Your board just approved an ambitious growth strategy. Marketing needs to drive 40% more qualified leads while building brand awareness in two new markets. The timeline? Six months. The budget? Flat from last year.
This scenario highlights why the chief marketing officer role has become one of the most complex executive positions.
A CMO is the senior executive responsible for an organization’s entire marketing strategy, brand positioning, and customer experience initiatives. They hold C-suite authority and report directly to the CEO, with accountability for driving revenue growth through customer acquisition, retention, and brand equity development. Unlike marketing managers who focus on specific campaigns, CMOs define how the organization creates value for customers and communicates that value across all touchpoints.
Let’s dive into the CMO’s evolving role in 2026 – from core responsibilities to career pathways and how top marketing leaders orchestrate complex initiatives that drive real business growth.
Key takeaways
- Drive measurable business growth through strategic marketing leadership: CMOs connect marketing activities to revenue outcomes, proving ROI through customer acquisition costs, lifetime value, and marketing-influenced revenue that justifies budget investments.
- Master cross-functional collaboration to create unified customer experiences: successful CMOs align marketing with sales, product, and operations teams through shared metrics, regular communication, and coordinated initiatives that deliver consistent brand promises.
- Coordinate complex marketing operations with centralized work management: a centralized platform provides portfolio visibility, automated workflows, and real-time performance tracking that helps CMOs optimize resources and maintain oversight across multiple campaigns and teams.
- Build diverse marketing expertise through 15-20 years of progressive experience: the path to CMO requires strategic thinking, data literacy, technology fluency, and leadership skills developed across multiple marketing functions, industries, and company sizes.
- Leverage AI and automation to maximize impact with lean teams: modern CMOs use predictive analytics, automated campaign management, and AI-powered customer insights to achieve more with limited resources while maintaining strategic focus on high-impact activities.
What is a chief marketing officer (CMO)?
A chief marketing officer (CMO) is the senior executive responsible for an organization’s entire marketing strategy, brand positioning, and customer experience initiatives. CMOs hold C-suite authority and report directly to the CEO, with accountability for driving revenue growth through customer acquisition, retention, and brand equity development.
While marketing managers execute campaigns, CMOs shape the entire customer value proposition. They’re strategists, team builders, budget hawks, and cross-departmental connectors all rolled into one. They sit at the intersection of business strategy and customer insight, translating market intelligence into actionable plans that impact every department.
CMO acronym and meaning
The acronym CMO stands for “chief marketing officer,” representing the highest-ranking marketing executive within an organization. This role encompasses comprehensive responsibility for brand stewardship, market positioning, customer experience design, and marketing technology implementation.
CMOs think big picture, defining how companies deliver and communicate value. The role evolved when businesses realized marketing isn’t just ads — it’s managing every customer touchpoint from first impression to loyal advocate. As business strategists first and marketing experts second, their decisions about which markets to enter, how to position products, and which customers to target can redirect an entire company’s future.
The strategic role of CMOs in modern organizations
Effective CMOs translate marketing efforts into hard business results — revenue growth, higher customer lifetime value, and competitive edge. Their calls on pricing strategy alone can transform a company’s market position overnight.
Consider a CMO deciding to target enterprise customers instead of small businesses. This single decision influences sales team structure, product development priorities, and customer service capabilities across the company. When CMOs identify emerging customer needs through market research, they work with product teams to develop solutions, with sales to refine messaging, and with operations to ensure delivery capabilities.
Great CMOs find the sweet spot between customer demands and profitable delivery. They’re relentless about proving every marketing dollar drives measurable returns. Organizations coordinate these complex, cross-departmental initiatives on a centralized work management platform, where CMOs gain visibility into how marketing activities connect to broader business goals through portfolio dashboards and real-time reporting.
CMO vs CEO and other C-suite executives
Understanding how the CMO role differs from other executive positions helps organizations structure leadership effectively.
