Your project just got approved, the team is excited, and stakeholders are asking the inevitable question: “When will it be done?” You confidently share your timeline, but three weeks later, you’re already behind schedule. Sound familiar? The gap between initial estimates and reality creates stress, erodes trust, and forces difficult conversations about scope, budget, and deadlines.
Project estimation helps you predict the time, cost, and resources needed to deliver successful outcomes. It’s the foundation that turns ambitious ideas into executable plans, giving teams the roadmap they need to coordinate work, allocate resources, and set realistic expectations with stakeholders. When estimates align with reality, projects flow smoothly. When they don’t, everything becomes harder.
This helpful post covers seven proven estimation methods that work across different project types and team sizes. We’ll explore when to use each approach, how to combine techniques for maximum accuracy, and practical strategies to improve your forecasting over time. You’ll also discover how the right work management platform helps teams create, track, and refine estimates throughout project execution.
Key takeaways
- Choose the right estimation method for your project type: use bottom-up for detailed projects, top-down for early planning, and three-point estimation when facing high uncertainty or risk.
- Build buffers strategically to protect project success: add 10-20% for individual work items and 15-25% for overall project timelines to handle unexpected challenges without derailing delivery.
- Track actual performance against estimates to improve accuracy: compare your forecasts to real outcomes and document lessons learned to make future estimates more reliable.
- Leverage monday work management’s visual timelines and automation: use interactive Gantt charts to see dependencies clearly and automate progress tracking to catch estimation issues before they become problems.
- Combine multiple estimation approaches for more accurate results: pair quantitative methods like parametric estimation with expert judgment to reduce bias and increase confidence in your forecasts.
What is project estimation?
Project estimation predicts what you’ll need — time, money, and resources — to deliver successful outcomes. It’s about breaking down your work into manageable pieces so you can forecast requirements with confidence.
It’s like mapping your route before a road trip — you wouldn’t start without knowing the distance, fuel needs, and potential detours. Good estimation gives you that same clarity for your project journey.
Understand project estimation fundamentals
Project estimation covers three key areas that work together to determine if your project is feasible. These dimensions constantly affect each other, forming the backbone of decisions you’ll make from kickoff to completion.
- Duration estimation: predicts how long your project schedule will take from start to finish. You’ll account for task sequences, dependencies, and team availability to create realistic project schedules. Complex projects can face significant duration challenges, as evidenced by major defense programs that take almost twelve years on average to deliver their first version, highlighting the importance of realistic schedule baselines.
- Cost estimation: calculates the financial resources required across all project phases. This includes labor, materials, equipment, and contingency reserves for unexpected expenses.
- Resource estimation: identifies the people, equipment, and infrastructure needed to execute the work. You’ll consider both quantity and skill requirements to ensure you have the right capabilities available.
These dimensions constantly pull against each other. Want to finish faster? You’ll need more people — and more budget. Working with limited funds? Your timeline might stretch or your deliverables might shrink. Your challenge is finding the sweet spot that satisfies stakeholders without promising the impossible.
Identifying essential components of project estimates
Strong estimates contain five essential pieces that give stakeholders everything they need to make decisions. When you nail these components, you build the confidence and alignment that keeps projects on track from approval to delivery.
Here’s what makes up a solid estimate:
- Scope definition: clear boundaries establish what your project includes and explicitly excludes, preventing scope creep and misaligned expectations.
- Time estimates: duration forecasts for individual work items and overall project timelines, accounting for dependencies and resource availability.
- Resource requirements: detailed inventories of people, equipment, and materials needed, including skill levels and availability windows.
- Cost projections: budget allocations across project phases, work streams, and cost categories for spending authority and financial controls.
- Risk buffers: contingency reserves that add time and budget cushions to handle uncertainties and unexpected challenges.
Recognizing how project estimation drives success
When your estimates hit the mark, your organization gets three major advantages that transform project results. Knowing these benefits helps you convince stakeholders why spending time on careful estimation pays off in the long run.
- Informed decision-making: executives and stakeholders receive realistic information about project feasibility, resource requirements, and expected returns. Leaders can prioritize initiatives and allocate budgets based on reliable forecasts rather than optimistic guesses.
- Effective resource allocation: you can balance workloads across project portfolios, prevent resource conflicts, and ensure teams have the capacity to deliver on commitments.
- Stakeholder alignment: reliable estimates create shared expectations about project scope, timeline, and budget. When everyone understands what’s possible and what it will take, you reduce friction and build confidence in project delivery.
Get estimation wrong, and the problems multiply fast. Underestimate, and you’ll face resource battles, burned-out teams, blown deadlines, and corner-cutting. Overestimate, and you’re leaving money on the table while eroding trust in your judgment.
