You’ve assembled a project team for your biggest initiative of the year. The kickoff meeting goes well, everyone seems aligned, and you’re confident about delivery. Three weeks later, you’re fielding confused emails about who owns what and watching deadlines slip because dependencies weren’t mapped. You realize your star developer is somehow committed to four different projects simultaneously. Sound familiar?
The difference between project teams that deliver and those that struggle isn’t talent or budget. It’s structure. A project team brings together people with different skills, from different departments, to achieve specific goals within set timelines. When roles are defined, responsibilities are transparent, and coordination flows smoothly, these temporary groups become execution powerhouses.
However, when structure is missing, even the most capable people end up working against each other instead of toward shared outcomes.
This article covers the five essential roles every project team needs, specific responsibilities that drive results, and how AI and automation are reshaping how teams coordinate work in 2026. You’ll discover proven strategies for building high-performing teams and creating accountability systems that scale, all within a single, visual workspace.
Key takeaways
- Build teams with five essential roles: every successful project needs a project manager, team members, sponsor, stakeholders, and business analyst to avoid gaps in accountability and execution.
- Define specific objectives before assembling your team: document measurable outcomes and project scope so everyone understands what success looks like from day one.
- Create transparent communication that connects to work: keep all project discussions tied to specific deliverables instead of scattered across emails and meetings that waste time.
- Use monday work management’s visual dashboards and automation: streamline cross-functional collaboration with real-time project visibility, automated task distribution, and AI-powered resource allocation that prevents burnout.
- Establish decision-making authority for each role: specify who can make which decisions independently to eliminate delays from unnecessary approvals and endless group discussions.
What is a project team?
A project team brings together people for a limited time to tackle a specific goal, unlike the permanent departments they normally work in. They assemble to launch products, upgrade systems, or run campaigns — then go their separate ways once the job’s done. They come together to launch products, upgrade systems, or run campaigns — then go their separate ways once the job’s done.
This temporary setup allows you to pull in the exact expertise you need from across the company. Need to launch software? Grab developers, designers, QA folks, and product managers for a few months. Moving offices? Your team might include facilities people, IT pros, HR, and operations staff until you’re settled.
Why not just rely on existing departments? Because projects need cross-functional expertise that rarely exists in one place. Marketing alone can’t launch a product without engineering input on capabilities, sales feedback on customer needs, and finance guidance on pricing.
This setup has its perks and pitfalls. Teams can zero in on the goal without their day jobs getting in the way. The flip side? You need well-defined roles from the start — there’s no runway to sort out who’s handling what.
The 5 essential roles in every project team
The best project teams build around five essential roles. Sure, enterprise projects might add specialized positions, and smaller teams might have people doubling up on responsibilities — but skip any of these core roles at your peril.
Get these roles right, and you’ll avoid the “who was supposed to do that?” conversations that derail so many projects:
- Project Manager: coordinates all project activities, maintains schedules and budgets, and serves as the central communication hub connecting all team members and stakeholders.
- Project Team Members: execute the actual project work, contribute specialized expertise, and transform project plans into tangible deliverables through their daily efforts.
- Project Sponsor: provides executive-level authority and resources, removes organizational obstacles, and ensures the project aligns with broader business strategy.
- Project Stakeholder: represents groups affected by the project, provides requirements and feedback, and ultimately determines whether deliverables meet business needs.
- Business Analyst: bridges business requirements and technical execution, translates stakeholder needs into actionable specifications, and ensures solutions address actual business problems.
Core responsibilities for each project team role
Each role within a project team carries distinct responsibilities that contribute to overall project success. Understanding these responsibilities helps organizations assign the right people to the right roles and ensures accountability across all project functions.
Project manager responsibilities
Project managers are your air traffic controllers — coordinating everything from initial planning and day-to-day execution to progress tracking. Their primary function is to keep the project on schedule and ensure all stakeholders remain happy and informed.
Planning and coordination responsibilities:
- Develop detailed project plans: create schedules, identify dependencies, allocate resources, and establish milestones that guide teams from initiation through closure.
- Facilitate cross-functional communication: schedule meetings that respect everyone’s time and ensure information flows smoothly across functional boundaries.
- Monitor progress and manage risks: track task completion against schedules, identify potential obstacles before they become problems, and implement mitigation strategies.
