Marketing organizations are under increasing pressure to demonstrate clear business impact. Budgets face tighter scrutiny, buying journeys span more channels, and leadership expectations extend well beyond campaign output. At the same time, teams are expected to move faster while maintaining accuracy, consistency, and accountability across every initiative.
As complexity grows, execution often outpaces structure. Processes vary by campaign, data lives across disconnected systems, and visibility into performance arrives too late to influence decisions. Without an operational foundation, marketing efforts become difficult to scale, measure, or defend at the executive level.
Marketing operations addresses this gap by creating the systems that connect strategy to execution. It establishes the processes, technology, and data standards that allow marketing teams to operate with discipline, predictability, and confidence. Instead of reacting to demand, organizations gain the ability to plan, prioritize, and optimize with clarity.
This article examines the five core functions of marketing operations, the signals that indicate it is time to invest, and the team structures that support scale in 2026 and beyond. It also explores how AI is reshaping marketing operations and outlines a practical framework for building an operational foundation that delivers measurable, long-term impact.
Key takeaways
- Marketing operations provides the structure modern teams need to scale: it connects strategy to execution through standardized processes integrated technology and reliable data.
- Five core functions underpin effective marketing operations: process management technology orchestration data analytics campaign execution and budget optimization work together to drive measurable outcomes.
- Operational gaps become visible as complexity increases: inconsistent workflows siloed data and delayed reporting often signal it is time to formalize marketing operations.
- AI is accelerating the evolution of marketing operations: automation predictive insights and digital workers improve efficiency accuracy and decision making across the full marketing lifecycle.
- Work management platforms support coordinated execution at scale: solutions such as monday work management help centralize workflows improve visibility and align cross-functional teams as operations mature.
What is marketing operations?
Marketing operations (MOps) connects strategy to measurable results through structured processes, the right technology, and trusted data. It shifts marketing from content creation alone to delivering clear, provable business impact.
While traditional marketing focuses on the what — campaigns, content, and creative — marketing operations focuses on the how. It builds the operational foundation that allows campaigns to run efficiently and scale without friction. As organizations face growing pressure to prove ROI and manage complex tech stacks, marketing operations provides the framework to turn fragmented workflows into reliable business systems.
The core functions of marketing operations deliver measurable value across the organization:
- Strategic alignment: every marketing activity maps directly to business objectives, reducing wasted effort on low-impact initiatives.
- Operational efficiency: standardized workflows and automation reclaim hours previously lost to manual coordination and administrative work.
- Data integrity: a single source of truth ensures decisions rely on accurate, real-time data rather than disconnected spreadsheets.
- Technology orchestration: integrated platforms enable consistent data flow across marketing, sales, and customer success teams.
Defining marketing operations for today's organizations
Marketing operations is the discipline of enabling marketing efficiency and effectiveness through the management of people, processes, technology, and data. It transforms marketing from a cost center into a measurable revenue driver by building infrastructure designed for scale.
In practice, marketing operations works behind the scenes, creating the foundation that enables visible wins. Campaign workflow automation replaces long email threads with centralized systems that route assets for approval, assign work based on capacity, and trigger launches automatically. Lead scoring frameworks prioritize prospects based on behavior and fit, ensuring sales teams focus on qualified opportunities rather than raw volume.
For executives, the value extends beyond surface-level metrics. Marketing operations provides reliable revenue forecasting, reduces risk, and supports smarter investment decisions. This clarity is increasingly important, as only 70% of CEOs say marketing’s role is clearly defined and understood at the executive level.
Organizations that invest in strong marketing operations see compounding benefits over time:
- Revenue predictability: marketing activities connect directly to sales outcomes, enabling forecasts based on pipeline data instead of historical averages.
- Cross-departmental alignment: shared workflows and data definitions reduce friction between marketing, sales, and product teams.
- Resource optimization: visibility into capacity and budget allocation helps leaders maximize spend while preventing burnout.
- Data-driven decision making: operational insights replace intuition with evidence-backed recommendations.
- Scalable growth: standardized systems support increased campaign volume without proportional headcount growth.

