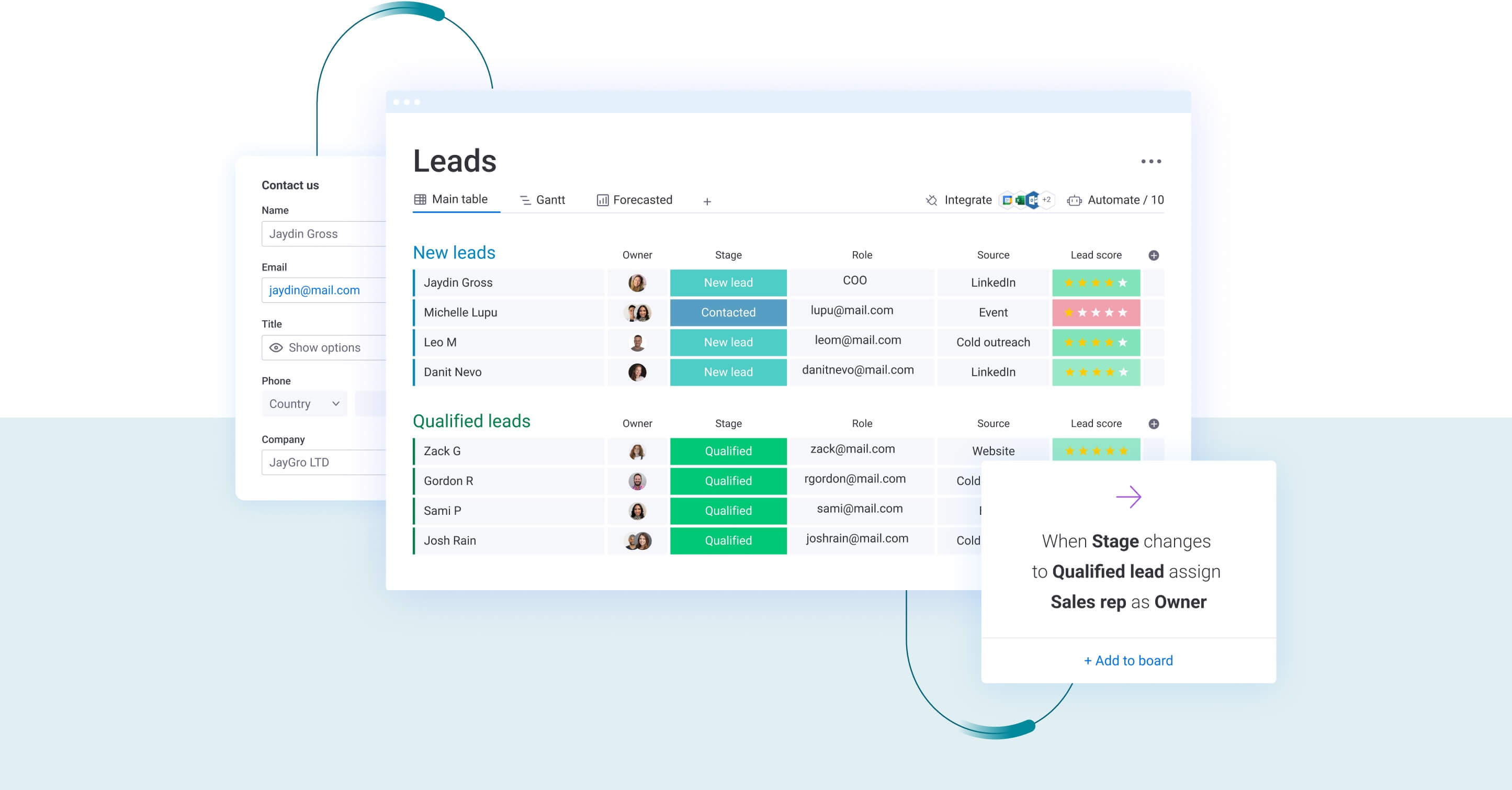
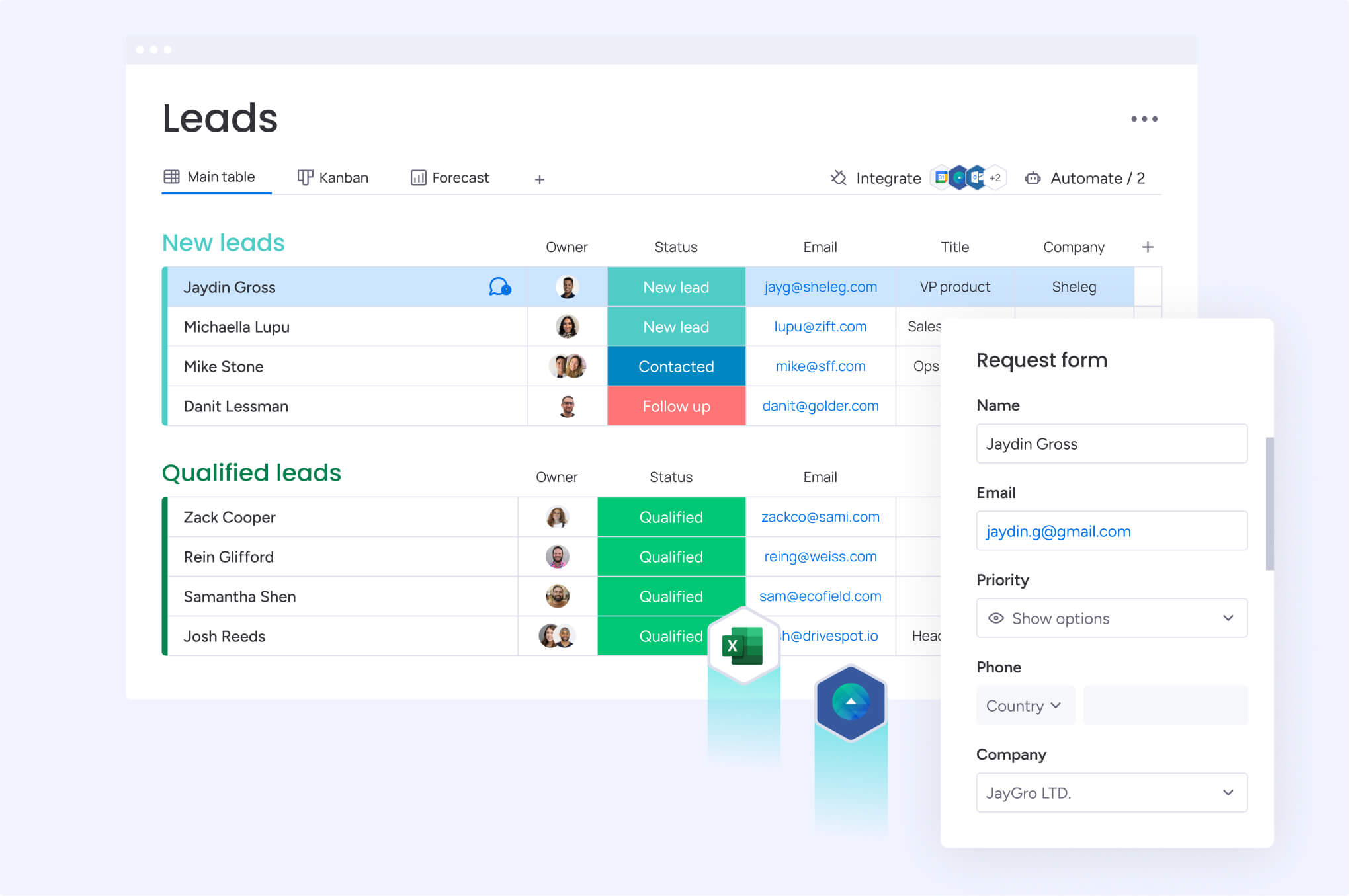
Sales teams close deals, but customer data often lives in scattered spreadsheets and email threads. This fragmentation causes revenue teams to lose the visibility needed to forecast accurately and coordinate smooth handoffs. By centralizing this data, you eliminate the “information silos” that prevent consistent customer experiences.