Each C-suite role brings distinct focus areas and responsibilities:
| Dimension | CMO | CEO | CFO | COO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary focus | Customer acquisition, brand strategy, revenue growth through marketing | Overall business strategy, stakeholder management, organizational vision | Financial performance, capital allocation, risk management | Operational efficiency, process optimization, service delivery |
| Key decisions | Market positioning, customer segmentation, marketing technology selection | Strategic direction, major investments, organizational structure | Budget allocation, financial planning, investor relations | Supply chain management, production efficiency, quality control |
| Success metrics | Customer acquisition cost, marketing ROI, brand awareness, revenue attribution | Revenue growth, profitability, shareholder value, market position | Profit margins, cash flow, cost management, financial compliance | Operational efficiency, production costs, delivery timelines |
| Cross-functional role | Collaborates with sales, product, IT to create customer experiences | Oversees all executives and sets company-wide priorities | Partners with all departments on budget and financial planning | Coordinates operations, logistics, and service delivery teams |
CMOs work collaboratively with other C-suite executives. They partner with CFOs to prove marketing ROI and justify budget allocation, with COOs to ensure operational capabilities support marketing promises, and with CEOs to align marketing strategy with overall business objectives.

What does a chief marketing officer do?
CMO responsibilities span five interconnected areas that directly impact business growth. These responsibilities require CMOs to balance strategic thinking with tactical execution, long-term brand building with short-term performance demands, and creative innovation with data-driven accountability.
Develop brand strategy and market positioning
CMOs develop and execute comprehensive brand strategies that differentiate their organizations in competitive markets. This responsibility begins with deep market research to understand customer needs, competitive positioning, and emerging trends.
CMOs also define brand voice, visual identity, and messaging frameworks that guide all customer communications. They ensure consistency whether a customer encounters the brand through advertising, social media, customer service, or product packaging.
When launching new products, CMOs determine positioning strategies that highlight unique value propositions and target specific customer segments.
How does a CMO know when brand positioning needs to change? They track metrics like brand awareness, consideration, and preference across target audiences, using data analytics and customer insights to inform brand decisions.
Own customer experience and journey management
CMOs own the entire customer journey from initial awareness through purchase, onboarding, retention, and advocacy. They map customer touchpoints across departments to identify friction points, inconsistencies, and opportunities for improvement.
This responsibility requires coordinating with multiple teams to create seamless experiences:
- Sales teams: lead handoff processes and qualification criteria.
- Product teams: user experience design and feature prioritization.
- Customer service: support interactions and issue resolution.
