the proportion of your customer base lost.
Practical example:
Your company starts January with 1,000 customers. By month-end, 50 customers have churned. Your monthly churn rate calculation is (50 ÷ 1,000) × 100 = 5%. This means you lost 5% of your customer base during January.
Common calculation mistakes to avoid:
- Denominator consistency: only count customers from the start of the period in your denominator to maintain calculation accuracy.
- Churn definition clarity: be consistent about when you consider customers “churned” versus temporarily inactive.
Step 2: choose between monthly vs annual calculations
Your measurement time frame matters. Monthly numbers help you spot problems fast, while annual rates give you the big picture for strategic planning.
| Aspect | Monthly churn rate | Annual churn rate |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | SaaS, subscription services, short sales cycles | Insurance, enterprise contracts, long sales cycles |
| Calculation period | Single month measurement | Full year or rolling twelve months |
| Compounding effect | 5% monthly = ~46% annual (compounded) | Direct annual measurement |
| Strategic use | Rapid iteration, quick trend identification | Long-term planning, board reporting |
| Sensitivity | Detects changes quickly, more volatile | Smooths seasonal variations, more stable |
It’s important to remember that monthly churn compounds. For an accurate annual projection, you must account for the shrinking customer base each month. It compounds, making the damage far worse over time. A 5% monthly churn rate doesn’t equal 60% annual churn (5% × 12 months). Instead, it compounds to approximately 46% annual churn because your customer base shrinks each month.
Conversion formula:
1 – (1 – monthly churn rate)^12
When to use each approach:
- Monthly tracking: businesses with monthly billing cycles and short customer lifecycles benefit from rapid response capabilities.
- Annual tracking: companies with annual contracts find yearly rates more strategically relevant since they align with renewal cycles.
Step 3: connect churn to revenue metrics
To understand the full financial impact, you must connect churn to the following two metrics:
Net Revenue Retention (NRR) measures revenue growth from existing customers minus revenue lost from churn:
- Formula: (Starting MRR + Expansion Revenue – Churned Revenue) ÷ Starting MRR × 100.
- Benchmark: NRR above 100% indicates your business is growing revenue from existing customers even after accounting for churn.
- Example: a company with $100,000 starting MRR that gains $20,000 in expansion revenue but loses $15,000 to churn has 105% NRR.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) represents the total revenue expected from a customer relationship:
- Lifespan calculation: 1 ÷ churn rate (5% monthly churn = 20-month average lifespan).
- CLV formula: (Average Revenue per Customer × Gross Margin) ÷ Churn Rate.
- Impact: higher churn rates reduce both NRR and CLV, making customer acquisition more expensive.
Revenue teams leveraging forecasting capabilities provided by platforms like monday CRM can predict these metrics by analyzing historical churn patterns, expansion trends, and customer cohort performance.
Why does customer churn matter for every business?
Churn isn’t just lost customers; it’s a wrecking ball to your financial forecasts, resource planning, and growth trajectory. It fundamentally changes how executives make decisions and ultimately determines whether you’ll thrive or merely survive. Understanding these impacts helps you prioritize retention investments and make informed strategic decisions.
Financial impact of customer churn
Customer churn creates revenue leakage that compounds over time, reducing the predictable recurring revenue that investors and executives rely on for planning and valuation. Each churned customer represents not just their current monthly or annual payment, but the entire future revenue stream they would have generated.
Immediate financial impacts:
- Revenue disappears instantly: monthly or annual payments vanish from your books the moment customers leave.
- Forecast gaps emerge: unexpected departures create holes in financial projections you were counting on.
- Acquisition becomes mandatory: you must sign new customers just to maintain current revenue before any growth happens.
- Planning becomes unreliable: unpredictable churn makes resource allocation decisions increasingly difficult.
Long-term financial consequences:
- Valuation multiples decline: investors apply lower valuations to companies with high churn rates.
- Growth gets delayed: revenue lost to churn must be replaced before any net growth can occur.
- Strategic flexibility shrinks: the growth tax imposed by churn limits expansion speed and market opportunities.
- Investor confidence erodes: high churn rates damage deal valuations and funding prospects.
The compounding nature of churn creates an accelerating decline. A 5% monthly churn rate doesn’t just reduce your customer base by 5% monthly; it requires increasingly aggressive acquisition efforts to overcome.
Churn rate vs customer acquisition costs
The relationship between retention and acquisition determines business sustainability. Because customer acquisition typically costs five to seven times more than retention, reducing churn is one of the highest-ROI activities for any revenue team.