Stakeholder management responsibilities:
- Communicate project status: provide regular updates to executives and business leaders on project health and progress.
- Negotiate scope changes: work with stakeholders when requirements shift to maintain project viability.
- Manage expectations: ensure stakeholders understand both possibilities and constraints throughout the project.
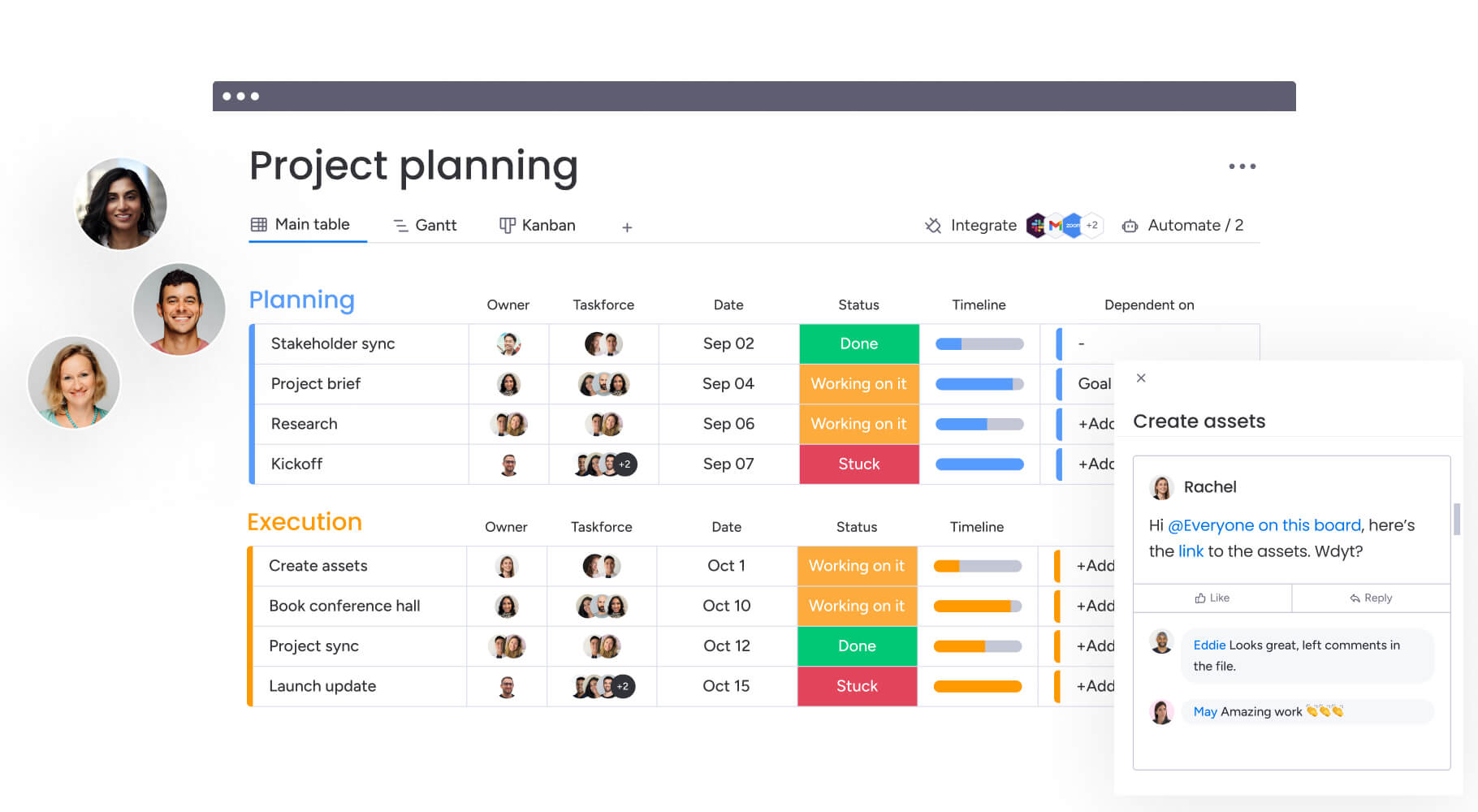
Teams using monday work management can see exactly how their projects are doing at a glance. Real-time dashboards show you budget status, goal progress, and resource allocation without digging through spreadsheets. You can focus on making decisions that matter instead of chasing status updates.