A CRM database puts contacts, deal history, and behavior patterns in one accessible location. It transforms raw interactions into organized intelligence, allowing sales reps to understand needs instantly and managers to forecast with confidence. Ultimately, it provides the foundation for scaling your operations without starting every conversation from scratch.
This guide explores how CRM databases resolve data chaos and drive revenue growth. We’ve covered the core components of these systems, compared different database types, and outlined a proven 5-step implementation process. Following this roadmap ensures your team can transition to a unified system without disrupting daily sales activities.
Key takeaways
- Replace spreadsheet chaos with unified customer data: stop losing deals to version control nightmares and get everyone working from the same real-time customer information.
- Automate repetitive tasks to focus on selling: let workflows handle follow-ups, data entry, and lead routing. According to McKinsey 2017, this can help your team spend up to 30% more time in actual customer conversations.
- Get predictable revenue forecasting: transform guesswork into confident board reporting with real-time pipeline visibility that shows exactly which deals will close.
- Scale without breaking your processes: CRM databases handle millions of records while spreadsheets collapse under the weight of growth — choose systems that grow with you.
- Leverage AI to work smarter: with platforms like monday CRM, automatically extract information from emails, compose personalized messages, and summarize deal timelines without manual data entry.
What is a CRM database?
A CRM database serves as the centralized repository for all customer information: contacts, deals, interactions, and history. More importantly, it provides the systematic control and visibility necessary for effective sales management and strategic decision-making.
When customer data disperses across email inboxes, spreadsheets, and individual calendars, organizations lack the visibility required to deliver consistent experiences or make confident decisions. A CRM database establishes a single source of truth for customer relationships, enabling teams to understand customer needs, anticipate opportunities, and coordinate seamlessly across departments.
For mid-market B2B organizations managing complex sales cycles, a CRM database tracks every touchpoint across the buying journey: from initial marketing engagement through contract negotiation to post-sale expansion. For small businesses, it ensures that any team member can immediately access purchase history, communication preferences, and previous support interactions without searching through multiple systems.
Modern CRM database software integrates AI capabilities that automate routine data entry and surface intelligent insights. Rather than manually logging every email or updating deal stages, teams benefit from systems that capture interactions automatically and suggest next best actions based on patterns across thousands of similar customer relationships.
Understanding CRM database fundamentals
CRM databases are the backbone of all your customer relationships. They take messy customer info and turn it into something your team can actually find and use. For maximizing investment and driving superior customer outcomes, it is essential to understand how those systems work.
CRM databases store four essential categories of information that work together to create comprehensive customer profiles:
- Contact information: names, titles, company details, phone numbers, email addresses, and communication preferences.
- Interaction history: emails, calls, meetings, support tickets, website visits, and document exchanges.
- Transaction data: purchase history, deal values, payment terms, contract details, and renewal dates.
- Behavioral insights: engagement patterns, product interests, communication frequency, and buying signals.
CRM databases connect all these dots to give you the complete picture of each customer relationship without interruption. When a sales representative views a customer record, they see the entire relationship timeline in one continuous flow: which marketing campaigns generated initial interest, what questions arose during evaluation, how implementation progressed, and which features the customer uses most.
Data structure components:
- Fields: individual data points like “email address” or “deal value”.
- Records: complete profiles like “John Smith’s contact information”.
- Tables: collections of similar records like “all customer contacts”.
Customization allows businesses to capture industry-specific information. Technology companies track product usage metrics and technical requirements, while professional services firms document project scopes and billing arrangements.