High churn puts you on a “growth treadmill” that keeps speeding up. If you have a 10% monthly churn rate, your team is exhausted just replacing the customers walking out the door before adding a single dollar of actual growth.
Resource allocation considerations:
- Unsustainable growth models: sales teams focused entirely on new business while existing customers churn create growth that can’t last.
- Balanced investment strategies: the most efficient growth strategies balance acquisition investment with systematic retention efforts.
- Reduced growth tax: churn reduction reduces the growth tax imposed by customer departures.
Unified platforms provide visibility into both lead management and customer success tracking, helping revenue leaders optimize the acquisition-retention investment mix based on actual performance data rather than assumptions.
How churn affects business growth and valuation?
Churn rate fundamentally determines whether your business can achieve sustainable growth and what valuation multiples it commands in the market. The impact extends beyond immediate revenue to affect strategic flexibility and market positioning.
Growth impacts:
- Reduced expansion opportunities: high churn limits the customer base available for upselling and cross-selling.
- Slower market penetration: resources diverted to replacing churned customers reduce capacity for new market expansion.
- Competitive positioning challenges: focus shifts from growth initiatives to retention firefighting.
Valuation impacts:
- Lower multiples: investors apply reduced valuations to companies with high churn due to product-market fit concerns.
- Strategic limitations: high churn restricts flexibility for expansion, partnerships, and market positioning.
- Predictability issues: unpredictable churn makes accurate forecasting and resource planning difficult.
Predictable churn rates enable accurate forecasting and resource planning. Revenue leaders who understand their churn patterns can accurately model future customer counts, revenue trajectories, and resource requirements.

7 leading causes of customer churn
Know why customers bail and you can fix the real problems, not just slap band-aids on the symptoms. Each churn driver requires specific identification methods and intervention approaches. Therefore, recognizing these patterns early allows you to implement preventive measures before customers make final departure decisions.
1. Poor product-market fit
Product-market fit issues manifest as fundamental misalignment between customer needs and product capabilities. Customers who churn due to fit problems typically use only basic features, maintain short engagement periods, and struggle to articulate the product’s value within their organization.
Warning signs through usage patterns and feedback:
- Limited feature adoption: customers complete onboarding but never expand usage beyond initial setup.
- Narrow implementation: teams adopt the product for one use case but resist broader implementation.
- Feature mismatch: accounts consistently ask for features outside the product’s core value proposition.
- Segment variance: different customer segments experience fit issues differently; what works for small businesses may not serve enterprise needs.
Teams using platforms like monday CRM can identify fit issues through engagement pattern analysis, revealing which customer segments actively use the platform versus those who struggle to find value. This visibility enables early intervention and potential repositioning before customers decide to leave.
2. Inadequate customer support experience
Support experience quality creates emotional associations with your brand that persist beyond individual issue resolution. Poor support doesn’t just fail to solve problems. It actively damages customer relationships and accelerates churn decisions.
Common support failures that drive churn:
- Unresolved issues: multiple interactions without resolution create frustration and erode confidence.
- Information repetition: customers forced to repeat issues to different representatives experience compounding friction.
- Reactive discovery: when customers discover issues themselves rather than being notified proactively, they feel neglected.
- Conflicting guidance: different representatives providing inconsistent information damages trust.
A unified communication timeline prevents information gaps by maintaining complete interaction history accessible to all team members. This visibility ensures consistent support experiences and enables proactive issue identification before customers escalate concerns.
3. Pricing and value perception mismatch
Customers evaluate ROI and value realization continuously throughout their relationship with a product. When perceived value falls below pricing expectations, churn risk increases regardless of actual product quality or feature set.
Value perception changes throughout the customer lifecycle. Initial enthusiasm during the sales process gives way to practical evaluation during implementation, then ongoing assessment during regular usage.
Common value perception triggers:
- Unexpected costs: hidden fees or surprise charges that weren’t disclosed during the sales process.
- Pricing increases: rate hikes without corresponding value improvements or new features.
- Competitive alternatives: competitors offering improved perceived value-to-price ratios.
Prevention strategies:
- Pricing transparency: clear communication of all costs throughout the customer journey.
- Regular value demonstration: usage reports and ROI analysis that quantify product impact.
- Success metrics tracking: documented outcomes that reinforce pricing-value alignment.
Deal tracking capabilities in solutions like monday CRM help sales teams address pricing concerns proactively by documenting value realization and ROI throughout the customer relationship.