- Operations: fulfillment and delivery processes.
CMOs develop customer segmentation strategies that enable personalized experiences at scale, using behavioral data and predictive analytics to anticipate needs. When customers report dissatisfaction with a specific touchpoint, CMOs investigate root causes and coordinate cross-functional solutions rather than simply adjusting marketing messages.
Lead marketing technology and digital transformation
CMOs select, implement, and optimize marketing technology stacks that enable efficient execution and accurate measurement across complex marketing operations.
CMOs lead digital transformation initiatives that modernize how organizations engage customers, often championing adoption of AI-powered personalization, predictive analytics, and automated campaign management. They work with IT teams to ensure data security, system reliability, and technical integration while maintaining marketing agility.
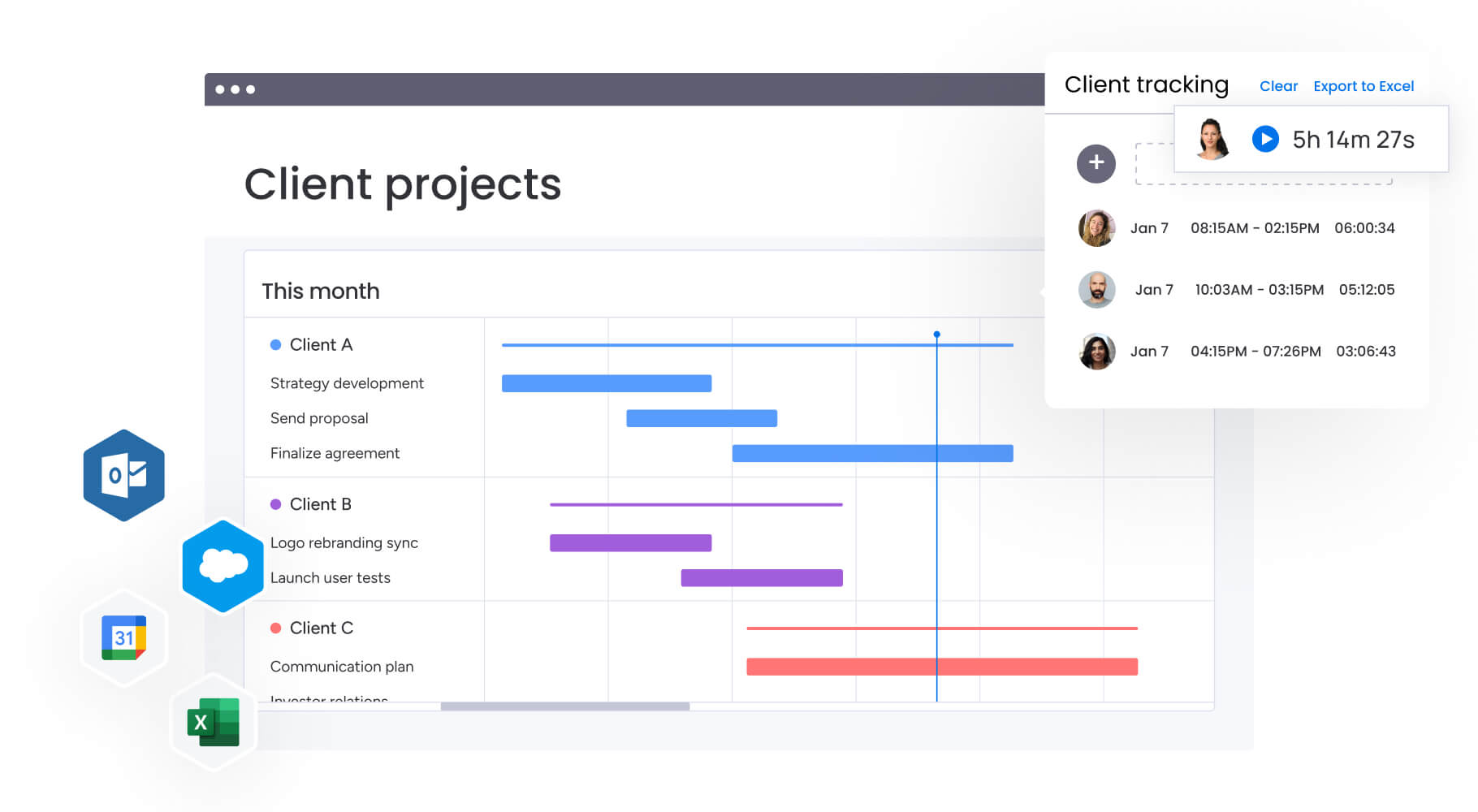
Organizations using monday work management coordinate complex marketing operations by gaining centralized visibility into campaign status, resource allocation, and performance metrics across multiple teams and initiatives. The platform’s dashboards help CMOs track dependencies between projects, identify bottlenecks before they impact delivery, and optimize resource allocation based on real-time workload data.
Drive revenue growth and performance measurement
CMOs drive measurable business growth by setting and achieving revenue targets through marketing initiatives. CMOs develop attribution models that connect marketing activities to revenue outcomes, enabling accurate measurement of marketing ROI and informed budget allocation decisions.
Key metrics CMOs track include:
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC): the total cost to acquire a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): the predicted revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the company.
- Marketing-influenced revenue: revenue from deals where marketing touchpoints played a role in the customer journey.
- Pipeline contribution: the percentage of sales pipeline generated through marketing activities.
CMOs balance short-term performance demands with long-term brand building, ensuring pressure for immediate results doesn’t undermine sustainable growth through brand equity development.
Build teams and develop talent
CMOs build and lead high-performing marketing teams across various specializations including brand management, digital marketing, content creation, analytics, and marketing operations. They hire talent with diverse skills, from creative storytellers to data scientists, ensuring the team can execute sophisticated strategies across multiple channels.
CMOs develop career paths and growth opportunities that retain top performers, providing mentorship, training, and advancement opportunities that build organizational capability. They foster collaboration between internal teams and external agencies, ensuring seamless coordination and knowledge transfer.
When teams face capacity constraints, CMOs optimize resource allocation and prioritize initiatives based on business impact. The resource management views on platforms like monday work management help CMOs balance team capacity and quickly adapt to changing priorities, ensuring project momentum is maintained without overloading any team members.