How CRM databases transform customer data management?
Try managing customer relationships without a CRM database and you’ll hit the same frustrating roadblocks every growing company faces, directly hurting your revenue. These pain points create operational inefficiencies that directly impact customer satisfaction and team productivity.
Common challenges without CRM databases:
- Information silos: customer information scatters across individual email inboxes, personal spreadsheets, and team members’ memories.
- Manual data burden: data entry consumes hours each week while human error introduces inconsistencies.
- Disconnected experiences: customer service teams lack visibility into sales conversations, leading to fragmented customer interactions.
- Forecasting difficulties: sales managers struggle to predict outcomes because pipeline data lives in disconnected systems.
CRM databases take all those scattered customer details and turn them into something your team can actually find, understand, and use to close deals. Every team member views the same real-time customer information regardless of department or device, a key benefit of customer tracking software. Automated data capture eliminates manual entry while maintaining accuracy and completeness.
Transformation benefits:
- Unified visibility: customer service representatives access complete interaction histories, enabling informed, personalized support.
- Predictable outcomes: revenue leaders report to boards with confidence because real-time pipeline data shows exactly which deals will close and which need intervention.
- Operational efficiency: sales teams operate more effectively because they spend time selling instead of updating spreadsheets.
For mid-market sales organizations, this transformation means predictability replaces guesswork across all customer-facing activities.
CRM database vs spreadsheets: the real cost
When comparing spreadsheets to CRM databases, it’s important to understand their fundamental differences in capability, scalability, and bottom-line impact. Grasping these distinctions helps organizations recognize when they’ve outgrown manual systems and need dedicated database infrastructure.
| Dimension | Spreadsheets & manual systems | CRM databases |
|---|---|---|
| Data accessibility | Single-user files create version control nightmares | Real-time multi-user access ensures everyone views current data |
| Scalability | Performance degrades as data grows | Handles millions of records with consistent performance |
| Automation | Minimal automation requires manual updates | Extensive workflow automation eliminates repetitive tasks |
| Integration | Isolated systems require manual data transfer | Native connections with marketing, finance, and support platforms |
| Security | Vulnerable to accidental deletion and data loss | Enterprise-grade security with role-based permissions |
| Reporting | Manual compilation of data for reports | Automated dashboards provide real-time insights |
Specific spreadsheet pain points:
- Version control chaos: multiple team members maintain separate customer lists so which version contains the most current information?
- Manual tracking burden: customer interaction timelines require manual note-taking that inevitably becomes inconsistent.
- Reporting bottlenecks: basic reporting demands hours of manual data compilation and calculation.
- Scaling failures: a small team managing fifty customers might coordinate through spreadsheets, but that approach collapses with five hundred customers across multiple regions.
CRM database advantages:
- Real-time collaboration: sales managers see pipeline changes as they happen.
- Automated workflows: consistent follow-up without requiring team members to remember every task.
- System integration: email, calendar, and communication platforms capture interactions automatically.
CRM databases solve these fundamental limitations while providing capabilities impossible with manual systems.
6 key benefits of CRM databases for revenue teams
Revenue teams face increasing pressure to deliver stronger quarterly results while managing growing portfolios of complex customer relationships. CRM databases provide the foundation for addressing these challenges through core benefits that directly impact revenue generation and operational efficiency.
1. Unified customer data across all touchpoints
CRM databases foster collaboration by putting all customer conversations in one place, creating shared ownership and a unified view of the customer. This unification transforms how teams collaborate and serve customers across the entire organization.
When marketing runs a campaign, sales teams immediately see which prospects engaged and how. When sales closes a deal, customer success teams access complete context about customer expectations and implementation requirements. When support resolves a ticket, account managers understand the issue history before renewal conversations.
Practical operational improvements:
- Marketing and sales alignment: marketing teams see which leads sales contacted, what responses they received, and which messaging resonated.