4. Low product adoption and engagement
Product adoption depth, not just login frequency, determines customer stickiness and long-term retention. Customers who use only surface-level features remain vulnerable to churn because they haven’t embedded the product into critical workflows.
Key adoption indicators:
- Feature usage breadth: number of different features or modules actively used by the customer team.
- User participation rate: percentage of licensed users who regularly engage with the product.
- Integration depth: number of connected platforms and systems creating switching costs.
- Workflow embedding: degree to which the product becomes essential to daily operations.
Engagement warning signs:
- Declining usage patterns: login frequency and session duration decrease steadily over time.
- Feature abandonment: customers stop using advanced capabilities after initial trial periods.
- Reduced team participation: fewer team members actively engage with the product compared to onboarding.
These indicators typically precede churn decisions by weeks or months, providing intervention opportunities. Customer health scoring in modern platforms like monday CRM monitors engagement levels automatically, alerting success teams when adoption metrics decline below healthy thresholds.
5. Superior competitor alternatives
Competitive displacement occurs when customers perceive alternatives offering improved features, pricing, or positioning.
The evaluation process customers undergo when considering alternatives typically follows this pattern: initial awareness of competitor options, active comparison of capabilities and pricing, trial or proof-of-concept testing, and finally migration decision.
Customers rarely switch to inferior alternatives; they leave because they believe the competitor serves their needs more effectively. Differentiation and unique value proposition maintenance become critical for retention.
Prevention approaches:
- Regular competitive analysis: monitor competitor positioning and refine your differentiation based on market changes.
- Proactive roadmap communication: share product improvements and upcoming features before customers discover alternatives.
- Competitive intelligence tracking: capture competitor mentions within customer interactions to identify displacement patterns early.
Competitive intelligence tracking within deal records enables teams to monitor competitor mentions, track win-loss reasons, and identify patterns in competitive displacement.
6. Ineffective customer onboarding
Onboarding represents the process of achieving initial value realization, not just completing setup tasks. Poor onboarding creates early churn risk by failing to demonstrate value quickly and setting negative expectations for the ongoing customer experience.
Successful onboarding requirements:
- Time-to-value expectations: customers need to understand when they’ll see results and what milestones indicate progress.
- Structured implementation paths: step-by-step guidance moves customers from setup through initial value achievement to expanded usage.
- Adequate training and enablement: resources and support enable customers to use the product effectively without constant assistance.
- Early win identification: quick successes build confidence and justify the purchase decision.
Common onboarding failures:
- Unclear expectations: customers don’t understand implementation timelines or what milestones indicate progress.
- Delayed value delivery: time-to-value extends beyond customer patience thresholds.
- Insufficient training: customers lack resources to leverage product capabilities effectively.
Project management capabilities enable structured onboarding processes with milestones, task assignments, and progress tracking that ensure consistent customer experiences.
7. Lack of personalization at scale
Generic approaches fail to address specific customer needs and use cases, creating experiences that feel irrelevant despite product quality.
Personalization means delivering relevant, timely communication and product experiences based on customer behavior, preferences, and business context.
The challenge of maintaining personal touch as your customer base grows drives many companies toward generic, one-size-fits-all approaches that accelerate churn. Customers expect communication that reflects their specific usage patterns, industry context, and business challenges.
Personalization components:
- Communication relevance: emails that reference specific customer actions feel more valuable than generic newsletters.
- Product customization: interfaces that adapt to user preferences and common workflows reduce friction.
- Behavioral adaptation: product experiences should adapt to individual workflows rather than forcing standardized processes.
AI-powered personalization capabilities in monday CRM enable customer interactions that feel individually tailored even at scale, using behavioral data to customize communication timing, content, and channel selection.
How to identify at-risk customers using predictive analytics?
Early identification of churn risk enables proactive intervention before customers make final departure decisions. Because behavioral indicators typically precede actual churn by weeks or months, they create critical windows for improving retention outcomes.
This section covers the warning signs, behavioral patterns, and monitoring systems essential for effective churn prevention.
1. Early warning signs of potential churn
Specific, measurable indicators consistently precede customer churn across industries. Recognizing these patterns enables timely intervention to prevent customer loss.
For instance, communication pattern changes often signal disengagement; when previously responsive customers begin delaying replies or ignoring messages, they are likely evaluating alternatives.
Usage decline indicators:
- Reduced login frequency: customers access the platform less often compared to their historical patterns.
- Narrowed feature usage: accounts retreat to basic capabilities only, abandoning advanced features they previously used.
- Decreased team participation: fewer team members actively engage with the product below historical averages.