Team member responsibilities
Team members are where the rubber meets the road. They’re the ones turning plans into actual deliverables, bringing their specialized skills to the table, and making sure the work hits quality targets.
Execution responsibilities:
- Complete assigned work on schedule: deliver specific deliverables according to project timelines while maintaining quality standards.
- Contribute specialized expertise: bring unique capabilities essential to project success, whether writing code, designing interfaces, analyzing data, or managing vendor relationships.
- Collaborate across functions: share information openly, seek input from team members with complementary skills, and participate constructively in team discussions.
Communication responsibilities:
- Report progress transparently: update task status regularly and communicate delays immediately rather than waiting for status meetings.
- Escalate blockers proactively: raise issues that require project manager intervention before they become major crises.
- Own commitments: take accountability for deliverables and ensure they meet defined acceptance criteria.
Project sponsor responsibilities
Project sponsors are your executive muscle. They make sure your project stays connected to what the business actually needs, unlock resources when you’re stuck, and run interference when other priorities threaten to derail your work.
Authority and resource responsibilities:
- Secure budget approvals: ensure projects have adequate financial resources throughout their lifecycle.
- Assign team members: coordinate with department heads to allocate skilled personnel to project teams.
- Remove organizational obstacles: use positional power to address barriers that project managers can’t resolve independently.
Strategic oversight responsibilities:
- Make high-level decisions: approve major scope changes, determine project continuation or cancellation, and ensure alignment with evolving business strategy.
- Champion projects organizationally: communicate project value to other executives and maintain visibility that prevents deprioritization.
- Navigate political dynamics: clear paths that allow teams to focus on execution without getting caught in organizational conflicts.
Stakeholder responsibilities
Stakeholders represent the business interests that projects serve. Their active participation ensures deliverables meet actual business needs rather than assumptions about what users want.
Requirements definition responsibilities:
- Define business requirements: articulate what the project must deliver and establish measurable outcomes that determine success.
- Provide business context: explain the problems the project should solve and how solutions fit into broader business operations.
- Set success criteria: define specific, measurable outcomes that indicate project completion and value delivery.
Engagement responsibilities:
- Provide timely feedback: review work-in-progress, validate that solutions meet needs, and raise concerns early enough for course correction.
- Participate in milestones: attend demos, reviews, and decision points where stakeholder input shapes project direction.
- Accept final deliverables: formally approve completed work and take ownership of implementing solutions within business areas.
Business analyst responsibilities
Business analysts bridge the gap between business needs and technical execution. They ensure that what gets built actually solves the problems that justified the project investment.
Translation responsibilities:
- Convert business needs to technical requirements: transform stakeholder descriptions of problems into detailed specifications that technical teams can implement.
- Document processes and workflows: map current-state operations, design future-state processes, and create documentation that guides development and user adoption.
- Bridge communication gaps: facilitate understanding between business stakeholders and technical team members who speak different languages.
Validation responsibilities:
- Facilitate requirements gathering: conduct interviews, lead workshops, and employ elicitation techniques that uncover unstated needs and hidden assumptions.
- Validate solutions against requirements: test deliverables to confirm they meet specifications and identify gaps between requirements and implementation.
- Ensure business value delivery: verify that technical solutions address actual business problems rather than just meeting technical specifications.

Why organizations need well-structured project teams
Today’s business challenges rarely fit neatly inside one department. When you’re juggling multiple teams, technologies, and stakeholders, well-structured project teams become your secret weapon for keeping everyone moving in the same direction — fast.
Enable cross-functional collaboration at scale
Modern business initiatives rarely fit within single department boundaries. Launching a new product requires engineering to build it, marketing to position it, sales to sell it, operations to deliver it, and finance to price it profitably. Without structured project teams, these cross-functional efforts devolve into endless email chains, conflicting priorities, and finger-pointing when deadlines slip.
Well-structured project teams create coordination mechanisms that make cross-functional work manageable. Consider a marketing team launching a product campaign without defined project roles. They struggle to get engineering input on feature capabilities, sales feedback on customer objections, and operations confirmation on delivery timelines. The campaign launches with messaging that doesn’t match product reality.
Contrast this with a structured project team where a project manager coordinates inputs, business analysts translate requirements, and defined stakeholders from each function have responsibilities for providing timely feedback. The same campaign launches with accurate messaging, effective sales tools, and realistic customer expectations.