Marketing operations vs traditional marketing approaches
Shifting to marketing operations fundamentally changes how organizations drive growth. The comparison below highlights the most meaningful differences between traditional marketing and an operationally mature approach.
| Feature | Traditional marketing | Marketing operations |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Campaign-focused (outputs) | Process-focused (outcomes) |
| Decision making | Creative-driven decisions | Data-driven decisions |
| Structure | Siloed activities and platforms | Integrated workflows and platforms |
| Execution | Manual execution and handoffs | Automated systems and triggers |
| Measurement | Qualitative metrics (brand awareness) | Quantitative analytics (revenue attribution) |
As digital channels expand and buying journeys grow more complex, manual marketing models struggle to keep pace. Marketing operations provides a competitive advantage through speed, consistency, and adaptability — allowing teams to execute with confidence at scale.
5 core functions of marketing operations
These five functions form the operational backbone of modern marketing teams. Together, they ensure strategy translates into execution without unnecessary friction, even as organizations grow in size and complexity.
Function 1: process management and standardization
Process management makes marketing work repeatable and scalable. Instead of rebuilding workflows for every campaign, teams rely on documented playbooks that deliver consistent results across regions and roles.
Standardization drives measurable gains in speed and quality, especially in these areas:
- Campaign workflow standardization: templates guide teams from brief to launch and post-campaign analysis.
- Content creation and approval: automated approval paths protect brand consistency and compliance without delays.
- Lead management procedures: defined rules govern how leads are captured, qualified, enriched, and routed.
- Performance review cycles: structured analysis ensures insights are documented and applied consistently.
Function 2: marketing technology stack orchestration
Marketing operations owns the marketing technology stack, from selection to integration and ongoing optimization. The goal is not more platforms, but the right platforms working together.
Effective orchestration prioritizes a central operational platform that connects systems such as CRM, email, analytics, and social scheduling. This integration eliminates data silos and provides leadership with a unified view of performance without manual data entry.
Function 3: data management and analytics
This function turns raw data into actionable insight. It establishes governance standards, maintains data quality, and delivers reporting that supports confident decision making.
Key components of marketing data management include:
- Data collection and validation: processes ensure accuracy, consistency, and regulatory compliance at the point of entry.
- Attribution modeling: multi-touch frameworks track value across the full customer journey.
- Performance measurement: dashboards focus on business impact rather than vanity metrics.