Support engagement changes:
- Support ticket increases: ticket volume rises above historical baseline, indicating growing friction.
- Basic issues or repeated problems: customers struggle with fundamental functionality, signaling frustration.
- Functionality struggles: persistent problems with core features indicate eroding patience and confidence.
Contract negotiation delays:
- Postponed renewal discussions: customers delay or avoid conversations about contract renewal.
- Significant pricing concessions: requests for substantial discounts suggest value perception issues.
- New stakeholders introduced: unfamiliar decision-makers appear late in the renewal process, often signaling competitive evaluation.
The typical timeline from warning signs to actual churn spans 30-90 days depending on contract terms and switching costs. Automated alert systems in advanced solutions like monday CRM track these indicators across the customer base, notifying success teams immediately when risk patterns emerge.
2. Behavioral indicators and usage patterns
Customer behavior data reveals risk patterns long before a conscious departure decision is made. Understanding healthy versus at-risk patterns enables accurate risk assessment and prioritized intervention.
| Behavioral dimension | Healthy customer patterns | At-risk customer patterns |
|---|---|---|
| Login frequency | Consistent daily or weekly logins by multiple team members | Declining login frequency, single-user access only |
| Feature usage | Expanding feature adoption over time, exploring new capabilities | Contracting to basic features only, abandoning advanced capabilities |
| Team participation | Growing number of active users, cross-departmental adoption | Declining active user count, single-department usage |
| Integration activity | Increasing connected platforms, data flowing between systems | Disconnecting integrations, reducing data synchronization |
| Support engagement | Proactive feature questions, expansion discussions | Reactive problem reports, basic functionality issues |
Furthermore, consider your specific segment:
- Enterprise customers: typically show slower adoption curves but deeper integration over time.
- Small business customers: often demonstrate rapid initial adoption but may plateau quickly.
- Pattern recognition: understanding segment-specific healthy patterns enables accurate risk identification.
Behavioral tracking through activity monitoring captures these patterns automatically, comparing individual customer behavior against segment benchmarks and historical trends to identify meaningful deviations that signal churn risk.
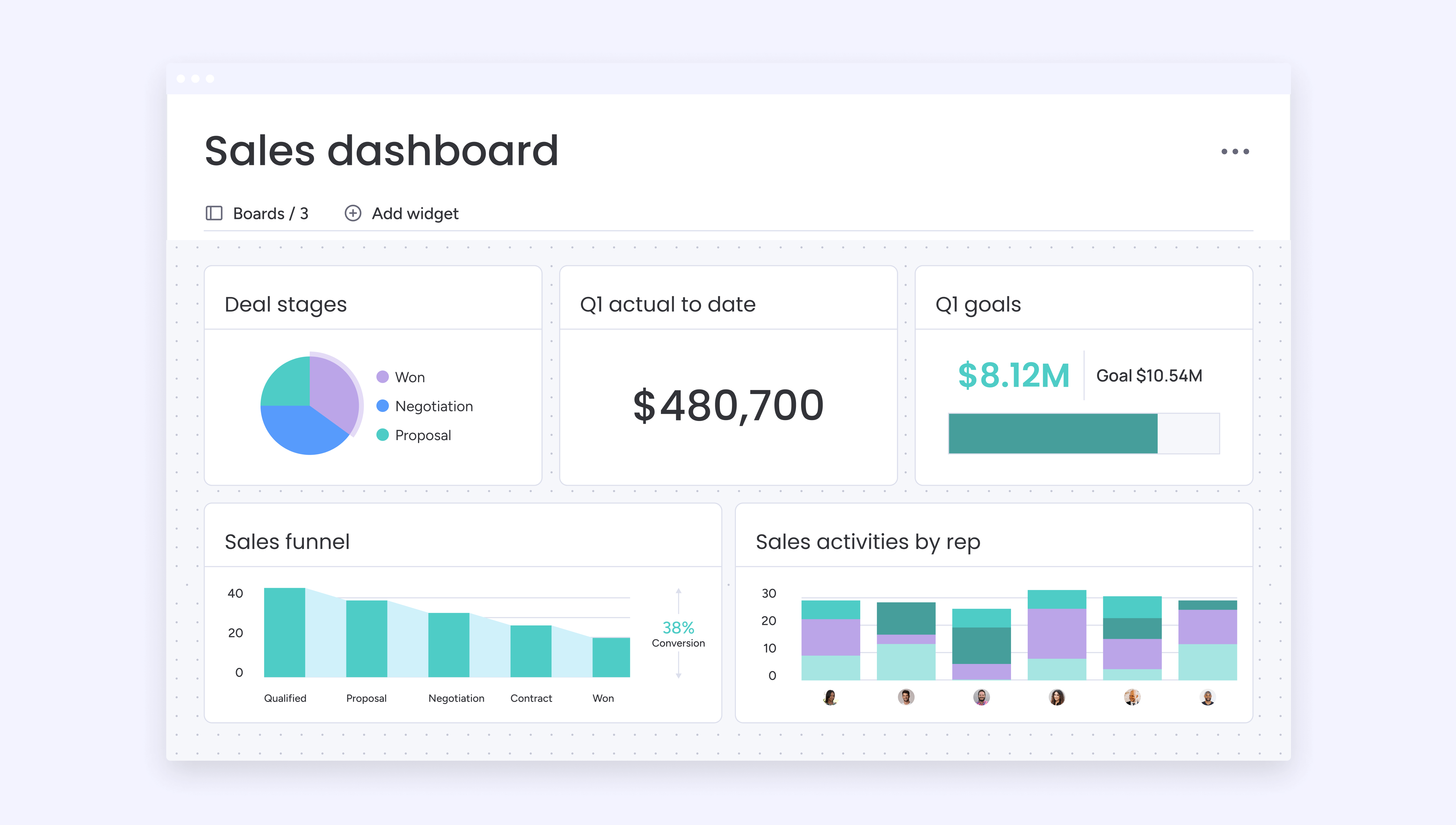
3. Real-time customer health dashboards
The most effective monitoring setups consolidate all relevant data into a single, comprehensive health score. You’ll spot trouble fast and know exactly which fires to put out first. Real-time visibility transforms churn prevention from reactive firefighting to proactive relationship management.
Essential dashboard elements:
- Composite health scores: combine usage, engagement, support, and financial indicators into overall customer health ratings for quick prioritization.
- Visual trend representations: health score changes over time reveal improving or declining customer relationships.