This is really important to remember as research shows that average cost overruns of about 80% occur in large-scale projects, demonstrating the real-world impact of estimation errors.

The value of accurate project estimation
When you see what’s really at stake with estimation accuracy, you’ll make it a priority. Bad estimates don’t just push deadlines — they crush morale, damage your reputation, and can sink projects that should have succeeded.
The hidden impact of estimation errors
The real cost of estimation errors isn’t just about money or time — it’s much worse. Underestimate a project, and suddenly you’re fighting for resources that were promised elsewhere, forcing impossible choices across your entire portfolio.
These conflicts force difficult trade-offs that damage project outcomes:
- Delayed lower-priority work: teams must postpone other initiatives to address resource shortfalls.
- Compromised quality: pressure to meet unrealistic deadlines leads to corner-cutting and inadequate testing.
- Scope reductions: stakeholders accept diminished deliverables to meet original timelines.
Underestimation also drives team burnout as staff work excessive hours attempting to deliver unrealistic commitments. Sustained overwork degrades both productivity and morale, creating turnover that further damages project performance.
On the other hand, overestimation creates different but equally damaging consequences.
Projects that finish significantly under budget or ahead of schedule suggest poor planning capability and damage project manager credibility. More importantly, overestimation leads to missed opportunities as organizations decline valuable initiatives based on inflated resource requirements.
How reliable estimates transform projects
Reliable estimates improve resource planning across project portfolios. Organizations can balance workloads effectively, ensuring teams have appropriate capacity without overcommitment. Resource managers can also make informed hiring decisions, plan training investments, and coordinate across projects to optimize utilization.
Further, quality improves when estimates reflect realistic timelines. Teams have adequate time for proper design, thorough testing, and iterative refinement rather than rushing to meet artificial deadlines.
This investment in quality reduces long-term costs and improves customer satisfaction.
Building stakeholder confidence through precision
Estimation accuracy directly influences stakeholder trust and project manager credibility. Consistent delivery on commitments builds confidence that enables greater autonomy and support for future initiatives. Stakeholders who trust project estimates provide resources more readily and interfere less in execution details.
Transparent estimation processes create shared understanding across all project participants. When stakeholders understand the assumptions, data sources, and reasoning behind estimates, they can provide informed input and set realistic expectations. This transparency prevents the disconnect between stakeholder hopes and project reality that creates conflict and disappointment.

7 project estimation methods that actually work
Selecting the right estimation approach depends on your project characteristics, available data, and timeline constraints. Each method below offers distinct advantages for specific situations, and understanding when to apply each technique helps you generate accurate forecasts efficiently.
1. Top-down estimation for strategic planning
Top-down estimation begins with overall project goals and systematically breaks them into progressively smaller components until reaching manageable work packages. This approach works best during early project phases when detailed requirements remain undefined but stakeholders need preliminary forecasts for budget allocation and strategic planning decisions.
Senior managers use top-down estimates to make go/no-go decisions about proposed initiatives, comparing resource requirements across competing projects to prioritize organizational investments. The method provides rapid estimates that enable strategic conversations without requiring extensive detailed analysis.
Implementation process:
- Identify reference projects: find similar completed projects that provide baseline estimates.
- Adjust for differences: modify historical estimates based on scope, complexity, or resource variations.
- Distribute across phases: allocate the total estimate across major project milestones.
While this method sacrifices precision for speed, it’s ideal when decisions require quick forecasts.
2. Bottom-up estimation for detailed accuracy
Bottom-up estimation builds project forecasts from individual work items upward, aggregating detailed estimates into comprehensive project totals. This method provides the highest accuracy when teams have detailed requirements and can analyze work at granular levels.
The process requires breaking projects into specific work items, estimating each individually based on historical data or expert judgment, then aggregating these estimates to calculate total project duration and cost. This granular approach reveals dependencies, resource needs, and potential bottlenecks that might otherwise remain hidden.
Bottom-up estimation demands significant time investment during planning but pays dividends through improved accuracy and reduced surprises during execution. Teams gain detailed understanding of project requirements, dependencies, and resource needs that inform both estimates and execution strategies.
3. Three-point estimation for risk management
Three-point estimation acknowledges uncertainty by collecting optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely scenarios for each project component, a technique commonly used in Agile estimation. This method provides realistic ranges rather than single-point forecasts, helping stakeholders understand confidence levels and make risk-informed decisions.
The calculation process involves three estimates for each work item:
- Best-case scenario: everything goes smoothly with no delays or complications.
- Worst-case scenario: significant challenges and setbacks occur.
- Most likely outcome: typical conditions based on past experience.