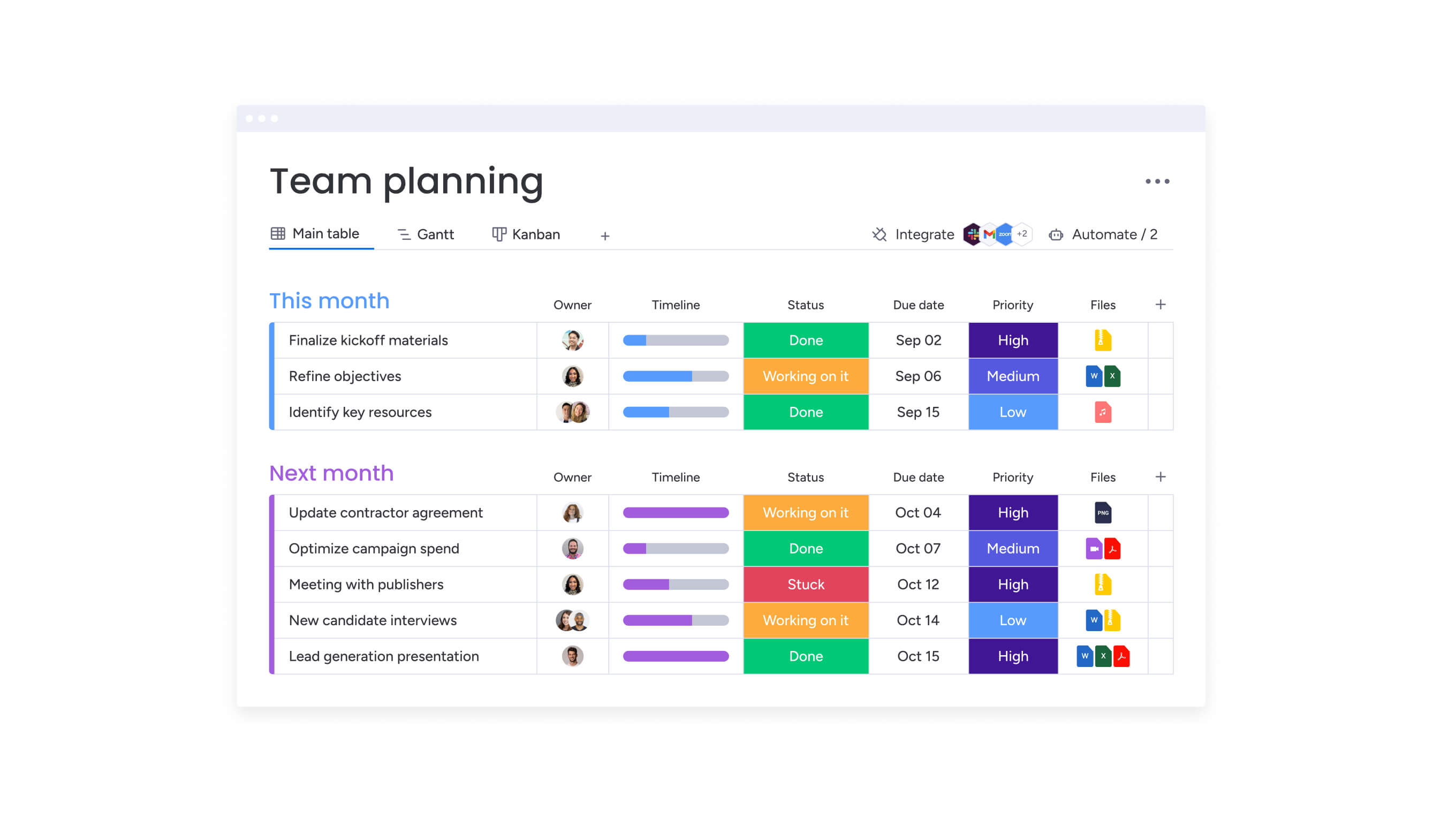
Teams can streamline cross-functional collaboration by leveraging solutions like monday work management. Within the platform they can use boards that visualize data and project plans with dynamic features and 15+ board views, including Kanban and Gantt charts.
Drive strategic business alignment
Projects consume significant organizational resources including employee time, budget, technology investments, and leadership attention. Without well-structured teams, projects drift from strategic intent as team members interpret objectives differently, pursue conflicting priorities, or lose sight of business outcomes amid execution details.