- Automated notifications: trigger when health scores cross critical thresholds or when specific risk indicators appear.
- Predefined workflows: activate automatically based on health score changes, such as assigning success manager outreach tasks when scores enter yellow zones.
Customization considerations:
- Indicator weighting: different metrics require different emphasis based on your business model and customer segments.
- Model-specific priorities: SaaS companies might weigh usage metrics heavily, while service businesses prioritize communication engagement.
- Real-time visibility: proactive intervention requires immediate updates as waiting for monthly reports means missing critical intervention windows.
Keeping that in mind, customization is key. SaaS companies might weigh usage metrics heavily, while service businesses prioritize communication engagement. Platforms like monday CRM allow teams to configure these algorithms and design layouts that surface the most critical information for their specific context.
8 data-driven strategies to reduce customer churn
To cut churn effectively, you must move past guesswork and build a repeatable system. These eight data-driven strategies connect specific actions to retention outcomes, allowing you to scale your efforts as your business grows.
Strategy 1: optimize your customer onboarding process
Onboarding optimization means systematic improvement based on data analysis of successful versus unsuccessful customer implementations. Track these key metrics to guide your optimization efforts: time to first value, feature adoption rates during first 30/60/90 days, and early engagement indicators like team member invitation rates and integration connections.
Optimization tactics that drive retention:
- Milestone-based progression: structure onboarding into phases with specific success criteria for advancement.
- Time-to-value acceleration: identify and eliminate friction points that delay initial value realization.
- Personalized implementation paths: create different onboarding tracks based on customer segment, use case, or technical sophistication.
Onboarding success correlates strongly with long-term retention rates. Customers who complete structured onboarding programs show 40-60% higher retention than those who self-implement without guidance.
Project management features in modern solutions like monday CRM enable onboarding workflow standardization with templates, automated task assignments, and progress tracking that ensures consistent implementation experiences.
Strategy 2: deploy proactive customer success programs
Proactive success means anticipating needs rather than reacting to problems. Build your program around scheduled lifecycle check-ins, automated usage alerts, and expansion planning. Crucially, start renewal preparations 90–120 days before a contract ends to secure the relationship early.
Success program elements that prevent churn:
- Quarterly business reviews: review customer goals, product usage, ROI achievement, and future objectives.
- Systematic engagement tracking: monitor customer engagement metrics with defined intervention triggers.
- Collaborative goal-setting: define success metrics and create shared commitment to outcomes.
Resource allocation models:
- High-touch models: dedicated success managers serve enterprise accounts with personalized attention and strategic guidance.