- Predictive analytics: historical patterns inform forecasts and proactive adjustments.
- Reporting and visualization: complex data is translated into clear, accessible formats for stakeholders.
Function 4: campaign operations and execution
Campaign operations ensures ideas move from planning to launch on time and within budget. It separates creative work from delivery management so teams can focus on their strengths.
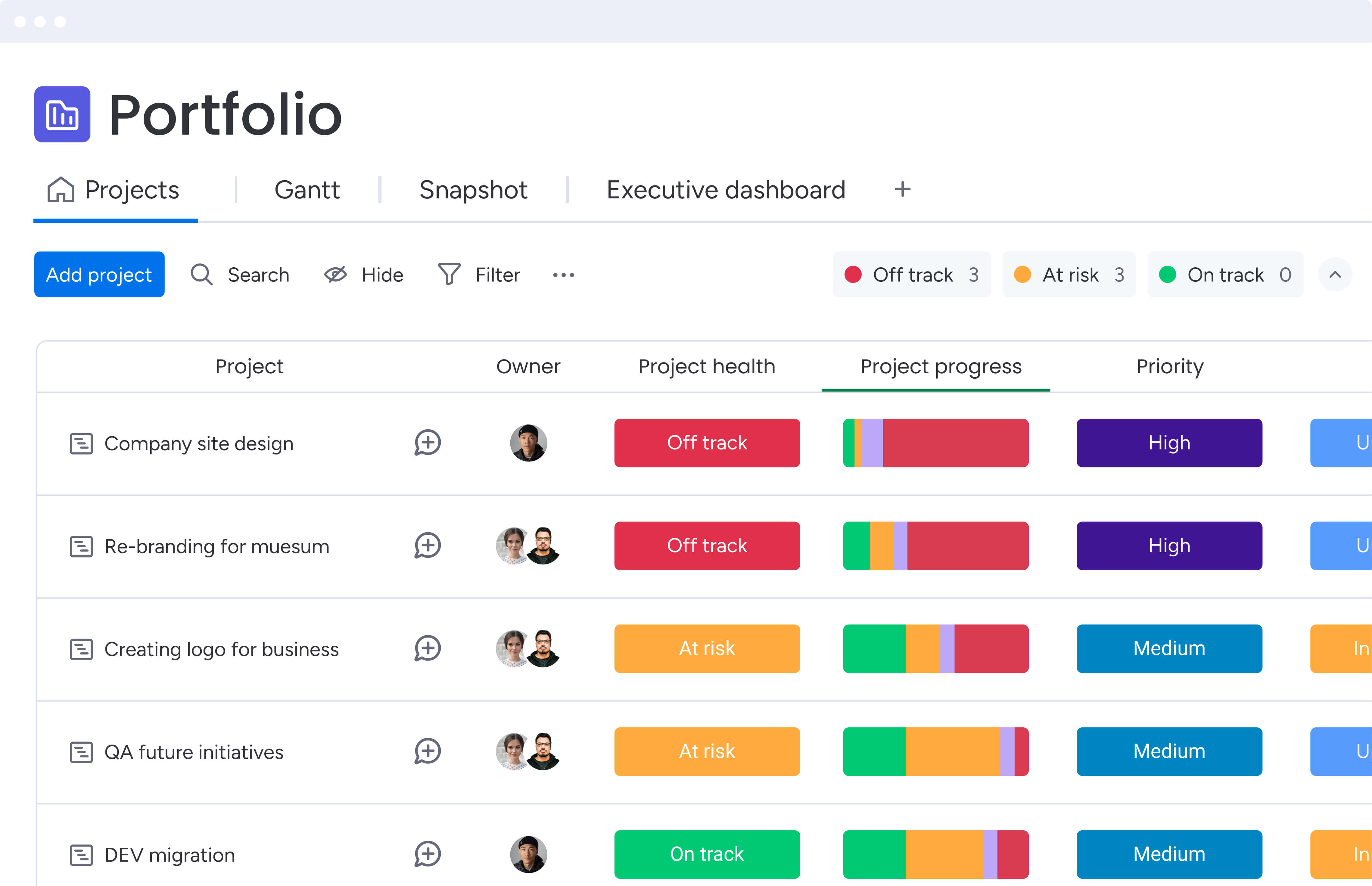
This involves rigorous project management, resource planning, and quality assurance. Teams use Gantt charts and workload views to identify dependencies and potential bottlenecks weeks in advance. By separating campaign management from asset creation, operations allows creative teams to focus on their craft while the delivery process runs efficiently.
Function 5: budget and resource optimization
Budget and resource optimization focuses on maximizing return, not just tracking spend. It ensures investments align with performance and capacity realities.
This function depends on clear visibility into both financial and human resources:
- Real-time budget tracking: prevents overspend and supports agile reallocation to high-performing channels.
- Continuous ROI monitoring: reinforces accountability and supports future budget planning.
- Resource capacity planning: balances workloads to sustain performance and inform hiring decisions.
Together, these functions position marketing operations as a strategic enabler — turning complexity into clarity and supporting sustainable, scalable growth.
When to invest in marketing operations
Timing plays a critical role when implementing marketing operations. Investing too late often results in technical debt that becomes costly and complex to resolve over time. Investing too early, however, can slow a small team with unnecessary processes and governance.
Most organizations reach a clear tipping point where the cost of inefficiency outweighs the cost of implementation. Recognizing that moment helps leaders invest with confidence and avoid both extremes.
7 signs your organization needs marketing operations
Knowing when that tipping point arrives requires watching for operational signals. The indicators below suggest it is time to formalize a marketing operations function and create a more scalable foundation.
- Marketing activities lack consistent processes: teams reinvent workflows for every campaign, resulting in uneven quality, missed deadlines, and avoidable rework.
- Data exists in silos: marketing performance metrics live in one system while revenue data lives in another, preventing clear connections between activity and outcomes.
- Technology stack is fragmented: platforms do not communicate effectively, forcing manual exports, imports, and spreadsheet-based workarounds.
- Campaign execution is unpredictable: there is no reliable way to forecast launch timelines, dependencies, or required resources.
- Marketing ROI is unclear: leadership cannot confidently identify which programs or channels are driving revenue.
- Cross-departmental friction exists: marketing, sales, and operations work in isolation, leading to misaligned goals and wasted effort.