Structured project teams maintain strategic alignment through sponsor and stakeholder roles. When IT departments implement new systems without structured project teams, they often optimize for technical elegance rather than business value. The system works beautifully from an architecture perspective but fails to address the workflow problems that justified the investment.
Strategic alignment benefits:
- Sponsor oversight: project sponsors ensure initiatives continue serving strategic objectives as conditions change.
- Business analyst validation: technical solutions address actual business problems rather than theoretical requirements.
- Stakeholder reality checks: ongoing feedback keeps teams focused on outcomes that matter to the business.
Accelerate project delivery and innovation
Organizations face increasing pressure to deliver results faster while maintaining quality. Unstructured project efforts move slowly because team members lack role definition about who makes decisions, what takes priority, and how their work fits into the larger initiative.
Structured project teams accelerate delivery through accountability and decision rights. Consider a product development team operating without defined roles. Simple decisions trigger lengthy debates because no one has authority to decide. The team schedules meetings to discuss the question, involves people who don’t need to be involved, and still reaches no conclusion because decision-making authority remains ambiguous.
Acceleration mechanisms:
- Business analyst assessment: evaluates whether features address documented requirements.
- Project manager evaluation: assesses schedule and resource impact of decisions.
- Stakeholder input: provides business value perspective on trade-offs.
- Sponsor authority: makes final decisions when trade-offs involve strategic considerations.
How to build high-performing project teams
Building high-performing project teams requires intentional planning, careful selection, and structured processes that set teams up for success from day one. The following steps provide a framework for assembling teams that deliver results consistently.
Step 1: define project objectives and scope
The best teams know exactly what winning looks like — and everyone can explain it the same way. Before you assign a single work item, nail down what you’re building, what you’re not building, and why it matters to the business. Vague goals create vague results.
Effective objective-setting answers these specific questions:
- What measurable outcomes must this project achieve? Define metrics that indicate success.
- What business problem does it solve? Connect the project to organizational needs.
- What constraints define the boundaries? Establish timeline, budget, and resource limits.
- What explicitly falls outside project scope? Prevent scope creep from day one.
Teams that can answer these questions focus their energy on activities that matter rather than debating fundamental direction. Organizations gain this focus using monday work management’s project templates that provide structured frameworks for defining objectives, capturing scope, and documenting success criteria.
Step 2: select team members based on skills and availability
Building high-performing teams requires matching project needs to individual capabilities while respecting existing workload constraints. Start by identifying the specific skills and expertise the project requires — not generic roles like “developer” but specific capabilities like “API integration experience” or “healthcare compliance knowledge.”
The most common team-building mistake is assigning people based on organizational politics or availability rather than fit. Projects fail when team members lack necessary skills, when high performers get overallocated across too many initiatives, or when part-time contributors can’t engage deeply enough to add value.
Effective team selection considerations:
- Creative problem-solvers: thrive with ambiguity and undefined challenges.
- Detail-oriented executors: excel with established processes and requirements.
- Proactive communicators: keep distributed teams connected and aligned.
- Deep specialists: deliver expertise in focused areas without constant oversight.