Teams apply weighted averages to calculate expected values and confidence intervals. The range between optimistic and pessimistic scenarios indicates risk levels, helping teams build appropriate buffers into project plans.
4. Analogous estimation using past projects
Analogous estimation leverages historical project data to predict current project outcomes. You identify similar completed projects and adjust their results based on differences in scope, complexity, or available resources. This method works best when organizations maintain detailed records of past project performance.
Effective analogous estimation requires selecting appropriate reference projects that share key characteristics with the current initiative: similar scope, technology, team size, and organizational context. Teams then adjust historical estimates based on identified differences.
The accuracy of analogous estimation depends on the quality and relevance of historical data. Organizations that systematically capture project performance metrics can quickly generate reliable estimates for similar future work.
5. Parametric estimation with data models
Parametric estimation uses mathematical relationships between project variables to calculate forecasts, a technique detailed in cost estimation methodologies. This works best for projects with measurable, repeatable components where statistical relationships exist between inputs and outcomes. Software development teams might estimate based on function points using Agile estimation techniques, while construction projects use square footage or unit counts.
The method requires developing and validating parametric models using historical data. Teams identify key variables that drive project duration or cost, collect data from past projects, and use statistical analysis to build predictive models.
Parametric estimation provides consistent, objective forecasts that remove subjective bias from the estimation process. However, the method requires substantial historical data to build reliable models and works best for projects with standardized components.
6. Expert judgment for complex projects
Expert judgment leverages experienced professionals’ insights for estimation, particularly valuable for unique projects, new technologies, or situations with limited historical data. This method recognizes that human expertise can assess factors that quantitative methods miss: organizational dynamics, stakeholder relationships, and implementation risks.
Effective expert judgment requires selecting appropriate experts with relevant experience, structuring estimation sessions to gather diverse perspectives, and combining multiple expert opinions to reduce individual bias. Documentation becomes critical: teams must record the assumptions and reasoning behind expert estimates to enable future learning.
Expert judgment works best when combined with other methods, using human insight to validate or adjust quantitative estimates rather than relying solely on subjective assessment.
7. AI-powered estimation for modern teams
AI-powered estimation uses machine learning algorithms to analyze project patterns and generate predictions based on vast amounts of historical data. These systems identify estimation patterns and correlations that human analysts might miss, processing multiple variables simultaneously to produce comprehensive forecasts.
Today’s leading platforms integrate AI capabilities that suggest estimates based on project characteristics, team performance data, and organizational patterns. AI systems continuously learn from actual project outcomes, improving prediction accuracy over time as they process more data.
With 88% of organizations now using AI in at least one business function, these estimation capabilities are becoming mainstream tools for project teams.
The most effective approach combines AI-generated estimates with human judgment and domain expertise. Algorithms excel at pattern recognition and data processing but lack the contextual understanding that experienced project managers provide.
Try monday work management
How to select the right estimation method for your project
Choosing the appropriate estimation technique requires evaluating your project characteristics, available resources, and accuracy requirements. Different situations call for different approaches, and understanding these relationships helps you generate reliable forecasts efficiently.
Match estimation techniques to project types
Not all projects are created equal — and your estimation approach shouldn’t be either. Knowing which method fits your specific situation saves you from spinning your wheels on techniques that won’t deliver.
Project characteristic Recommended methods Why it works
Early planning phase with limited detail Top-down, analogous Provides rapid forecasts when detailed requirements aren't defined
Detailed requirements fully documented Bottom-up, parametric Enables precise work-level analysis using complete information
High uncertainty or significant risks Three-point, expert judgment Explicitly acknowledges uncertainty and builds appropriate contingencies
Similar past projects available Analogous, AI-powered Leverages proven patterns from comparable historical data
Unique or innovative projects Expert judgment, three-point Relies on human insight when historical patterns don't apply
Repeatable standardized work Parametric, bottom-up Uses statistical relationships for consistent, objective forecasts
Evaluate your data and resources
Data availability fundamentally shapes method selection. Organizations with extensive historical project databases can leverage analogous estimation or AI-powered methods that analyze patterns across past initiatives for more accurate cost estimation. Teams with limited historical data should focus on expert judgment or three-point estimation that leverage human experience.
Resource constraints also influence method selection. Bottom-up estimation requires significant time investment during planning. This investment makes sense for large, complex projects where accuracy justifies the planning effort. Smaller initiatives benefit from faster approaches like top-down or analogous estimation.
Consider team experience and timeline
Team expertise affects both method selection and estimation accuracy. Experienced teams can effectively use sophisticated methods like parametric estimation that require understanding statistical relationships. Newer teams should start with simpler approaches that provide reasonable accuracy without requiring advanced analytical skills.