- Tech-touch approaches: automated outreach and self-service resources serve smaller customers efficiently at scale.
Customer success tracking and communication management capabilities enable both high-touch and tech-touch programs from a unified platform.
Strategy 3: personalize every customer touchpoint
Personalization means delivering relevant, contextual communication based on customer data rather than generic messaging that ignores individual circumstances. Map all customer interactions to create customization opportunities for each touchpoint.
Personalization opportunities that reduce churn:
- Behavioral email triggers: send messages based on specific customer actions rather than calendar schedules.
- Industry-specific content: deliver case studies and feature guidance relevant to customer industry and use case.
- Usage-based recommendations: suggest features or workflows based on current product usage patterns.
Data-driven personalization uses customer behavior, preferences, and business context to customize interactions. Customers who receive personalized communication show 30-40% higher engagement rates than those receiving generic outreach. AI-powered personalization features analyze behavioral data to optimize message timing, content selection, and channel choice automatically.
Strategy 4: establish continuous feedback mechanisms
Systematic feedback collection and analysis processes reveal customer satisfaction trends and product improvement priorities. Multiple feedback channels provide comprehensive understanding of customer needs and pain points.
Feedback methods that inform retention strategies:
- In-app surveys: triggered by specific user actions to capture feedback when experiences are fresh.
- Customer advisory boards: representative customers provide strategic product feedback and validate roadmap priorities.
- Support conversation analysis: systematic review identifies recurring issues and feature gaps.
Closing the feedback loop:
- Communicate changes made: share product updates and improvements that resulted directly from customer feedback.
- Explain roadmap decisions: acknowledge suggestions and provide context for prioritization choices and implementation timelines.
- Track implementation progress: demonstrate responsiveness by documenting how customer input shapes product development.
Feedback tracking and analysis capabilities within customer records enable systematic collection, categorization, and action tracking for customer input.
Strategy 5: align pricing with customer value
Value-based pricing strategies reduce price-related churn by ensuring customers perceive fair exchange between cost and benefit. Demonstrate value through ROI calculators, usage reports, and comparative analysis showing performance improvements since customer onboarding.
Value alignment tactics:
- Transparent pricing structure: clear communication of costs and billing terms eliminates surprise expenses.
- Value-metric pricing: align pricing to customer success metrics rather than arbitrary limits.
- Regular value reviews: scheduled discussions quantify ROI and demonstrate ongoing value delivery.
Pricing transparency and competitive positioning both influence value perception. Customers who understand exactly what they’re paying for and why show lower price sensitivity than those confused by complex pricing structures.
Modern CRM platforms enable teams to document value realization and ROI throughout the customer relationship, supporting renewal conversations with concrete performance data that reinforces pricing decisions.
Strategy 6: design engaging loyalty and rewards programs
Loyalty programs create systematic customer appreciation and incentive systems that increase customer stickiness through recognition and exclusive benefits. Design your program around meaningful rewards that customers actually value, achievable milestones that create regular positive reinforcement, and exclusive benefits that make customers feel special and appreciated.
Program elements that reduce churn:
- Tenure-based rewards: recognize customer longevity with anniversary gifts or exclusive features.
- Advocacy incentives: reward customers who provide referrals or testimonials with account credits or premium features.
- Community access: create exclusive communities or events for loyal customers that provide networking opportunities.
Program types by business model:
- B2B companies: often focus on executive networking and strategic partnership opportunities.
- B2C businesses: might emphasize points, discounts, and exclusive access.
Customer segmentation capabilities enable targeted loyalty program management based on customer value, engagement level, and advocacy potential.