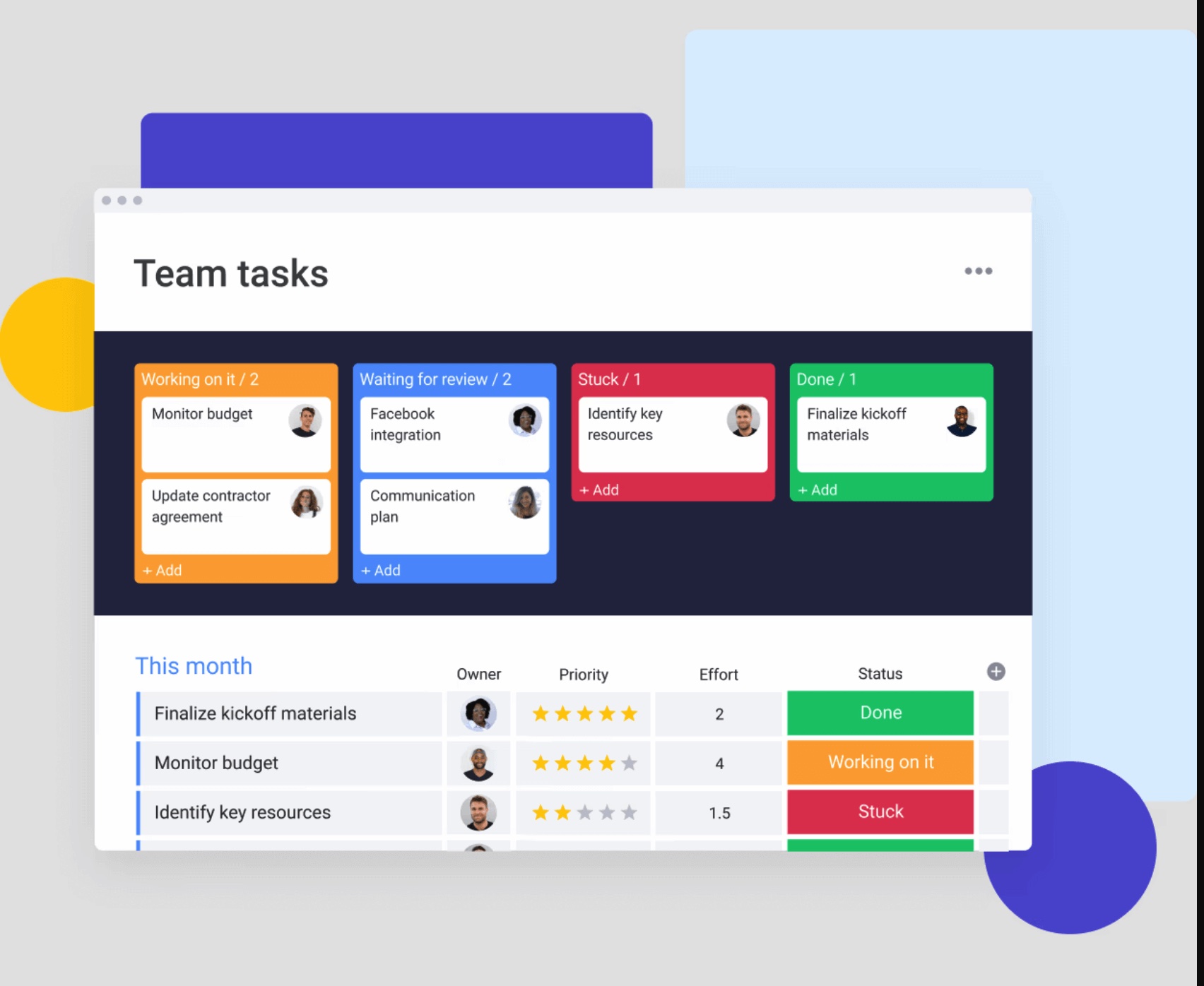
Resource management capabilities on monday work management help organizations visualize team member availability through Workload View, which balances team resources and quickly adapts to changing priorities.
Step 3: establish transparent communication frameworks
High-performing teams communicate with intention and structure rather than defaulting to constant meetings or endless message threads. Define how different types of information flow through your team.
Create explicit agreements about communication tools and norms:
- Status updates: happen in project management platforms where they’re visible to everyone.
- Quick questions: go in team chat channels organized by topic.
- Complex discussions: that need real-time dialogue happen in focused meetings with agendas.
Common communication failures include update meetings where people read status reports they could have read asynchronously, important decisions made in side conversations that other team members miss, and information scattered across email, chat, and documents that no one can find later.
Teams using monday work management keep project conversations connected to relevant work items through monday workdocs, which enable real-time collaboration with live boards, dashboards, and videos embedded directly into documents.
Step 4: create accountability and ownership systems
High-performing teams operate with ownership where every deliverable has a single person accountable for its completion. Shared accountability becomes no accountability — when everyone is responsible, no one feels responsible.
Accountability systems include these key components:
- Regular progress check-ins: surface obstacles early before they become major blockers.
- Transparent tracking: make status visible to the entire team through shared dashboards.
- Escalation paths: provide routes when blockers arise that individuals can’t resolve alone.
These systems create psychological safety where team members can raise problems without fear while maintaining high standards for delivery. Role-based permissions and work assignment features within monday work management create ownership at the item level while maintaining visibility that helps project managers identify risks before they become crises.