Essential CMO skills and qualifications
Top CMOs blend sharp business instincts with marketing mastery and leadership chops — all honed through years of hands-on experience. While requirements differ across industries, every marketing chief needs strategic vision, data fluency, tech savvy, and the ability to communicate complex ideas simply.
Educational background for CMOs
Most CMOs hold bachelor’s degrees in marketing, business administration, communications, or related fields that provide foundational knowledge in consumer behavior, market research, and business strategy. Many CMOs pursue advanced degrees, particularly MBAs with marketing concentrations, which provide deeper strategic training and valuable professional networks.
Educational requirements vary significantly by industry:
- Consumer goods companies: often prefer candidates with traditional marketing education.
- Technology companies: may value technical backgrounds or product management experience.
- Regulated industries: benefit from education in compliance, risk management, and industry-specific regulations.
Professional experience requirements
The typical path to CMO roles involves 15–20 years of progressive marketing experience across multiple functions, industries, or company sizes. Early career experience in areas like brand management, digital marketing, or marketing analytics provides tactical expertise and understanding of execution challenges.
Mid-career roles as marketing directors or VPs develop strategic thinking, team leadership, and cross-functional collaboration skills essential for CMO success. Many successful CMOs gain experience across different marketing disciplines, building comprehensive understanding of how different functions interconnect.
The most valuable experience involves demonstrable results. CMOs who can point to specific revenue growth, market share gains, or successful brand repositioning efforts stand out regardless of their exact career path.
Core competencies for CMO success
Modern CMOs need a diverse skill set that spans analytical, creative, technical, and interpersonal capabilities. These competencies distinguish effective CMOs from their peers:
- Strategic thinking: developing long-term plans that align marketing activities with business objectives and anticipate market changes.
- Data literacy: interpreting complex data sets, understanding statistical significance, and translating analytics into actionable insights.
- Technology fluency: evaluating marketing technologies, understanding technical capabilities, and leading digital transformation initiatives.
- Financial acumen: building budgets, forecasting revenue impact, calculating ROI, and communicating marketing value in financial terms.
- Leadership: inspiring teams, developing talent, navigating organizational dynamics, and building high-performing cultures.
- Communication: presenting complex ideas simply, influencing stakeholders, and representing the brand externally.
- Cross-functional collaboration: building productive relationships with sales, product, IT, finance, and operations teams.

How CMOs navigate marketing transformation
Today’s CMOs face unprecedented challenges as they balance increasing performance expectations with tighter budgets, rapidly evolving technologies, and changing consumer behaviors. Successful CMOs navigate these challenges by embracing Agile methodologies, leveraging automation and AI, and focusing on high-impact activities.
Operating with lean teams and tight budgets
CMOs maximize impact with limited resources through strategic prioritization that focuses team effort on initiatives with the highest potential return. CMOs implement Agile marketing methodologies that enable rapid testing, learning, and iteration rather than lengthy planning cycles that consume resources before generating results.
Automation plays a critical role in lean operations. CMOs use marketing automation platforms to handle repetitive work like email nurturing, social media scheduling, and lead scoring, freeing team members for strategic work. Strategic partnerships with agencies and freelancers provide specialized capabilities without the overhead of full-time employees.
Teams using monday work management optimize productivity by gaining visibility into workload distribution, identifying bottlenecks before they cause delays, and enabling data-driven resource allocation decisions.
The platform’s automations and templates save valuable time and get new projects started faster by automating crucial elements of work.
Proving marketing ROI with data-driven insights
CMOs demonstrate marketing value through rigorous measurement frameworks that connect marketing activities to business outcomes. They implement attribution modeling that tracks customer journeys across multiple touchpoints, assigning appropriate credit to different marketing interactions.
What separates CMOs who secure budget increases from those who face cuts? The ability to communicate marketing impact using financial language and business metrics. Successful CMOs discuss customer lifetime value, payback periods, and contribution margin instead of impressions, engagement rates, and brand awareness scores.
Performance dashboards on monday work management provide real-time visibility into key metrics, enabling quick responses to performance changes. CMOs can automatically display live high-level project data for insights on budget, goals, schedules, and resources, customizing dashboards based on their needs with drag-and-drop widgets.