- Growth is constrained by manual processes: increasing output requires a linear increase in headcount because workflows are not automated.
Building your business case for marketing operations
Justifying investment in marketing operations requires framing it as both risk reduction and revenue enablement. A strong business case highlights the cost of inaction alongside the measurable value of implementation.
Effective business cases typically include the following components:
- Quantify inefficiencies: calculate hours lost to manual data entry, asset searches, duplicated work, and recurring status meetings.
- Project efficiency gains: estimate the increase in campaign volume and speed made possible by standardized workflows.
- Calculate implementation costs: outline required investment in technology, personnel, and enablement.
- Present risk mitigation: highlight exposure related to compliance gaps, data integrity issues, or brand inconsistency without governance.
- Demonstrate competitive necessity: show how operational maturity supports the speed, visibility, and agility required in today’s market.
Choosing your implementation approach
Organizations can implement marketing operations through several models, depending on size, resources, and tolerance for change. Each approach balances speed, risk, and organizational impact differently.
The pilot program approach focuses on a single high-impact area, such as lead management or content production, proving value quickly while building momentum. A phased rollout introduces functions sequentially, often beginning with process standardization, followed by technology integration and advanced analytics. A comprehensive transformation delivers all core functions at once and is best suited for organizations undergoing significant restructuring or digital change.

How AI transforms marketing operations
AI is no longer a buzzword. It is a practical capability that strengthens every core function of marketing operations. By automating repetitive work and delivering predictive insights, AI enables operations teams to focus on strategy, optimization, and innovation instead of administrative overhead.
Across modern organizations, AI supports faster execution, improves accuracy, and creates the operational clarity required to scale marketing programs without sacrificing consistency or quality.
AI-powered automation for marketing processes
Automation powered by AI reduces the manual effort that slows teams down and introduces errors. By embedding intelligence directly into workflows, marketing operations functions become more reliable, responsive, and efficient.
AI-driven automation supports key marketing operations activities, including:
- Campaign workflow automation: analyzes project parameters, assigns work automatically, sets deadlines based on historical performance, and identifies critical path dependencies.
- Content categorization and tagging: organizes digital assets automatically, improves searchability, and reduces time spent locating files.
- Lead scoring and routing: evaluates prospect behavior using machine learning, assigns more accurate scores, and routes leads to the appropriate sales representative instantly.
- Performance monitoring: tracks campaign activity continuously and flags anomalies or underperformance for timely human review.
- Resource allocation: reviews team capacity and schedules to recommend optimal workload distribution and prevent bottlenecks.
Within structured platforms, teams can apply these capabilities directly to everyday work. For example, AI Blocks in monday work management allow marketing operations teams to embed ready-made AI functionality into workflows, improving speed and consistency across routine activities.
Predictive analytics and decision intelligence
AI shifts marketing operations from a reactive reporting function to a proactive planning discipline. Instead of focusing solely on past performance, teams can anticipate outcomes and adjust strategies in advance.
Forecasting models estimate campaign performance before launch, allowing teams to refine budgets, timing, and creative direction earlier in the process. AI also detects emerging market trends by analyzing data volumes that are impractical for manual review.
As a result, strategic planning becomes more data-driven. Teams can simulate different scenarios, compare potential outcomes, and make informed decisions about budget allocation and resource planning with greater confidence.
Digital workers revolutionizing marketing work
AI-powered Digital Workers operate as specialized contributors within marketing operations teams. Unlike static automation rules, these agents analyze data continuously, reason through changes, and surface recommendations as conditions evolve.
A campaign manager Digital Worker can monitor live performance across channels, identify budget inefficiencies, and recommend reallocations that improve return on investment. By handling ongoing analysis and reporting, these digital workers extend operational capacity without increasing headcount.
This shift allows human teams to spend more time on creative strategy, cross-functional collaboration, and relationship building, while AI manages the operational complexity behind the scenes.
7 steps to build your marketing operations framework
A strong marketing operations framework moves organizations from fragmented execution to operational excellence. The structure below outlines how to build a scalable foundation that supports growth while maintaining consistency and quality across initiatives.
Step 1: assess current marketing maturity
A clear assessment establishes the baseline for transformation. This includes reviewing existing workflows to identify bottlenecks, auditing the current technology stack for overlap or inefficiency, and evaluating data quality across systems.