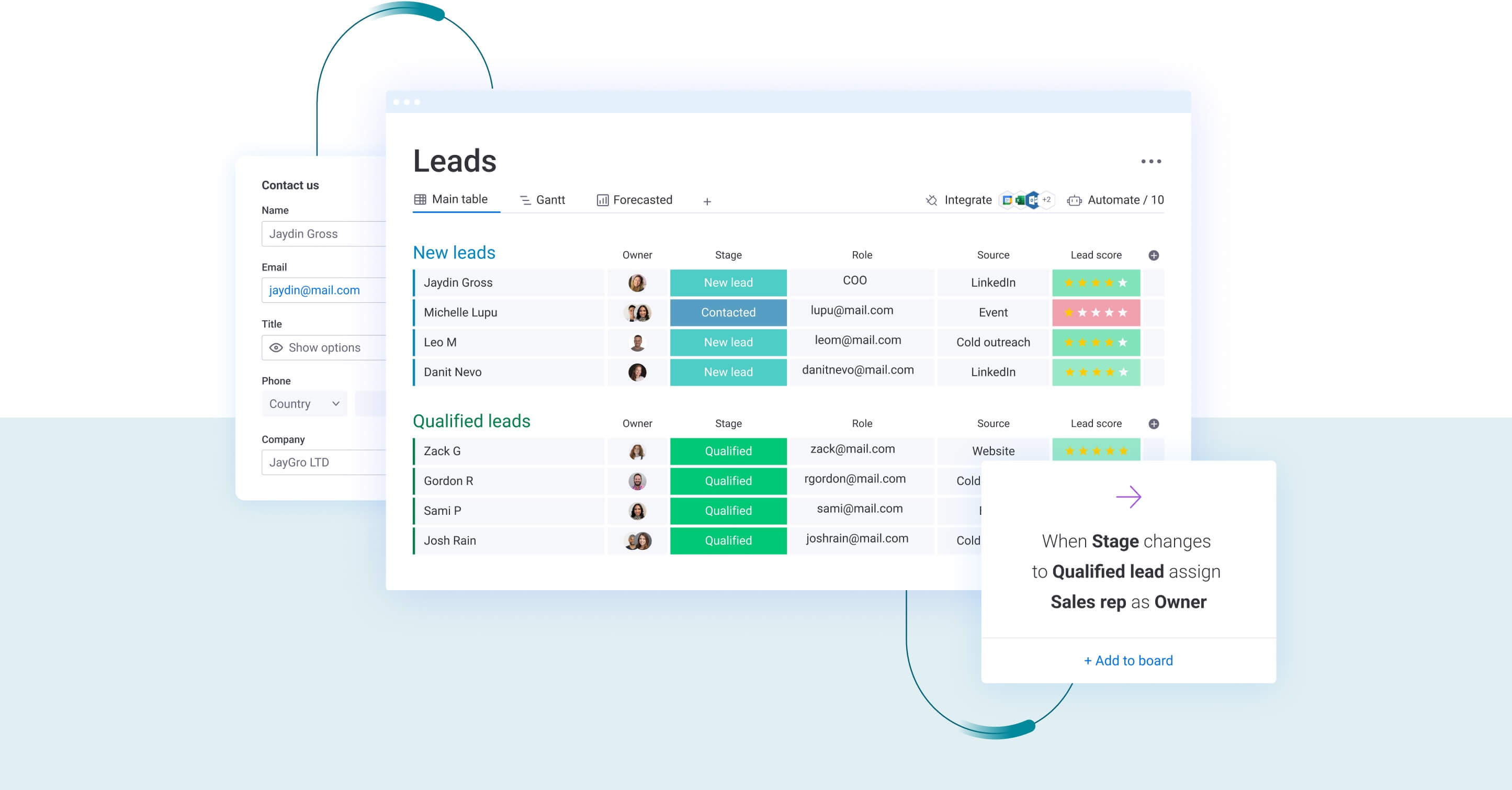
Strategy 7: automate retention workflows and triggers
Workflow automation enables consistent, scalable retention efforts that don’t require constant manual intervention. Trigger-based systems respond automatically to specific customer behaviors or risk indicators, ensuring timely intervention without team member oversight for every situation.
Automation opportunities that prevent churn:
- Usage decline responses: automatically trigger re-engagement campaigns when customer activity drops below thresholds.
- Renewal preparation: initiate renewal workflows 90-120 days before contract end.
- Expansion identification: automatically flag accounts showing expansion signals and assign opportunity development tasks.
Sample retention workflow:
- Customer health score drops to yellow zone: automated monitoring detects declining engagement and triggers retention workflow.
- AI analyzes usage patterns and identifies likely cause: system reviews behavioral data to pinpoint specific risk factors driving the decline.
- System assigns task to success manager with personalized outreach template: workflow creates intervention task with context-specific messaging based on identified issues.
- Automated follow-up reminders ensure timely response: scheduled notifications keep retention efforts on track without manual oversight.
- If health score doesn’t improve within 14 days, escalate to management for strategic intervention: persistent risk triggers executive involvement for high-stakes retention decisions.
Automation capabilities for retention process management in solutions like monday CRM enable sophisticated workflows that scale with customer base growth while maintaining personalization and timely intervention.
Strategy 8: launch strategic win-back campaigns
Win-back campaigns represent systematic efforts to re-engage churned customers through targeted outreach that addresses their original departure reasons. Campaign timing matters significantly — immediate win-back attempts address recent decisions while memories are still fresh, while delayed campaigns target customers whose circumstances may have changed.