Project timeline pressures create trade-offs between estimation speed and accuracy. Urgent estimates needed for quick go/no-go decisions might require top-down or expert judgment methods. Projects with longer planning phases can invest in detailed bottom-up analysis.
The most effective approach often combines multiple methods: using top-down estimation for initial feasibility assessment, then refining forecasts with bottom-up analysis as requirements become defined.
Critical factors that influence estimation accuracy
Several key variables significantly impact estimation precision, and understanding these factors helps you build more reliable forecasts:
Project complexity and dependencies
Interconnected work items create estimation challenges that extend beyond simple duration calculations. Dependencies amplify delays: when one activity runs late, it affects multiple downstream activities in cascading fashion. A two-day delay in design work might push development back two days, which delays testing two days, ultimately extending the project timeline significantly.
Critical path dependencies deserve particular attention during estimation. Activities on the critical path directly affect project completion dates, making their estimates especially important for overall timeline accuracy.
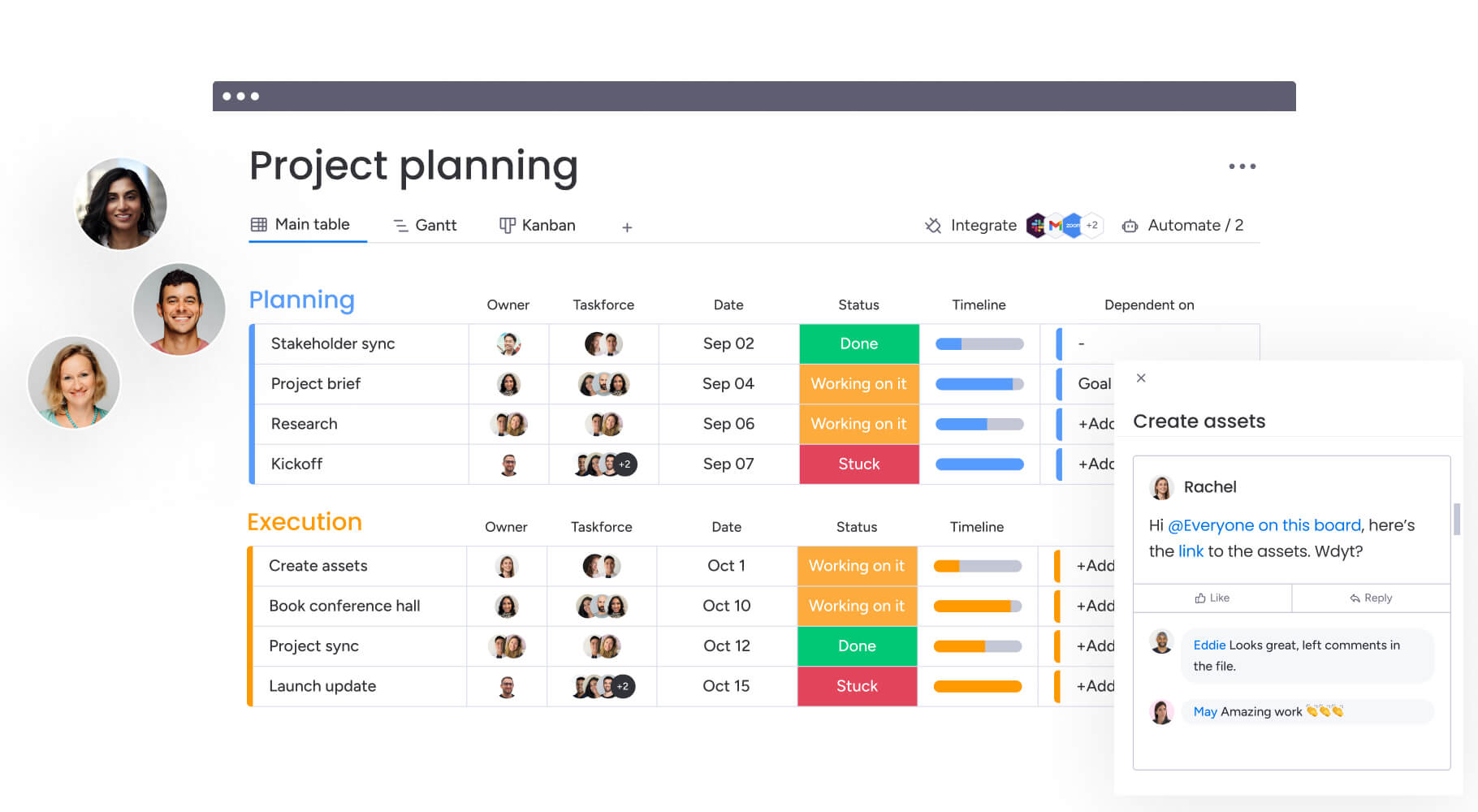
Teams using monday work management can visualize these dependencies through Gantt charts, identifying critical paths and building appropriate buffers to protect project deadlines.