- Seamless handovers: complete qualification conversations, pain points discussed, and stakeholder information transfer automatically between teams.
- Support coordination: support teams view complete relationship health before addressing issues.
2. Real-time visibility into sales performance
CRM databases provide instant access to pipeline health, deal progression, and team performance metrics that enable accurate forecasting and confident decision-making. Rather than waiting for weekly reports compiled from individual spreadsheets, revenue leaders view current pipeline status and identify bottlenecks immediately.
Pipeline forecasting becomes reliable when deal probability updates automatically based on stage progression and activity levels. Revenue projections reflect current reality rather than outdated assumptions.
Visibility benefits by role:
- Executive leadership: accurate, current forecasts for board reporting and strategic decisions.
- Sales managers: coaching opportunities from activity and conversion analysis.
- Individual representatives: deal prioritization and opportunity tracking.
- Revenue operations: process optimization based on stage-by-stage performance data.
3. Automated workflows that reduce manual work
CRM databases eliminate repetitive manual tasks through intelligent automation that frees revenue teams to focus on high-value activities. The time savings are substantial and measurable across all customer-facing functions.
Key automation capabilities:
- Lead management: assigns new opportunities to appropriate representatives based on territory, product expertise, or workload.
- Follow-up scheduling: ensures no prospect goes uncontacted beyond defined timeframes.
- Data maintenance: enriches contact records, detects duplicates, and updates information from external sources.
Measurable time savings:
- Sales productivity: representatives spend 30% more time in customer conversations rather than administrative tasks.
- Response speed: qualified leads receive personalized outreach within minutes rather than hours or days.
- Process consistency: implementation follows standardized sequences that coordinate multiple departments.
Platforms like monday CRM use AI to automatically extract information from emails and documents, compose personalized messages, and summarize entire deal timelines, eliminating hours of manual work each week.
4. Data-driven insights for informed decisions
CRM databases transform raw customer data into actionable business intelligence that drives strategic decisions across the organization. Rather than relying on intuition or anecdotal evidence, revenue leaders make choices based on patterns across hundreds or thousands of customer relationships.
Customer behavior pattern analysis reveals purchase cycles, engagement preferences, and churn indicators that inform relationship strategies. Sales performance analytics identify win/loss factors, deal velocity trends, and conversion optimization opportunities at each pipeline stage.
Strategic decision improvements:
- Product development: feature prioritization using usage data and feedback patterns.
- Territory management: assignment adjustments based on performance analysis and market potential.
- Campaign optimization: marketing investment decisions using conversion data and customer journey insights.
- Resource planning: hiring and budget allocation based on pipeline coverage and growth projections.
5. Enhanced collaboration between departments
CRM databases break down departmental silos by providing shared visibility into customer relationships and project status. Sales, marketing, customer success, legal, and finance teams coordinate effectively because they access the same real-time information.
Sales and marketing alignment improves through shared lead definitions, campaign performance visibility, and feedback loops. Marketing teams see which campaigns generate qualified opportunities that convert to revenue.
Collaboration scenarios:
- Complex negotiations: sales representatives coordinate with legal on contract terms while finance reviews payment arrangements.
- Customer onboarding: implementation teams see sales commitments and customer expectations.
- Account management: success teams identify expansion opportunities based on usage patterns.
6. Measurable ROI and revenue growth
A CRM database provides clear visibility into what’s working in your sales process, which relationships are most valuable, and the direct revenue impact of your investment. Organizations track improvements across multiple dimensions that quantify business impact.
Sales efficiency improvements:
- Cycle length reduction: faster deal progression through improved coordination and automation.
- Deal size increases: representatives position solutions more effectively with complete customer context.
- Conversion rate improvements: consistent processes and prompt responses drive higher win rates.
Customer retention gains:
- Renewal rate improvements: proactive relationship management drives higher retention.
- Account expansion acceleration: teams identify upsell opportunities based on usage patterns.
- Churn reduction: saves acquisition costs while preserving revenue streams.