Leading through market volatility
CMOs adapt strategies during economic uncertainty, competitive pressure, and changing consumer behavior without losing sight of long-term brand building. They develop scenario plans that prepare for multiple potential futures, enabling faster response when market conditions shift unexpectedly.
During economic downturns, successful CMOs resist the temptation to cut marketing budgets proportionally across all initiatives. Instead, they protect high-ROI activities while eliminating low-performers. Agile decision-making becomes critical during volatility. CMOs who can quickly assess new information, adjust strategies, and redeploy resources outperform those who stick rigidly to annual plans.

What is the path to becoming a CMO?
Becoming a CMO requires intentional career planning, continuous skill development, and strategic experience building over 15–20 years. The path isn’t linear. Successful CMOs take lateral moves to gain diverse experience, sometimes step back to smaller companies for broader responsibility, and continuously seek opportunities to develop new capabilities.
Step 1: build your marketing leadership foundation
Early-career professionals aspiring to CMO roles should gain diverse marketing experience across multiple channels, customer segments, and business models. Working in both B2B and B2C environments provides different perspectives on customer decision-making, sales cycles, and marketing effectiveness.
Developing analytical skills early establishes credibility and prepares for the data-driven decision making CMOs require. Building measurable results creates the track record needed for advancement. Aspiring CMOs should document specific outcomes like revenue growth, cost reduction, or market share gains rather than just describing responsibilities.
Step 2: advance through progressive leadership roles
The typical progression from individual contributor to CMO includes roles like marketing manager, director, and VP of marketing. Each level requires developing new capabilities:
- Managers: must learn to delegate and develop others.
- Directors: must coordinate across functions and manage budgets.
- VPs: must think strategically and influence senior leadership.
Cross-functional collaboration experience becomes increasingly important at senior levels. Aspiring CMOs should seek opportunities to work with sales, product, IT, and finance teams, building relationships and understanding different functional perspectives.
Step 3: develop executive presence and strategic thinking
Aspiring CMOs develop leadership qualities needed for C-suite success through deliberate practice and feedback. Communication skills improve through repeated experience presenting to senior leadership, board members, and external audiences.
Strategic vision develops by studying successful companies, analyzing market trends, and practicing the skill of connecting current activities to future outcomes. Executive presence encompasses confidence without arrogance, decisiveness without rigidity.
These qualities develop through experience, feedback, and self-awareness.
CMO compensation and career trajectory
CMO compensation varies significantly based on company size, industry, location, and individual performance. Understanding compensation factors and career progression opportunities helps aspiring CMOs make informed decisions about roles, negotiations, and long-term career planning.
CMO salary ranges across industries
CMO paychecks start around $150,000 but can stretch beyond $400,000 depending on company size, industry, and location. technology, finance, and healthcare typically pay top dollar, while retail, nonprofits, and education tend to offer more modest packages.
Company size dramatically impacts compensation:
- Companies under $50M revenue: $200,000–$300,000 total compensation.
- Companies $500M–$1B revenue: $400,000–$700,000 total compensation.
Performance bonuses typically represent 30–50% of base salary, tied to metrics like revenue growth, customer acquisition, and brand performance.
Future career paths for CMOs
Experienced CMOs pursue various career directions after their CMO tenure. Many transition to CEO roles in marketing-intensive industries like consumer goods, retail, or media. Board positions provide opportunities to apply marketing expertise across multiple companies while maintaining flexibility.
Consulting roles enable CMOs to leverage their experience helping multiple organizations solve marketing challenges. Some CMOs transition to private equity or venture capital firms as operating partners, helping portfolio companies improve marketing effectiveness and drive growth.

How CMOs excel at cross-functional leadership
Modern CMOs must work effectively across all business functions to drive growth and customer satisfaction. The siloed marketing department that operates independently has become obsolete. CMOs spend significant time on cross-functional collaboration, building relationships, aligning objectives, and coordinating initiatives that require organizational support.
Aligning marketing with sales and product teams
CMOs create alignment between marketing, sales, and product development through shared goal setting that ties all three functions to common revenue and customer satisfaction objectives. Regular communication through weekly pipeline reviews, monthly planning sessions, and quarterly business reviews ensures all teams understand priorities, dependencies, and performance trends.