Team capacity and skill levels
Individual productivity varies significantly based on experience, skills, and current workload. A senior team member might complete work in two days that takes a junior team member five days, yet many estimation approaches assume uniform productivity. Accurate estimation requires adjusting forecasts based on actual team composition.
Team member availability creates additional complexity. People rarely dedicate 100% of their time to single projects. Competing priorities, meetings, and administrative work reduce productive time. Realistic estimates account for these competing demands, typically assuming 60-70% productive time rather than full-time availability.
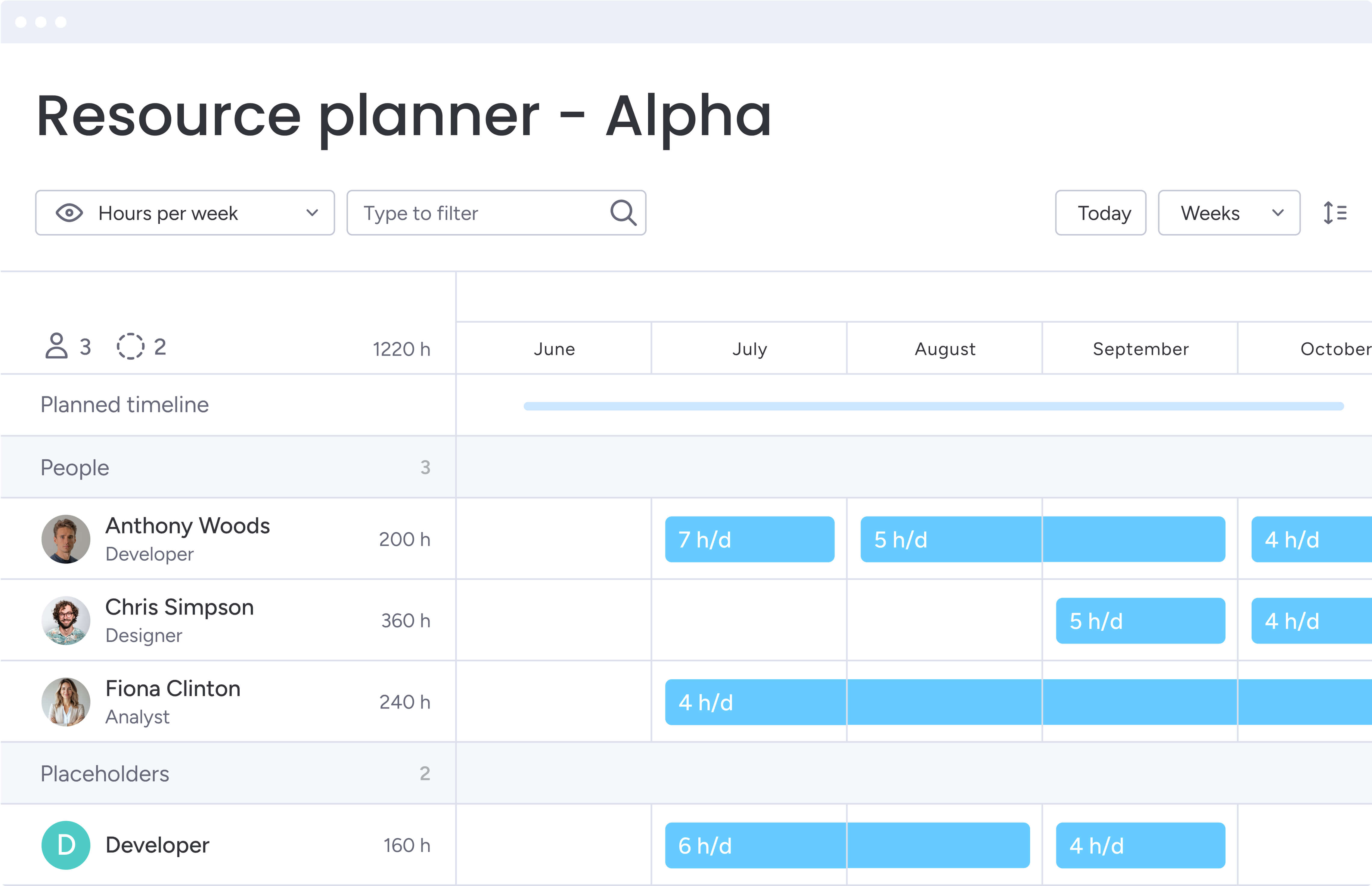
Organizations using monday work management can leverage the Workload View to see actual capacity across teams, making it easier to balance resources and quickly adapt when priorities shift.