Customer retention gains deliver compounding value over time through sustained revenue growth.

“With monday CRM, we’re finally able to adapt the platform to our needs — not the other way around. It gives us the flexibility to work smarter, cut costs, save time, and scale with confidence.”
Samuel Lobao | Contract Administrator & Special Projects, Strategix
“Now we have a lot less data, but it’s quality data. That change allows us to use AI confidently, without second-guessing the outputs.”
Elizabeth Gerbel | CEO
“Without monday CRM, we’d be chasing updates and fixing errors. Now we’re focused on growing the program — not just keeping up with it."
Quentin Williams | Head of Dropship, Freedom Furniture
“There’s probably about a 70% increase in efficiency in regards to the admin tasks that were removed and automated, which is a huge win for us.“
Kyle Dorman | Department Manager - Operations, Ray White
"monday CRM helps us make sure the right people have immediate visibility into the information they need so we're not wasting time."
Luca Pope | Global Client Solutions Manager at Black Mountain
“In a couple of weeks, all of the team members were using monday CRM fully. The automations and the many integrations, make monday CRM the best CRM in the market right now.”
Nuno Godinho | CIO at VelvTypes of CRM databases for different business needs
CRM databases serve different purposes depending on organizational priorities and maturity levels. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations choose solutions that match current needs while providing room for growth and adaptation.
Operational CRM databases for daily workflows
Operational CRM databases streamline customer-facing processes and daily sales activities through intuitive interfaces, workflow automation, and real-time collaboration capabilities. They prioritize ease of use over analytical depth, enabling teams to manage customer relationships effectively without extensive training.
Core operational capabilities:
- Contact and lead management: centralized customer information with interaction tracking accessible to all team members.
- Sales pipeline management: visual deal progression with stage-based workflows and automated follow-ups.
- Task and activity automation: meeting scheduling, email sequences, and reminder systems that eliminate manual tracking.
Ideal use cases:
- Sales development representatives: manage lead qualification and handoff processes efficiently.
- Account executives: track deal progression and stakeholder communications.
- Customer success teams: coordinate onboarding and identify expansion opportunities.
Analytical CRM databases for strategic insights
Analytical CRM databases transform customer data into strategic business intelligence through advanced reporting, predictive analytics, and deep segmentation capabilities. These systems prioritize data analysis and insight generation over day-to-day operational tasks.
Advanced analytical capabilities:
- Custom reporting: trend analysis and performance benchmarking across teams, territories, and time periods.
- Predictive analytics: lead scoring, churn risk prediction, and opportunity forecasting using historical patterns.
- Customer segmentation: grouping by behavioral patterns, value potential, and engagement preferences.
Strategic applications:
- Revenue operations: analyze sales performance across dimensions like territory, product, and representative.
- Executive leadership: make data-driven decisions about market expansion using comprehensive territory analysis.
- Marketing teams: optimize campaign targeting based on behavioral analysis and conversion data.
Collaborative CRM databases for team alignment
Collaborative CRM databases prioritize team coordination, information sharing, and cross-departmental visibility. Those solutions excel at breaking down silos and ensuring consistent customer experiences across complex organizations.
Key collaborative features:
- Shared customer timelines: complete interaction history visible to all relevant team members.
- Cross-departmental workflows: automated handovers between sales, support, and account management.
- Communication integration: email, chat, and meeting coordination within customer context.
Organizations with complex sales processes, multiple customer touchpoints, and cross-departmental coordination requirements gain maximum value from collaborative CRM databases. These systems prove particularly valuable in mid-market B2B environments where deals involve multiple stakeholders.