Try monday work managementManaging modern project teams with AI and automation
Modern project teams leverage artificial intelligence and automation to handle routine coordination tasks, optimize resource allocation, and provide insights that human managers struggle to maintain across multiple complex projects. These technologies augment human capabilities rather than replacing them.
How can you allocate resources without guesswork?
AI transforms resource allocation from reactive firefighting into proactive optimization. Traditional resource management relies on project managers manually tracking who’s working on what, identifying conflicts when team members get overallocated, and negotiating with other project managers when resources need rebalancing.
AI-powered resource allocation continuously analyzes workload across all projects, identifies potential conflicts before they impact delivery, and suggests optimal resource distribution based on skills, availability, and project priorities. When a critical team member gets assigned to three projects simultaneously, AI flags the conflict immediately and recommends alternatives.
Advanced AI capabilities:
- Historical analysis: predicts how long work actually takes versus estimates based on past project data.
- Skills matching: identifies which team members excel at which types of work.
- Resource forecasting: anticipates when projects will need additional resources based on typical patterns.
Organizations leveraging monday work management’s AI capabilities can categorize project requests at scale, analyze incoming requests, assign labels, and streamline workflows automatically. The platform provides intelligent recommendations for balancing workloads.
Automated work distribution and progress tracking
Automation eliminates the coordination overhead that consumes project manager time and creates delays. When project phases complete, automation can instantly distribute next-phase work to appropriate team members based on skills and availability. When dependencies resolve, automation notifies downstream team members that they can begin their work.
These automated workflows reduce status meeting time dramatically. Instead of spending an hour each week hearing each team member report what they completed, project managers review automated status dashboards that surface this information continuously. Meetings shift from status reporting to problem-solving.
Automation benefits:
- Instant work distribution: assigns tasks automatically when dependencies complete.
- Stakeholder notifications: alerts relevant parties when milestones are reached.
- Escalation management: flags overdue items to project managers without manual monitoring.
Teams save valuable time with monday work management’s automation recipes that handle repetitive coordination including assigning work when dependencies complete, notifying stakeholders when milestones are reached, and escalating overdue items to project managers.
Digital workers augmenting human teams
Digital workers take automation to the next level. Instead of just handling one-off tasks, they manage entire workflows. Think of the Project Analyzer as your 24/seven project watchdog — constantly checking schedules, budgets, team capacity, and risk factors so you can focus on solving problems, not just finding them.
These digital workers don’t replace human project managers — they augment human capabilities by handling the continuous monitoring and analysis that humans struggle to maintain across multiple projects. Digital workers provide this continuous vigilance, freeing project managers to focus on strategic decisions, stakeholder management, and team development.
The Project Analyzer on monday work management monitors projects in real-time, flags bottlenecks, and provides proactive insights to keep everything on track. Teams can instantly create detailed project plans with AI-suggested phases, getting a head start on projects while ensuring nothing gets overlooked.
7 strategies to optimize project team performance
Optimizing project team performance requires systematic approaches that address communication, visibility, workload management, and continuous improvement. These strategies help teams work more efficiently while maintaining high-quality deliverables.
1. Create transparent communication channels
Project teams waste time searching for information, miss important updates, and make decisions based on incomplete or outdated information when communication happens across disconnected tools and channels.
Establish a single source of truth where all project-related communication connects directly to relevant work items. When team members discuss a deliverable, that conversation lives with the work itself rather than buried in email threads or chat messages.
Communication benefits:
- Reduced meeting time: information is continuously visible rather than reported in status meetings.
- Faster onboarding: new team members review conversation history to understand project context.
- Quicker decisions: relevant stakeholders provide input asynchronously without scheduling delays.
2. Implement visual project management dashboards
Project managers struggle to identify risks early when they rely on status reports that team members create manually, often days after actual events occur.
Create visual dashboards that automatically aggregate real-time project data into formats that make patterns and anomalies immediately obvious. Use color-coding to highlight items requiring attention, trend lines to show whether metrics are improving or degrading, and comparative views to spot differences across projects or teams.
Dashboard advantages:
- Early risk identification: project managers spot at-risk projects weeks earlier through visual warning signs.
- Executive confidence: stakeholders see current data rather than outdated reports.
- Team focus: dashboards make priorities and progress visible to everyone.
3. Monitor and balance team workload in real time
Team members burn out or deliver lower-quality work when they’re overallocated across multiple projects, but project managers often don’t realize overallocation exists until people miss deadlines.