Managing external variables and risks
External factors frequently affect project timelines in ways that internal estimates cannot fully control. Client feedback cycles introduce delays when stakeholders take longer than expected to review deliverables. Vendor dependencies create risks when third-party deliveries don’t arrive on schedule.
Effective estimation identifies potential external risks during planning and builds appropriate contingencies. Regular risk assessment throughout project execution helps teams adjust estimates as conditions change.
monday work management helps teams stay ahead of these challenges through Portfolio Risk Insights, which scans project boards and flags potential risks by severity. This proactive approach helps teams address issues before they escalate into major delays.
Proven strategies to improve estimation accuracy
ven the best estimation method won’t deliver reliable results if the process around it is weak. Accuracy improves when teams treat estimation as an evolving practice, not a one-time exercise done at kickoff.
The strategies below focus on what actually moves the needle: learning from past projects, reducing bias, building realistic buffers, and using data and collaboration to refine forecasts over time.
Create a comprehensive historical database
Systematic data collection transforms project experience into organizational knowledge that improves future estimation. Track actual time spent on work items, challenges encountered during execution, successful techniques that accelerated work, and final project outcomes compared to initial forecasts.
Standardized data collection ensures consistency across projects and team members. Define what information to capture, how to record it, and where to store it for future reference.
Organizations using monday work management automatically capture execution data, creating the historical database that enables analogous estimation and AI-powered forecasting for future projects.
Combine multiple estimation methods
Using multiple approaches provides more reliable estimates than relying on single methods. Triangulation reveals inconsistencies and improves confidence in final forecasts. Teams might pair bottom-up estimates with expert judgment, using detailed analysis as the foundation while leveraging experienced professionals to validate assumptions.
AI predictions validated against analogous project data create another effective combination. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns across historical projects, while human analysis ensures the reference projects truly compare to current initiatives.
Build smart buffers into your timeline
Contingency reserves protect project success without padding estimates excessively. Different buffer strategies address different uncertainty sources, and understanding when to apply each helps teams build resilience into project plans.
Consider these buffer approaches for different situations:
- Work-level buffers: add 10-20% to individual estimates for minor variations and unexpected complications.
- Project-level buffers: reserve 15-25% of total timeline for overall risks, scope adjustments, and coordination overhead.
- Resource buffers: account for team availability issues, competing priorities, and productivity variations.
Buffer communication matters as much as buffer sizing. Stakeholders should understand that contingency time protects project success rather than indicating poor planning.
Engage key stakeholders early
Stakeholder involvement improves both estimation accuracy and buy-in. Subject matter experts provide technical insights that refine estimates, end users identify requirements that might otherwise be overlooked, and resource providers confirm availability assumptions.
Structured stakeholder estimation sessions document assumptions and constraints that affect project scope. Teams collaborating on monday work management can use workdocs to capture estimation assumptions in real-time, with live boards and dashboards embedded directly into documentation for seamless planning and execution.
Try monday work managementLeverage AI and automation for smarter estimates
Modern technology transforms estimation from manual, subjective processes into data-driven, systematic approaches. AI and automation capabilities enhance human judgment while reducing the time and effort required to generate accurate forecasts.
How machine learning enhances accuracy
AI systems analyze patterns in historical project data to identify estimation insights that human analysts might miss. Machine learning algorithms recognize correlations between project characteristics and actual outcomes, discovering that projects with certain team compositions consistently finish faster, or that specific types of scope changes typically add predictable delays.
These systems process multiple variables simultaneously, considering team performance, project complexity, external factors, and organizational patterns to generate comprehensive estimates. Human analysts struggle to weigh dozens of factors consistently, while AI maintains objectivity across large datasets.
Automated risk detection and alerts
AI-powered continuous monitoring flags potential estimation issues before they escalate into major problems. Automated analysis compares actual progress against original estimates in real-time, identifying when projects deviate from forecasts and suggesting corrective actions.
Organizations leveraging monday work management benefit from AI that detects project risks across portfolios: the intelligent platform analyzes patterns across multiple projects simultaneously, identifying systemic estimation issues that affect organizational performance.
Dynamic estimation adjustments in real-time
AI-powered systems update estimates automatically as project conditions change, maintaining forecast accuracy throughout execution. Real-time data integration reflects current team capacity, scope changes, and external factors in updated predictions.
Automated adjustments eliminate the manual effort required to recalculate estimates when conditions change. Teams receive updated forecasts that reflect current reality rather than outdated initial assumptions.
monday work management’s automations handle repetitive estimation updates, integrating with existing workflows to save valuable time.