Service level agreements define expectations between functions:
- Marketing commitments: lead quality and quantity targets.
- Sales commitments: follow-up timeframes and feedback quality.
Shared metrics like revenue attribution, customer acquisition cost, and customer lifetime value create common language and accountability across functions.
Building strategic partnerships across departments
CMOs develop productive relationships with IT, finance, operations, and human resources by understanding their priorities and finding opportunities for mutual benefit. IT partnerships enable marketing technology implementation, data integration, and system security. Finance partnerships help CMOs prove marketing ROI, justify budget requests, and optimize resource allocation.
Cross-departmental initiatives like digital transformation, customer experience improvement, or new market entry require CMOs to coordinate across multiple functions. Teams and departments using monday work management easily build workflows that connect people to the right information in real-time, improving cross-functional collaboration with one workspace that brings teams together to achieve shared goals.
Creating unified customer experiences
CMOs orchestrate consistent customer experiences across all touchpoints by establishing brand standards, message frameworks, and service expectations that guide every department’s customer interactions. Brand consistency requires coordination between marketing, sales, customer service, and product teams.
Journey mapping exercises bring together representatives from all customer-facing functions to identify friction points, inconsistencies, and opportunities for improvement that no single function can address alone. The most successful CMOs recognize that they don’t directly control most customer touchpoints. Their role involves coordinating, influencing, and enabling other functions to deliver experiences that fulfill brand promises.
The CMO-CFO alliance for business growth
The CMO-CFO relationship is critical for sustainable business growth and financial accountability. These two executives must work together closely despite different perspectives. CMOs focus on growth and customer acquisition while CFOs prioritize profitability and risk management. Companies with strong CMO-CFO partnerships consistently outperform those where these executives operate independently.
Establishing shared financial metrics
CMOs and CFOs collaborate to define marketing success metrics that align with financial objectives. Customer acquisition cost provides a shared metric that connects marketing efficiency to financial performance, with both executives monitoring trends and investigating increases.
Both executives must agree on measurement frameworks, data sources, and reporting standards before campaigns launch rather than debating methodology after results disappoint. Regular reporting using agreed-upon metrics builds trust and enables productive conversations about performance, optimization opportunities, and resource allocation.
Translating marketing impact to business outcomes
CMOs communicate marketing value in financial terms that CFOs and other executives understand. Instead of reporting impressions, engagement rates, or brand awareness scores, CMOs present marketing-influenced revenue, contribution margin, and return on investment.
Budget justifications connect requested resources to specific business outcomes. Rather than asking for a 20% budget increase, successful CMOs request funding for initiatives projected to generate specific revenue or customer acquisition results.

How AI is reshaping CMO responsibilities
AI is fundamentally changing how CMOs approach marketing strategy, execution, and measurement. Modern CMOs who embrace AI gain significant competitive advantages through more precise targeting, faster optimization, and deeper customer insights.
AI-powered customer intelligence
CMOs use AI to gain deeper customer insights through data analysis that identifies patterns, predicts behaviors, and segments audiences with precision impossible through manual analysis. Machine learning algorithms analyze millions of customer interactions to identify behavioral patterns that signal purchase intent, churn risk, or expansion opportunities.
Advanced segmentation moves beyond demographic categories to behavioral and psychographic clusters that enable more relevant messaging and personalized experiences.
The most effective CMOs combine AI-driven insights with human interpretation, using technology to surface patterns while applying business judgment to determine strategic implications.
Automated campaign management at scale
CMOs leverage AI for campaign optimization, content creation, and performance management across multiple channels simultaneously. Automated bidding in digital advertising adjusts spend in real-time based on performance, maximizing conversions within budget constraints without manual intervention.
AI capabilities within monday work management help CMOs identify risks across their portfolio in real-time. Portfolio Risk Insights scans all project boards, quickly flagging potential issues by severity. CMOs can spot critical issues at a glance without manually combing through data, and with just a click, notify the right person about an emerging risk.

Predictive analytics for strategic decision-making
CMOs use AI-powered predictive analytics to forecast market trends, customer behavior, and campaign performance before launching initiatives. Demand forecasting predicts future customer needs based on historical patterns, market trends, and external factors like seasonality or economic conditions.