Choosing between cloud-based and on-premise solutions
The decision between cloud-based and on-premise CRM databases fundamentally impacts deployment speed, cost structure, and operational requirements. Each approach offers distinct advantages depending on organizational priorities and constraints.
| Consideration | Cloud-based solutions | On-premise solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation timeline | Operational within weeks | Requires months for hardware and configuration |
| Upfront costs | Subscription-based with predictable monthly costs | Significant capital investment in hardware and licenses |
| Scalability | Instant scaling as users and data grow | Scaling requires hardware upgrades and planning |
| Maintenance | Vendor manages updates and infrastructure | Internal IT handles all maintenance and troubleshooting |
| Data control | Shared responsibility with vendor | Complete control over data location and security |
| Accessibility | Access from any device with internet | Limited to corporate network or VPN access |
Cloud-based advantages:
- Rapid deployment: organizations prioritizing quick implementation, predictable costs, and minimal IT overhead choose cloud-based solutions.
- Fast time-to-value: teams begin using CRM capabilities within weeks rather than months.
- Automatic updates: access to latest features without requiring internal resources or downtime.
On-premise considerations:
- Data control: organizations requiring complete data control or meeting specific compliance requirements consider on-premise solutions.
- Customization flexibility: maximum flexibility for unique business processes and custom integrations.
- IT requirements: significant IT resources required for ongoing maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting.
5 steps to build your CRM database successfully
CRM database implementation follows a structured approach that ensures success regardless of organization size or complexity. Following these sequential steps minimizes risk while maximizing user adoption and business value.
Step 1: map your customer journey and data needs
Successful implementation begins with understanding how customers interact with your organization and what information teams need to manage those relationships effectively. This foundational work prevents costly mistakes and ensures the system supports actual business processes.
Document your complete customer journey:
- Awareness stage: how prospects discover your organization.
- Consideration phase: evaluation process interactions and touchpoints.
- Purchase process: sales cycle stages and stakeholder involvement.
- Post-purchase experience: onboarding, support, and expansion opportunities.
Essential data requirement activities:
- Team interviews: gather input from different departments about their specific needs and current pain points.
- Touchpoint documentation: map current customer interactions and information collection methods.
- Requirement prioritization: rank data needs based on business impact and implementation complexity.
- Value focus: concentrate on capabilities that deliver immediate, measurable results.
Step 2: select the right CRM platform
The next step is selecting your platform based on the customer journey and data requirements identified in Step 1, prioritizing functional alignment over superficial features. The right platform scales with your organization and adapts to evolving requirements without necessitating complete system replacement.
Critical evaluation factors:
- Functional requirements: core capabilities needed to support identified customer journey stages.
- Scalability considerations: ability to handle growth in users, data volume, and complexity.
- Integration capabilities: compatibility with existing systems and future technology needs.
- User experience: adoption likelihood based on team technical skills and preferences.
- Total cost: implementation, training, subscription, and customization expenses.
Selection best practices:
- Involve end users: ensure the chosen platform matches how teams actually work by including them in the selection process.
- Request demonstrations: use actual organizational data and scenarios to evaluate real-world functionality.
- Consider future needs: plan for growth while avoiding over-engineering initial requirements.
Step 3: design your data structure and workflows
This step translates business requirements into concrete system configuration, ensuring the CRM aligns with your team’s workflows rather than forcing adaptation to rigid structures. Thoughtful design prevents future complications and drives user adoption by creating intuitive, logical information organization.
Core design principles:
- Logical organization: group related information together and establish clear hierarchies.
- Consistent naming: use terminology that matches organizational language.
- Field optimization: balance data completeness with user experience.
- Validation rules: ensure information accuracy through automated checks.
Workflow automation design:
- Lead qualification workflows: automatically assign and route prospects based on defined criteria.
- Deal progression automation: update stages based on specific activities and milestones.
- Customer onboarding sequences: coordinate multiple departments through automated task assignment.
Step 4: execute data migration and validation
Data migration transfers existing customer information into the new CRM database. Proper planning ensures smooth transitions without data loss while maintaining business continuity throughout the implementation process.
Migration planning steps:
- Data inventory: catalog all existing customer information sources and formats.