Measure and optimize your estimation process
Continuous improvement in estimation accuracy requires systematic measurement and analysis of forecasting performance. Understanding where estimates succeed or fail enables targeted improvements that enhance organizational capability over time.
Track estimation versus actual performance
Systematic comparison between initial estimates and actual project outcomes reveals patterns that drive continuous improvement. Monitor three key variance metrics to understand your estimation accuracy:
- Time variance: calculate the difference between estimated and actual duration for work items and overall projects.
- Cost variance: compare budgeted expenses against actual spending across cost categories.
- Scope variance: assess delivered features against originally planned scope.
These metrics reveal whether teams consistently under-estimate, over-estimate, or achieve reasonable accuracy. Patterns across multiple projects indicate systemic estimation issues that require process changes.
Extract insights from completed projects
Post-project estimation reviews identify lessons that improve future forecasts. Analyze both successful estimates and significant variances to understand contributing factors. Successful estimates reveal what techniques, data sources, or approaches work well. Large variances highlight overlooked factors or incorrect assumptions.
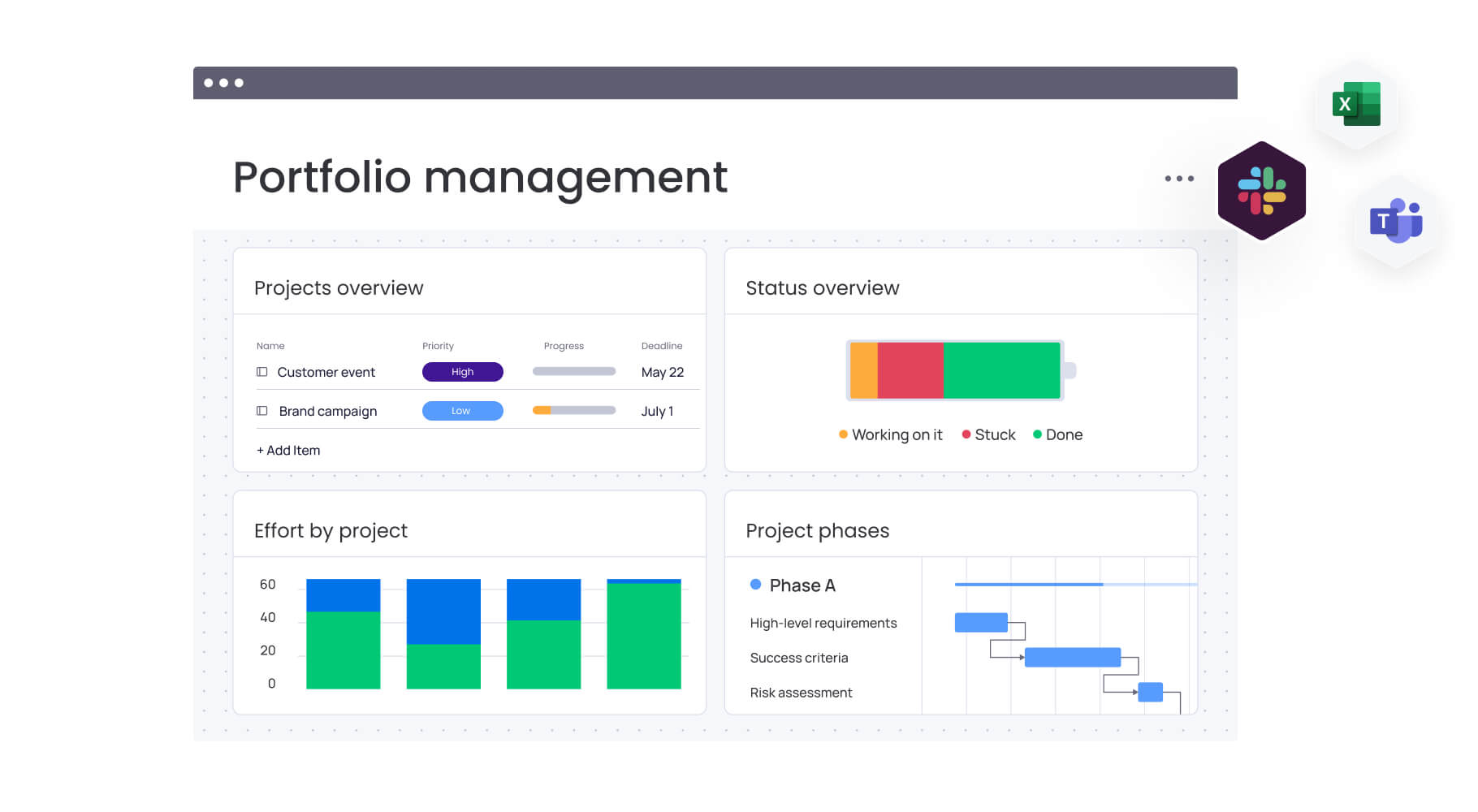
Teams using monday work management can leverage dashboards that automatically display live project data for insights on budget, goals, schedules, and resources. Customizable dashboards with drag-and-drop widgets help teams view estimation performance data and make sharper, faster decisions.