Campaign performance forecasts estimate expected results before launch, helping CMOs allocate budget to highest-return opportunities. The most effective CMOs combine AI predictions with market knowledge and business judgment, using technology to inform decisions while recognizing that predictions are probabilities.
Best CMO work management platforms for marketing excellence
Today’s marketing operations are too complex for spreadsheets and email chains. Without a robust work management platform, CMOs face a perfect storm of crossed wires, blown deadlines, and wasted resources across their teams.
Managing complex marketing portfolios
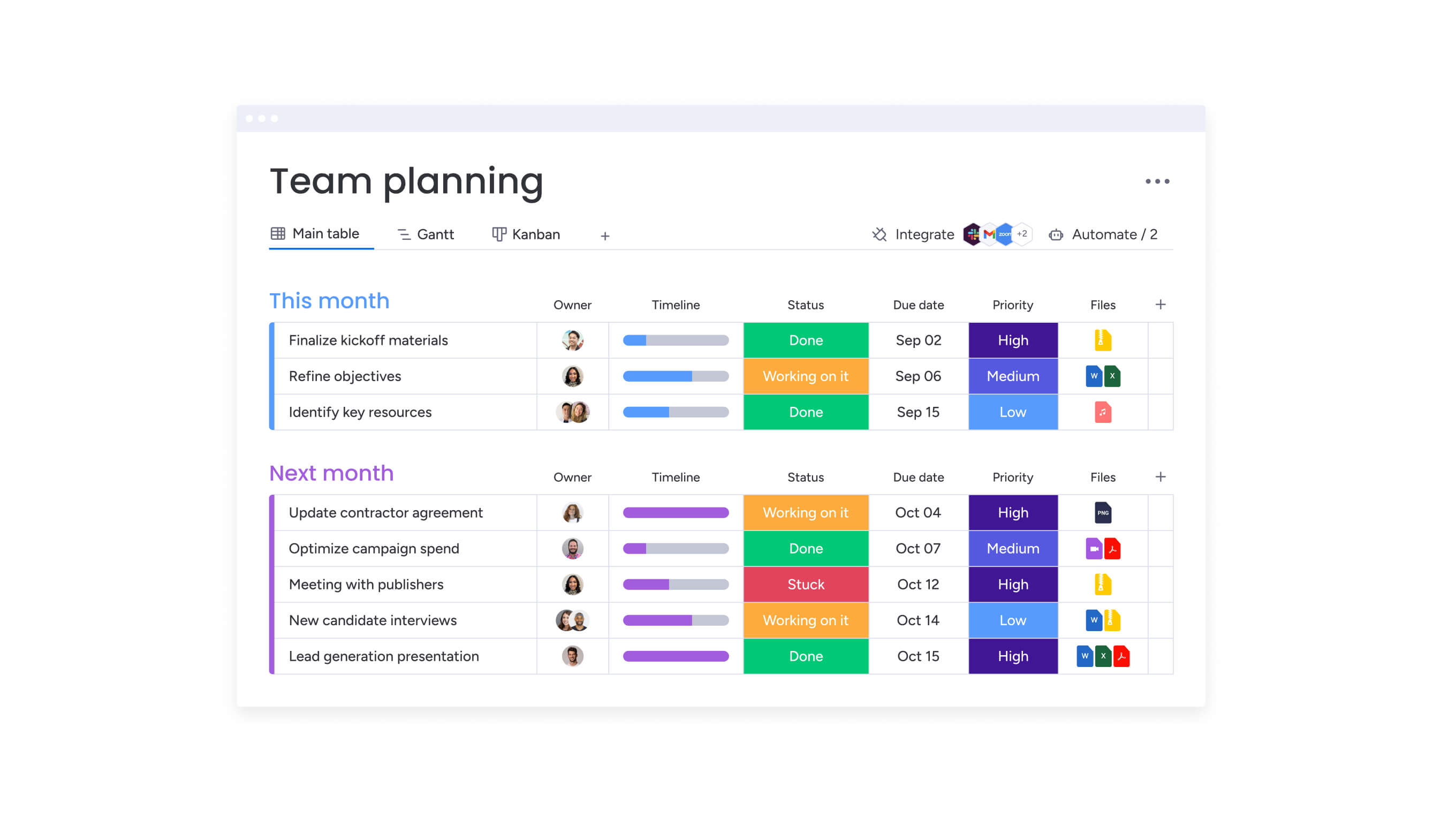
Advanced solutions like monday work management enable CMOs to oversee multiple campaigns, projects, and initiatives simultaneously through centralized dashboards that provide portfolio-level visibility. The platform’s project templates standardize campaign setup, ensuring consistent planning, execution, and measurement across different initiatives.