The process also requires an honest review of team capabilities, highlighting gaps in technical or analytical skills that may require training or additional support.
Step 2: define strategic objectives and KPIs
Objectives must align directly with business priorities and remain measurable over time. Marketing operations teams should define success across several critical dimensions, including:
- Revenue impact: the contribution marketing makes to pipeline growth and closed revenue.
- Operational efficiency: improvements in speed, such as reduced time to market for campaigns.
- Data quality: standards for accuracy, completeness, and integration across platforms.
- Cross-department alignment: feedback scores from sales, product, and other partner teams.
- Technology ROI: utilization levels and value generated by each platform in the stack.
- Team productivity: output per employee and overall satisfaction across the team.
Step 3: map and document marketing processes
Process documentation is a prerequisite for standardization and automation. Teams begin by mapping the current state of critical workflows, identifying friction points, and designing future-state processes that remove inefficiencies.
This documentation defines approval paths, handoff protocols, and quality checkpoints, ensuring consistent execution regardless of who completes the work.
Step 4: select your technology foundation
Technology decisions should prioritize architecture over isolated features. The goal is to establish a central work management platform that acts as the operational backbone for marketing, connecting specialized systems and providing a unified view of work.
Key evaluation criteria include scalability, integration capabilities, security, and ease of adoption. The platform should support long-term growth without requiring frequent system replacements.
Step 5: design your team structure
Team structure should reflect strategic priorities and scale alongside organizational growth. This includes defining clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines within marketing operations.
Organizations may choose generalist roles that manage workflows end to end or specialist roles focused on areas such as data management or technology, depending on size and complexity.
Step 6: implement governance standards
Governance establishes consistency and reduces risk across marketing activities. Standards typically include naming conventions, data privacy requirements, and brand guidelines that protect quality and compliance.
A strong governance model also clarifies who can modify processes or introduce new technology, maintaining stability across the operational environment.
Step 7: establish continuous optimization
Marketing operations must evolve alongside the business and market conditions. Continuous optimization introduces feedback loops that support ongoing improvement, including regular process reviews, technology audits, and skills development.
With these mechanisms in place, the marketing operations function remains adaptable, effective, and aligned with organizational goals over time.
Marketing operations team structure for scale
As organizations grow, marketing operations structures must evolve to support greater complexity, volume, and cross-functional alignment. There is no universal model that fits every organization, and structure choices depend on company size, culture, and operational maturity.
Understanding the available models helps leaders design marketing operations teams that scale effectively while maintaining clarity, efficiency, and accountability.
3 proven organizational models
Marketing operations teams are commonly structured using one of three models. Each approach offers clear advantages depending on organizational context, growth stage, and complexity.
| Model | Structure | Best for | Pros and cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized | A single MOps team serves the entire marketing org | Mid-size organizations | Pros: consistency, efficiency, defined standards. Cons: can become a bottleneck; may lack context on specific campaigns |
| Distributed | Ops specialists sit within specific marketing functions | Large, complex organizations | Pros: deep expertise in specific areas; agility. Cons: inconsistent processes; data silos; difficult to coordinate |
| Hybrid | A central "Center of Excellence" sets standards, with embedded specialists in teams | Growing enterprises | Pros: balances consistency with agility. Cons: complex reporting lines; requires strong governance |
Essential marketing operations roles and skills
Effective marketing operations teams combine strategic oversight with technical and execution expertise. While responsibilities vary by organization, most teams rely on a core set of roles that work together to support scalable marketing execution.
- Marketing operations manager: oversees strategy, prioritization, and team leadership with strong organizational and stakeholder management skills.
- Marketing data analyst: maintains data quality, reporting, and insights with proficiency in SQL and business intelligence platforms.
- Marketing technology specialist: manages the marketing technology stack, integrations, and administration with expertise in APIs and automation.
- Campaign operations coordinator: supports campaign delivery and execution with strong project management and coordination skills.
- Marketing process designer: optimizes workflows and documentation using process mapping and change management expertise.
Scaling from individual contributor to enterprise team
Marketing operations teams typically evolve through four stages as organizational needs mature. Early-stage teams often rely on a single generalist responsible for technology administration, reporting, and campaign execution, with a primary focus on maintaining basic functionality.