Implement continuous improvement workflows
Regular estimation review cycles systematically enhance forecasting processes. Monthly variance analysis identifies immediate issues requiring attention, quarterly process assessments evaluate whether estimation methods remain appropriate, and annual methodology updates incorporate new techniques and organizational learning.
Continuous improvement requires incorporating team feedback into evolving estimation practices. Practitioners who execute estimates daily often identify improvement opportunities that managers miss. Creating channels for this input and acting on valuable suggestions builds estimation capability throughout the organization.

Transform project estimation with monday work management
Intuitive solutions like monday work management transform project estimation from manual, error-prone processes into systematic, data-driven workflows that connect forecasts directly to execution. The platform integrates estimation capabilities into project management workflows, eliminating separate estimation spreadsheets that create data silos.
Visualize estimates with interactive timelines
Gantt charts and timeline views help teams create and communicate project estimates visually, making complex dependencies and resource allocations immediately understandable. Interactive timelines allow dynamic estimate adjustments: teams can drag work items to different dates and immediately see the impact on project deadlines, resource allocation, and dependent activities.
Timeline visualization reveals critical path dependencies that might otherwise remain hidden. Teams identify which activities directly affect project completion dates and focus estimation accuracy efforts where they matter most.
Automate estimation tracking and updates
Automation capabilities reduce manual effort in estimation management while improving accuracy and consistency. Automated workflows update estimates based on actual progress, send alerts when projects deviate from forecasts, and generate estimation reports for stakeholders without manual data compilation.
Automated progress tracking compares actual completion against original estimates continuously, providing immediate feedback on estimation accuracy. Teams receive alerts when work exceeds estimated duration or when accumulated delays threaten project deadlines.
Gain portfolio-wide estimation intelligence
Executive-level visibility into estimation accuracy across multiple projects helps organizations improve forecasting systematically. Dashboard capabilities aggregate estimation data to show portfolio-level trends, identify consistently over- or under-performing project types, and highlight teams that need estimation support.
Estimation approach Traditional methods monday work management
Data integration Manual spreadsheet updates and status reports Automated real-time tracking with live data feeds
Visualization Static charts requiring manual updates Interactive timelines and dashboards with dynamic adjustments
Collaboration Email coordination and meeting-based updates Integrated stakeholder engagement with transparent progress visibility
Historical analysis Manual data compilation from multiple sources Automated pattern recognition across project portfolios
Risk monitoring Periodic manual reviews and status meetings Continuous AI-powered alerts and proactive risk detection
Portfolio oversight Separate reporting requiring data consolidation Unified cross-project intelligence with executive dashboards
The platform connects estimation to execution in ways that create feedback loops, systematically enhancing forecasting accuracy over time. Teams move from reactive scrambling to proactive planning, with the visibility and tools needed to deliver projects predictably.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between effort estimation and time estimation?
The difference between effort estimation and time estimation is that effort estimation measures the actual work hours required to complete a work item, while time estimation includes the total calendar duration, accounting for team availability, dependencies, and other factors. A task might require 20 hours of effort but take five days to complete when accounting for other commitments.
How do you estimate projects without historical data?
Use expert judgment and three-point estimation to leverage team experience when historical data isn't available. Document actual results from these initial projects to build your historical database for future estimates.
Which estimation method is most accurate for software projects?
Bottom-up estimation combined with three-point techniques typically provides the highest accuracy for software projects when detailed requirements are known. This approach accounts for technical complexity while acknowledging the uncertainty inherent in software development.
What buffer percentage should I include in project estimates?
Include 10-20% buffers for well-defined projects and 25-50% for projects with high uncertainty or new technologies. The appropriate buffer depends on project complexity, team experience, and organizational risk tolerance.
How frequently should estimates be updated during execution?
Update estimates weekly during active project phases and whenever significant scope changes or unexpected issues arise. Regular updates help teams maintain accurate forecasts and identify problems early.
Can AI completely automate project estimation?
AI enhances estimation accuracy by analyzing patterns and suggesting estimates, but human judgment remains essential for understanding context and unique project factors. The most effective approach combines AI insights with expert knowledge.