Automated workflows reduce manual coordination by triggering notifications, status updates, and handoffs based on project progress. Cross-project dependencies help CMOs identify how delays in one initiative impact others, enabling proactive problem-solving before cascading delays affect delivery.
Real-time performance visibility
monday work management provides CMOs with real-time insights into marketing performance, team productivity, and budget utilization through customizable dashboards. The platform’s integration capabilities connect marketing tools like automation platforms, analytics systems, and advertising channels to provide unified performance views.
CMOs track campaign performance across channels without switching between multiple systems. Team productivity metrics reveal workload distribution, task completion rates, and potential bottlenecks that affect delivery speed and quality. Budget tracking shows spending against plan in real-time, enabling CMOs to identify overruns early and adjust resource allocation.
Resource optimization
Intuitive management capabilities within monday work management help CMOs optimize team allocation, balance workloads, and ensure efficient use of marketing budgets. Workload views show team capacity and current assignments, enabling CMOs to identify overloaded team members and underutilized resources.
| Capability | monday work management approach | Alternative solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Portfolio visibility | Unified dashboard showing all marketing initiatives with customizable views; AI-powered risk identification across portfolio | Multiple disconnected platforms requiring manual consolidation; limited cross-project visibility |
| Cross-functional collaboration | Integrated platform connecting marketing with sales, product, and other teams; shared boards with role-based permissions | Email and meeting-based coordination; separate platforms for different functions |
| AI integration | Built-in AI for resource optimization, risk management, and workflow automation | AI capabilities require separate platforms and custom integration |
| Customization | No-code customization enabling CMOs to adapt workflows to their specific processes | Rigid templates requiring workarounds; customization requires technical resources |
Accelerate your marketing leadership with strategic work management
The CMO’s job has transformed from brand custodian to business architect. Today’s marketing leaders need equal parts visionary thinking, cross-team leadership skills, and data fluency to connect every campaign directly to the bottom line.
Modern CMOs navigate AI integration, operate with lean teams and tight budgets, and prove marketing ROI with unprecedented precision while maintaining brand strength and customer satisfaction.
Success requires sophisticated work management capabilities that provide portfolio visibility, enable resource optimization, and facilitate cross-functional collaboration across increasingly complex marketing operations. CMOs who embrace strategic work management approaches gain competitive advantages through faster execution, improved resource utilization, and performance visibility that enables data-driven optimization.
In 2026, monday work management has become the platform for marketing excellence, connecting strategy to execution and ensuring that daily activities align with business objectives. The advanced solution also provides the flexibility to adapt as markets, technologies, and customer behaviors evolve.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com’s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between a CMO and a VP of marketing?
A Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) is a C-suite executive responsible for shaping the company’s overall marketing vision and its connection to broader business strategy. The CMO typically influences decisions across departments such as sales, product, and revenue.
Can a company succeed without a CMO?
Companies can succeed without a CMO, especially smaller organizations where marketing responsibilities are distributed among other executives or handled by a VP of marketing who reports to the CEO.
How long does a CMO typically stay in their role?
CMO tenure typically ranges from two–four years, depending on company performance, strategic alignment with other executives, and market conditions that affect marketing effectiveness.
What industries pay CMOs the highest salaries?
Technology, financial services, and healthcare typically offer the highest CMO compensation due to industry profitability, competitive talent markets, and the critical role marketing plays in customer acquisition and retention.
Should startups hire a CMO or VP of marketing first?
Most startups should hire a VP of marketing first to establish marketing operations and prove market traction before investing in CMO-level leadership, usually around $20–50 million in revenue.
How do CMOs measure marketing success?
CMOs measure success through revenue attribution that connects marketing activities to closed deals, customer acquisition metrics like CAC and conversion rates, brand awareness tracking, and return on marketing investment calculated across all marketing activities.