Campaign elements that drive successful win-back:
- Segmented messaging: customize win-back communications based on churn reason.
- Product improvement highlights: showcase new features or capabilities implemented since customer departure.
- Limited-time incentives: offer time-bound pricing discounts or exclusive features that create urgency.
Success measurement and optimization:
- Track win-back rates by segment: measure success by churn reason and time since departure to identify the most effective re-engagement approaches.
- Typical win-back success rates: range from 10-30% depending on industry and churn cause, with higher rates for involuntary churn.
- Customers who return after churning: often show higher lifetime value than new customers because they understand the product and made conscious decisions to return.
Campaign tracking and customer re-engagement workflow capabilities enable systematic win-back program management with automated outreach sequences, response tracking, and conversion measurement.

“With monday CRM, we’re finally able to adapt the platform to our needs — not the other way around. It gives us the flexibility to work smarter, cut costs, save time, and scale with confidence.”
Samuel Lobao | Contract Administrator & Special Projects, Strategix
“Now we have a lot less data, but it’s quality data. That change allows us to use AI confidently, without second-guessing the outputs.”
Elizabeth Gerbel | CEO
“Without monday CRM, we’d be chasing updates and fixing errors. Now we’re focused on growing the program — not just keeping up with it."
Quentin Williams | Head of Dropship, Freedom Furniture
“There’s probably about a 70% increase in efficiency in regards to the admin tasks that were removed and automated, which is a huge win for us.“
Kyle Dorman | Department Manager - Operations, Ray White
"monday CRM helps us make sure the right people have immediate visibility into the information they need so we're not wasting time."
Luca Pope | Global Client Solutions Manager at Black Mountain
“In a couple of weeks, all of the team members were using monday CRM fully. The automations and the many integrations, make monday CRM the best CRM in the market right now.”
Nuno Godinho | CIO at VelvTransform churn into a strategic growth driver
Customer churn is a critical threat that destabilizes revenue, stifles growth, and erodes company valuation. To move beyond treating symptoms, businesses must understand the nuances of churn — distinguishing between voluntary and involuntary losses, as well as the difference between customer count and revenue impact.
Success depends on early detection. By leveraging predictive analytics and real-time health dashboards, revenue teams can spot at-risk behavior months in advance. This proactive window allows for strategic interventions that significantly shift retention outcomes before a customer decides to leave.
Ultimately, managing churn is a high-ROI investment. Reducing departures increases lifetime value, lowers acquisition costs, and stabilizes predictability. For scaling organizations, mastering customer retention transforms a defensive necessity into a powerful engine for long-term growth.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com’s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.
Frequently asked questions
What does 5% churn mean for my business?
A 5% monthly churn rate means you're losing 5% of your customer base each month, which compounds to approximately 46% annual customer loss. This requires significant new customer acquisition just to maintain current revenue levels before any net growth can occur, effectively creating a growth tax that limits expansion speed and reduces business valuation.
What is an example of customer churn?
Customer churn examples include a SaaS customer canceling their subscription after six months, a retail customer not making any purchases for 12 consecutive months, or a mobile service customer switching to a competitor provider. Each example shows a customer ending their relationship with the business during a specific measurement period.
What is another word for customer churn?
Alternative terms for customer churn include customer attrition, customer turnover, customer defection, and customer loss. These terms are used interchangeably across different industries, though "churn" has become the standard terminology in subscription-based businesses and SaaS companies.
How much customer churn is acceptable?
The amount of customer churn that is considered acceptable varies significantly by industry, business model, and customer segment. SaaS companies typically target monthly churn rates below 5%, while consumer subscription services might accept higher rates. Enterprise B2B businesses often achieve annual churn rates below 10%, while SMB-focused businesses might experience 20-30% annual churn.
Can you win back churned customers?
Win-back campaigns can effectively re-engage churned customers, especially when addressing the original reasons for departure. Success rates typically range from 10-30% depending on churn cause, time elapsed since departure, and the quality of the win-back approach. Customers who return after churning often show higher lifetime value than new customers because they understand the product and made conscious decisions to return.
What's the difference between gross churn and net churn?
Gross churn measures total customer or revenue loss without considering expansion from existing customers, while net churn accounts for both losses and gains from the existing customer base. Net churn can be negative when expansion revenue from existing customers exceeds revenue lost from churned customers, indicating strong account growth that more than compensates for departures.