- Cleaning requirements: identify duplicate records and formatting inconsistencies.
- Field mapping: determine how existing data corresponds to new database structure.
- Timeline planning: phase the approach to minimize business disruption.
Implementation best practices:
- Complete backups: create full data backups before beginning migration.
- Clean data foundation: start with deduplicated, accurate information.
- Phased testing: test migration processes using small data sets before full implementation.
- Relationship verification: verify that connections between contacts, accounts, and opportunities transfer correctly.
Step 5: launch with team training and adoption
To realize the full value of your investment, successful implementation must be paired with strong team training and a focus on user adoption. Proper training and change management ensure the CRM database delivers intended business benefits by creating confident, capable users across all departments.
Training program components:
- Role-based training: customize instruction based on how different team members use the system.
- Hands-on practice: provide opportunities to work with actual customer data.
- Workflow integration: show how CRM database usage fits into existing daily routines.
- Ongoing support: establish resources for questions and continued learning.
Adoption strategies:
- Executive sponsorship: drive adoption through leadership support that signals importance to the entire organization.
- Early adopter champions: identify enthusiastic users to help train and support colleagues.
- Phased rollout: implement across teams gradually to manage change effectively.
- Success metrics: track usage and business outcomes to demonstrate value.
Maximizing your 2026 CRM investment
Transitioning to a CRM database is more than a technical upgrade; it is a fundamental shift from managing chaotic spreadsheets to building an engine that drives results. By following a structured approach — mapping customer journeys, designing logical workflows, and executing a clean data migration — you transform raw data into a strategic asset.
Organizations that commit to this process achieve measurable improvements in sales efficiency, team coordination, and forecast accuracy.
The long-term value of this infrastructure is realized through reduced manual burdens and enhanced customer experiences that foster loyalty. Modern systems, particularly those leveraging AI, allow your team to work smarter by automating routine tasks and surfacing insights that were previously hidden in disconnected files.
Ultimately, this investment pays significant dividends through sustained revenue growth and the ability to scale your operations without compromising the quality of your customer relationships.
The content in this article is provided for informational purposes only and, to the best of monday.com’s knowledge, the information provided in this article is accurate and up-to-date at the time of publication. That said, monday.com encourages readers to verify all information directly.
Frequently asked questions
What is a CRM database?
A CRM database is a centralized digital repository that stores all customer information, interactions, and relationship data in one accessible location. It transforms scattered customer data from emails, spreadsheets, and individual notes into organized, actionable intelligence that teams use to manage relationships and make informed decisions.
What is CRM data?
CRM data encompasses all information related to customer relationships including contact details, company information, interaction history, purchase records, communication preferences, and behavioral patterns. This includes emails, meeting notes, call logs, support tickets, deal stages, and any other touchpoints throughout the customer lifecycle.
Why collect CRM data?
Organizations collect CRM data to gain predictability in their sales pipeline, improve forecast accuracy, and make data-driven decisions about resource allocation and strategy. Centralizing customer information enables teams to deliver consistent experiences, identify opportunities faster, and coordinate effectively across departments.
What is a CRM system?
A CRM system includes three integrated components: the database where customer information lives, the software interface that teams use to interact with that data, and the workflows that automate processes and guide customer interactions. Together, these elements create a comprehensive platform for managing customer relationships from initial contact through retention.
What is SaaS CRM?
SaaS CRM refers to cloud-based customer relationship management systems accessed through web browsers without requiring on-premise installation or maintenance. These solutions offer rapid deployment within days, automatic updates, accessibility from any device with internet connection, and subscription-based pricing that eliminates large upfront investments.
How does a CRM database differ from spreadsheets?
CRM databases provide real-time multi-user access, automated workflows, and scalability that spreadsheets cannot match. While spreadsheets create version control problems and require manual updates, CRM databases offer automatic data capture, integration with other business systems, enterprise security, and instant reporting capabilities.