Implement real-time workload monitoring that aggregates all commitments across every project each team member supports. Visualize capacity versus allocation for each person, highlight overallocation immediately when it occurs, and provide tools for rebalancing work.
Workload management outcomes:
- Reduced burnout: organizations identify and address overallocation proactively.
- Predictable delivery: teams work at sustainable paces that maintain quality.
- Improved utilization: managers identify underutilized team members for high-priority initiatives.
4. Build continuous feedback and improvement loops
Project teams repeat the same mistakes across multiple projects when lessons learned are captured only in post-project retrospectives that get filed away and forgotten.
Create continuous feedback mechanisms that capture insights throughout project execution. Conduct brief retrospectives after each project phase, document what’s working and what isn’t in accessible formats, and build successful patterns into templates and processes that guide future projects.
Continuous improvement benefits:
- Higher success rates: teams systematically apply lessons learned across projects.
- Faster ramp time: new project managers leverage accumulated organizational knowledge.
- Accelerated innovation: teams build on proven approaches rather than starting from scratch.
5. Establish role-based decision authority
Teams move slowly when decision-making authority remains unclear and every choice requires group consensus or escalation to senior leadership.
Define decision rights for each role within the project team structure. Specify which decisions project managers can make independently, when business analysts have authority to approve requirements changes, and what circumstances require sponsor involvement.
6. Implement predictive project analytics
Traditional project management relies on backward-looking reports that show what already happened rather than predicting what might happen next.
Use analytics that identify patterns in project data to forecast potential issues before they occur. Track leading indicators like requirement change frequency, team velocity trends, and stakeholder engagement levels that predict project health.
7. Create cross-project learning systems
Organizations miss opportunities to apply successful approaches across multiple projects when knowledge remains trapped within individual project teams.
Establish systems that capture and share successful practices, templates, and lessons learned across all project teams. Create searchable repositories of project artifacts, maintain libraries of proven approaches, and facilitate knowledge transfer between project managers.
Transform your project teams with monday work management
Organizations struggling with fragmented project tools, unclear team accountability, and limited visibility into project health need a platform that unifies project management, resource allocation, and cross-functional collaboration in a single workspace.
Advanced solutions like monday work management transform how project teams operate by combining visual work management, intelligent automation, and AI-powered insights that scale from individual projects to enterprise portfolios.
Unlike traditional project management platforms that force teams into rigid methodologies, monday work management’s flexible frameworks adapt to how teams actually work. Teams customize boards, workflows, and automations to match their specific needs without requiring IT support. Marketing teams, IT departments, operations groups, and executive leadership can all manage their projects in ways that make sense for their unique requirements while maintaining visibility across the organization.
The platform also goes beyond basic tracking to provide comprehensive capabilities that address every aspect of project team management. These capabilities include resource allocation that prevents burnout, automated workflows that eliminate coordination overhead, and AI-powered insights that identify risks before they impact delivery.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com‘s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.

Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between a project team and a functional team?
A project team is a temporary group assembled to achieve specific objectives within defined timelines, while a functional team is a permanent department that handles ongoing operational responsibilities. Project teams disband upon completion; functional teams continue indefinitely.
How do you manage remote project teams effectively?
Remote project teams require structured communication frameworks, visual project management platforms that provide continuous status visibility, and regular synchronous check-ins balanced with asynchronous collaboration that respects different time zones and work schedules.
What is the ideal size for a project team?
The ideal project team size ranges from five-nine members for most initiatives, following the "two-pizza team" principle where teams remain small enough for effective communication while including necessary expertise. Larger projects use multiple coordinated teams rather than single oversized teams.
What skills are most important for project team members?
Critical skills include digital collaboration across distributed teams, adaptability to rapidly changing requirements and technologies, data literacy for making evidence-based decisions, and the ability to work effectively with AI tools that augment human capabilities.
How do you resolve conflicts within project teams?
Address conflicts immediately through direct conversation focused on project objectives rather than personal disagreements. Involve the project manager or sponsor when team members can't resolve issues independently, and establish decision-making authority to prevent recurring debates.
Can AI replace project team members?
AI augments rather than replaces human project team members by handling repetitive coordination, continuous monitoring, and pattern recognition. This frees humans to focus on strategic decisions, creative problem-solving, and relationship management that require human judgment and empathy.