As volume increases, roles begin to separate into technical and process-focused responsibilities, enabling stronger foundations for scale. More mature organizations introduce specialized roles for analytics, automation, and governance, shifting the focus toward optimization and efficiency.
At the enterprise level, teams often adopt a hybrid structure, combining centralized strategy with embedded execution. This stage emphasizes innovation, cross-functional alignment, and measurable business impact.

Revolutionize your marketing operations with monday work management
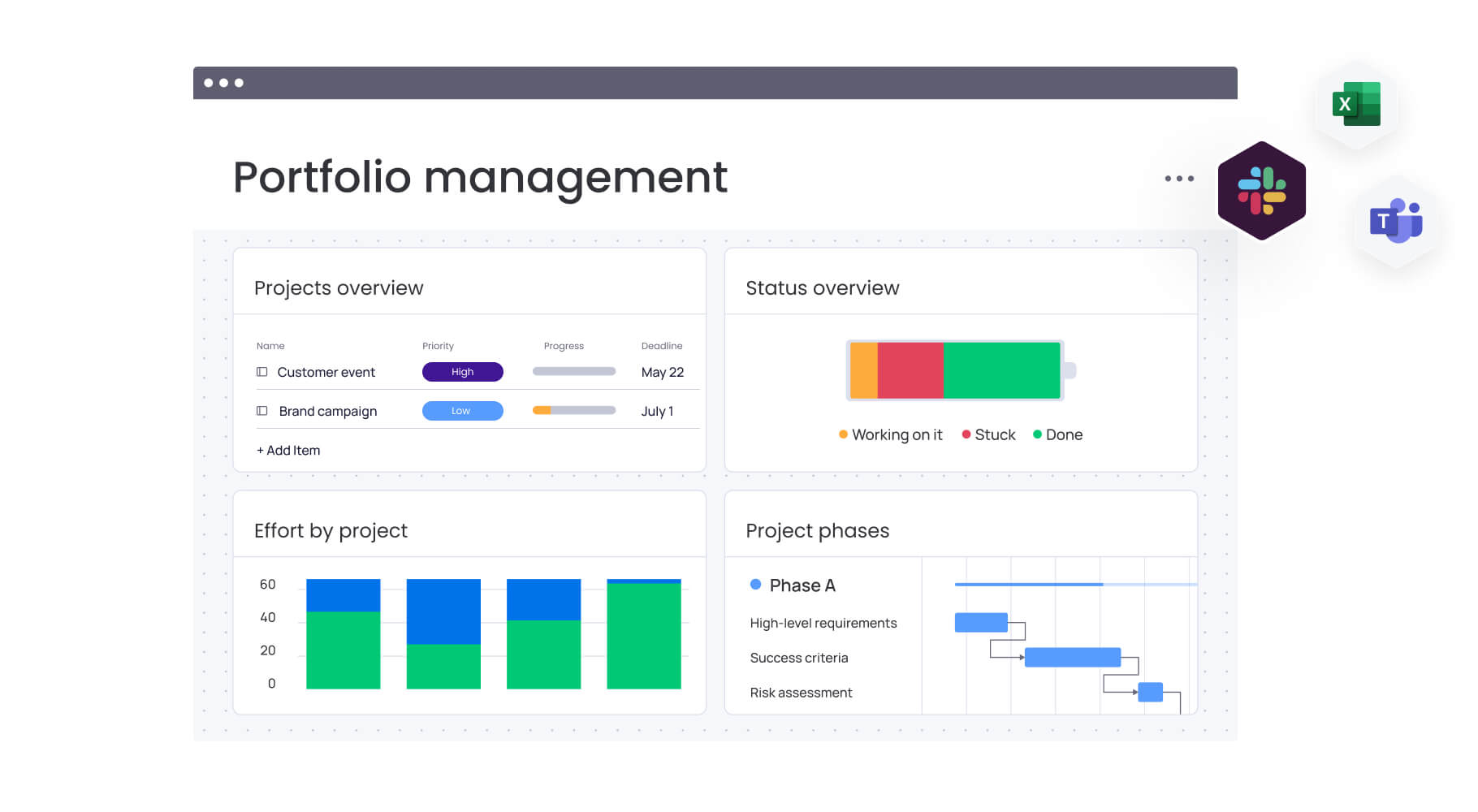
As marketing operations become more complex, teams need systems that support structure, visibility, and automation at scale. Modern platforms like monday work management provide an operational backbone that connects strategy to execution while maintaining flexibility.
Compared with fragmented toolsets or rigid project management software, unified work management platforms offer clear advantages across collaboration, automation, and scalability.
| Feature | monday work management | Traditional solutions | Marketing-only platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Unified work management platform | Fragmented ecosystem | Limited to marketing functions |
| Collaboration | Cross-departmental (sales, product, etc.) | Siloed operations | Marketing team only |
| Automation | AI-powered automation and insights | Manual processes | Basic, rule-based automation |
| Scalability | Enterprise-grade scalability | Limited scalability | Function-specific limitations |
| Visibility | Real-time, cross-functional reporting | Delayed or incomplete data | Marketing metrics only |
Organizations adopt unified work management platforms to establish a single source of truth for marketing activities, budgets, and performance. Shared digital workspaces reduce silos, while no-code automation ensures process consistency and reduces administrative overhead.
Modern work management platforms support the full scope of marketing operations through purpose-built capabilities that align with daily execution needs.
- Process standardization: custom workflow templates create consistent execution across campaign types, from social media initiatives to global product launches.
- Technology orchestration: over 200 native integrations connect the marketing technology stack, pulling data from CRMs, advertising platforms, and creative tools.
- Data management: real-time dashboards consolidate performance data into customizable views, supported by advanced reporting.
- Campaign execution: Gantt charts and timeline views provide sophisticated project management capabilities with dependency tracking.
- Budget optimization: budget tracking columns and dashboards monitor spend in real time against allocated funds.
AI Blocks automate routine activities such as content categorization, sentiment analysis, and data extraction. Digital workers like the Campaign Manager analyze campaign data to surface optimization opportunities and flag risks before performance is affected.

Build marketing operations that drive measurable growth
Marketing operations has shifted from a support role to a strategic function that directly influences organizational competitiveness. Teams with strong operational foundations move beyond faster execution toward better decision-making, smarter resource allocation, and clearer performance measurement.
This transformation requires sustained investment in processes, technology, and people. The payoff includes predictable revenue growth, stronger cross-functional alignment, and the agility to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
By bringing strategy, execution, and measurement into a single environment, monday work management helps marketing teams operate with clarity and confidence. From standardizing workflows to tracking performance through real-time dashboards, it enables consistent, high-quality outcomes at scale.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com’s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.
Frequently asked questions
What are the 4 pillars of marketing operations?
The four pillars of marketing operations are process management, technology orchestration, data analytics, and performance optimization. Together, they enable marketing teams to operate as measurable, scalable business functions.
What is the difference between marketing operations and regular marketing?
Marketing operations focuses on the "how" — the systems, processes, and data that enable effectiveness. Regular marketing focuses on the "what" — the creative strategy, messaging, and campaign execution. Operations provides the infrastructure that makes marketing activities measurable, scalable, and aligned with business objectives.
What does a marketing operations professional do?
A marketing operations professional designs and manages the processes, technology, and data systems that enable marketing teams to execute campaigns efficiently. They bridge the gap between strategy and execution, ensuring marketing activities contribute to measurable business outcomes through technology management, data analysis, and workflow optimization.
How much does it cost to implement marketing operations?
Implementation costs depend on organization size and complexity. Small teams may invest primarily in platform licensing and basic training, while enterprise implementations often include technology licensing, personnel salaries, and implementation services. Most organizations see a positive ROI within six to twelve months through efficiency gains and improved revenue attribution.
Can small businesses benefit from marketing operations?
Small businesses gain significant value from marketing operations by implementing scaled-down processes and technology. Practices such as workflow standardization, centralized asset management, and performance tracking improve efficiency and ROI, enabling growing companies to achieve more with limited resources.
What's the difference between marketing operations and revenue operations?
Marketing operations is a specific discipline focused on marketing processes and technology. Revenue operations (RevOps) is a broader function that unifies marketing, sales, and customer success operations into a single strategy. Marketing operations typically serves as a critical component of a holistic RevOps approach.

.jpg)